J Breast Cancer.
2012 Dec;15(4):478-480. 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.4.478.
Differentiating Lymphovascular Invasion from Retraction Artifact on Histological Specimen of Breast Carcinoma and Their Implications on Prognosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Jefferson Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, USA.
- 2Department of Pathology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, USA.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA. gary.freedman@uphs.upenn.edu
- 4Department of Pathology, Jefferson Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, USA.
- KMID: 2286448
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2012.15.4.478
Abstract
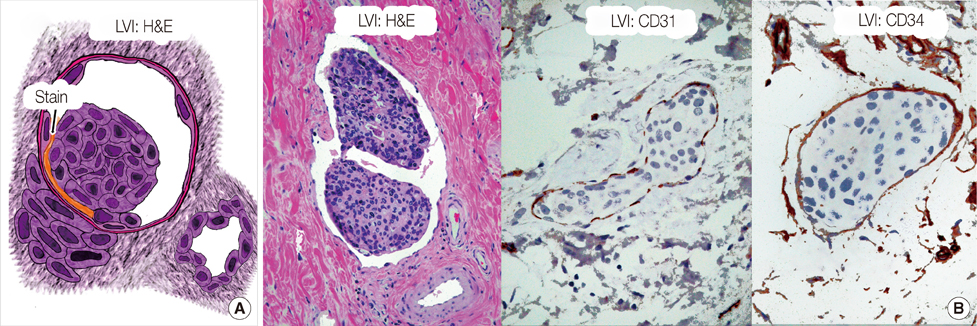
- On a pathological specimen of breast cancer cells, retraction artifact during histological processing mimics true lymphovascular invasion (LVI). The accurate determination of the presence or absence of LVI is a factor in determining risk of having a positive sentinel node, or having additional positive axillary nodes after a positive sentinel node biopsy in women with early-stage breast cancer. The determination of nodal risk influences the decision of the treating physicians as to whether a sentinel node biopsy or completion axillary dissection is necessary. On slide preparation, ideal factors favoring true LVI include: a definite endothelial lining, with endothelial nuclei that seem to protrude into the lymphatic space; invasion in one lymphatic vessel (LV) lumen with nearby cancer glands that have minimal or no retraction; a tumor embolus in a LV clear lumen with outside nearby tumor bulk; a tumor embolus that is different in shape than its surrounding clear LV space; and a positive stain for fibrin, CD31, or CD34 on tumor embolus periphery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lester SC. Kumar VK, Abbas AK, Fausto N, editors. The breast. Robbins and Cotran's Pathological Basis of Disease. 2005. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, Saunders;1148.
Article2. Rosen PP. Tumor emboli in intramammary lymphatics in breast carcinoma: pathologic criteria for diagnosis and clinical significance. Pathol Annu. 1983. 18 Pt 2:215–232.3. Bevilacqua JL, Kattan MW, Fey JV, Cody HS 3rd, Borgen PI, Van Zee KJ. Doctor, what are my chances of having a positive sentinel node? A validated nomogram for risk estimation. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:3670–3679.
Article4. Van Zee KJ, Manasseh DM, Bevilacqua JL, Boolbol SK, Fev JV, Tan LK, et al. A nomogram for predicting the likelihood of additional nodal metastases in breast cancer patients with a positive sentinel node biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003. 10:1140–1151.
Article5. Gilchrist KW, Gould VE, Hirschl S, Imbriqlia JE, Patchefsky AS, Penner DW, et al. Interobserver variation in the identification of breast carcinoma in intramammary lymphatics. Hum Pathol. 1982. 13:170–172.
Article6. Yeh I, Brooks JSJ, Pietra GG. Atlas of Microscopic Artifacts and Foreign Materials. 1997. 1st ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;144.7. Acs G, Paragh G, Chuang ST, Laronga C, Zhang PJ. The presence of micropapillary features and retraction artifact in core needle biopsy material predicts lymph node metastasis in breast carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009. 33:202–210.
Article8. Irie J, Manucha V, Ioffe OB, Silverberg SG. Artefact as the pathologist's friend: peritumoral retraction in in situ and infiltrating duct carcinoma of the breast. Int J Surg Pathol. 2007. 15:53–59.
Article9. Lee AK, DeLellis RA, Wolfe HJ. Intramammary lymphatic invasion in breast carcinomas. Evaluation using ABH isoantigens as endothelial markers. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986. 10:589–594.
Article10. Saigo PE, Rosen PP. The application of immunohistochemical stains to identify endothelial-lined channels in mammary carcinoma. Cancer. 1987. 59:51–54.
Article11. Acs G, Dumoff KL, Solin LJ, Pasha T, Xu X, Zhang PJ. Extensive retraction artifact correlates with lymphatic invasion and nodal metastasis and predicts poor outcome in early stage breast carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007. 31:129–140.
Article12. Ren S, Abuel-Haija M, Khurana JS, Zhang X. D2-40: an additional marker for myoepithelial cells of breast and the precaution in interpreting tumor lymphovascular invasion. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011. 4:175–182.13. Bose S, Derosa CM, Ozzello L. Immunostaining of type IV collagen and smooth muscle actin as an aid in the diagnosis of breast lesions. Breast J. 1999. 5:194–201.
Article14. Prasad ML, Hyjek E, Giri DD, Ying L, O'Leary JJ, Hoda SA. Double immunolabeling with cytokeratin and smooth-muscle actin in confirming early invasive carcinoma of breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999. 23:176–181.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of Lymphovascular Invasion as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- alphaB-Crystallin is a Novel Oncoprotein Associated with Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer
- Micropapillary Carcinoma of Breast
- Predictive Factors Affecting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Invasive Breast Carcinoma of 1 cm or Less
- Strategies for the Endoscopic Management and Post-Resection Treatment of Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma