J Clin Neurol.
2013 Jan;9(1):36-42. 10.3988/jcn.2013.9.1.36.
Clinical Efficacy of Plasmapheresis in Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Effects on Circulating Anti-Aquaporin-4 Antibody Levels
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Research Institute and Hospital of National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. hojinkim@ncc.re.kr
- KMID: 2287569
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2013.9.1.36
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Although plasmapheresis is becoming standard practice as a rescue therapy for neuromyelitis optica (NMO), evidence for the therapeutic efficacy of plasmapheresis is limited, and the effect of plasmapheresis on anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) levels in patients with NMO has not been reported. Here, our objective was to evaluate the clinical efficacy of therapeutic plasmapheresis and its effect on anti-AQP4 antibody levels in patients with NMO spectrum disorder (NMOSD).
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 15 patients with NMOSD who had 18 acute attacks and received plasmapheresis because they did not respond to high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone (IVMP) therapy. Anti-AQP4 antibodies were measured before and after plasmapheresis. The primary outcomes were functional improvements immediately and 6 months after plasmapheresis, and the secondary outcome was the change in anti-AQP4 antibody serum levels following plasmapheresis.
RESULTS
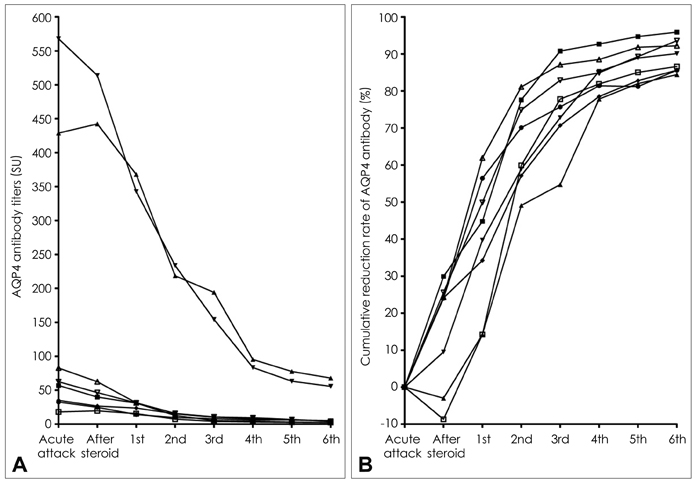
Plasmapheresis following IVMP therapy led to significant improvement in 50% of the 18 attacks in 15 patients immediately after the procedure was completed, and in 78% (14 attacks) after 6 months. Plasmapheresis was generally well tolerated in all patients. Anti-AQP4 antibody serum levels declined significantly following plasmapheresis, to a mean of 15% of the preplasmapheresis levels. Lower scores on the visual outcome scale recorded before an attack were associated with significant immediate improvement upon the completion of plasmapheresis (p=0.03).
CONCLUSIONS
Plasmapheresis following IVMP therapy effectively removed anti-AQP4 antibodies and was accompanied by a substantial improvement in the neurological disability of patients with NMOSD. Lower levels of pre-existing neurological damage may be associated with an improved acute response to plasmapheresis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lehmann HC, Hartung HP, Hetzel GR, Stüve O, Kieseier BC. Plasma exchange in neuroimmunological disorders: Part 1: Rationale and treatment of inflammatory central nervous system disorders. Arch Neurol. 2006. 63:930–935.2. Lennon VA, Wingerchuk DM, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Fujihara K, et al. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2004. 364:2106–2112.
Article3. Saadoun S, Waters P, Bell BA, Vincent A, Verkman AS, Papadopoulos MC. Intra-cerebral injection of neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G and human complement produces neuromyelitis optica lesions in mice. Brain. 2010. 133:349–361.
Article4. Weinshenker BG, Wingerchuk DM, Vukusic S, Linbo L, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, et al. Neuromyelitis optica IgG predicts relapse after longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Ann Neurol. 2006. 59:566–569.
Article5. Matiello M, Lennon VA, Jacob A, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Wingerchuk DM, et al. NMO-IgG predicts the outcome of recurrent optic neuritis. Neurology. 2008. 70:2197–2200.
Article6. Bennett JL, Lam C, Kalluri SR, Saikali P, Bautista K, Dupree C, et al. Intrathecal pathogenic anti-aquaporin-4 antibodies in early neuromyelitis optica. Ann Neurol. 2009. 66:617–629.
Article7. Bradl M, Misu T, Takahashi T, Watanabe M, Mader S, Reindl M, et al. Neuromyelitis optica: pathogenicity of patient immunoglobulin in vivo. Ann Neurol. 2009. 66:630–643.
Article8. Kim W, Kim SH, Kim HJ. New insights into neuromyelitis optica. J Clin Neurol. 2011. 7:115–127.
Article9. Keegan M, Pineda AA, McClelland RL, Darby CH, Rodriguez M, Weinshenker BG. Plasma exchange for severe attacks of CNS demyelination: predictors of response. Neurology. 2002. 58:143–146.
Article10. Llufriu S, Castillo J, Blanco Y, Ramió-Torrentà L, Río J, Vallès M, et al. Plasma exchange for acute attacks of CNS demyelination: Predictors of improvement at 6 months. Neurology. 2009. 73:949–953.
Article11. Magaña SM, Keegan BM, Weinshenker BG, Erickson BJ, Pittock SJ, Lennon VA, et al. Beneficial plasma exchange response in central nervous system inflammatory demyelination. Arch Neurol. 2011. 68:870–878.
Article12. Watanabe S, Nakashima I, Misu T, Miyazawa I, Shiga Y, Fujihara K, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of plasma exchange in NMO-IgG-positive patients with neuromyelitis optica. Mult Scler. 2007. 13:128–132.
Article13. Wang KC, Wang SJ, Lee CL, Chen SY, Tsai CP. The rescue effect of plasma exchange for neuromyelitis optica. J Clin Neurosci. 2011. 18:43–46.
Article14. Collongues N, de Seze J. Current and future treatment approaches for neuromyelitis optica. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2011. 4:111–121.
Article15. Sellner J, Boggild M, Clanet M, Hintzen RQ, Illes Z, Montalban X, et al. EFNS guidelines on diagnosis and management of neuromyelitis optica. Eur J Neurol. 2010. 17:1019–1032.
Article16. Szczepiorkowski ZM, Winters JL, Bandarenko N, Kim HC, Linenberger ML, Marques MB, et al. Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice--evidence-based approach from the Apheresis Applications Committee of the American Society for Apheresis. J Clin Apher. 2010. 25:83–177.
Article17. Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology. 2006. 66:1485–1489.
Article18. Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Lucchinetti CF, Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG. The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2007. 6:805–815.
Article19. Wingerchuk DM, Hogancamp WF, O'Brien PC, Weinshenker BG. The clinical course of neuromyelitis optica (Devic's syndrome). Neurology. 1999. 53:1107–1114.
Article20. Kim W, Lee JE, Li XF, Kim SH, Han BG, Lee BI, et al. Quantitative measurement of anti-aquaporin-4 antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using purified recombinant human aquaporin-4. Mult Scler. 2012. 18:578–586.
Article21. Narita YM, Hirahara K, Mizukawa Y, Kano Y, Shiohara T. Efficacy of plasmapheresis for the treatment of severe toxic epidermal necrolysis: Is cytokine expression analysis useful in predicting its therapeutic efficacy? J Dermatol. 2011. 38:236–245.
Article22. Bonnan M, Valentino R, Olindo S, Mehdaoui H, Smadja D, Cabre P. Plasma exchange in severe spinal attacks associated with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Mult Scler. 2009. 15:487–492.
Article23. Brecher ME. Plasma exchange: why we do what we do. J Clin Apher. 2002. 17:207–211.
Article24. Bonnan M, Cabre P. Plasma exchange in severe attacks of neuromyelitis optica. Mult Scler Int. 2012. 2012:787630.
Article25. Okafor C, Ward DM, Mokrzycki MH, Weinstein R, Clark P, Balogun RA. Introduction and overview of therapeutic apheresis. J Clin Apher. 2010. 25:240–249.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolated Tongue Paralysis as Presentation of Seropositive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder
- Differential Diagnosis between Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder
- A Case of NMOSD with Double Seropositive for AQP-4 and MOG Antibodies
- Postpartum Relapse of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder after a Long Period of Spontaneous Remission
- A Case of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder of a Patient Who Present for Fungal Sinusitis