J Breast Cancer.
2015 Mar;18(1):63-72. 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.1.63.
Effectiveness of Breast MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT for the Preoperative Staging of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma versus Ductal Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sghnk@catholic.ac.kr
- 3Department of Radiology, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2286339
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2015.18.1.63
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated the utility of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) for the preoperative staging of invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) of the breast and compared the results with those of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC).
METHODS
The study included pathologically proven 32 ILCs and 73 IDCs. We compared clinical and histopathological characteristics and the diagnostic performances of MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT for the primary mass, additional ipsilateral and/or contralateral lesion(s), and axillary lymph node metastasis between the ILC and IDC groups.
RESULTS
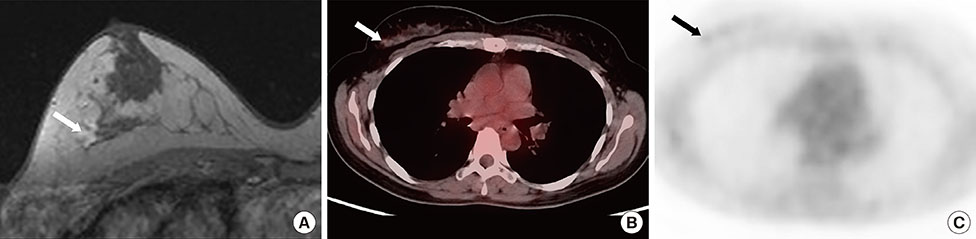
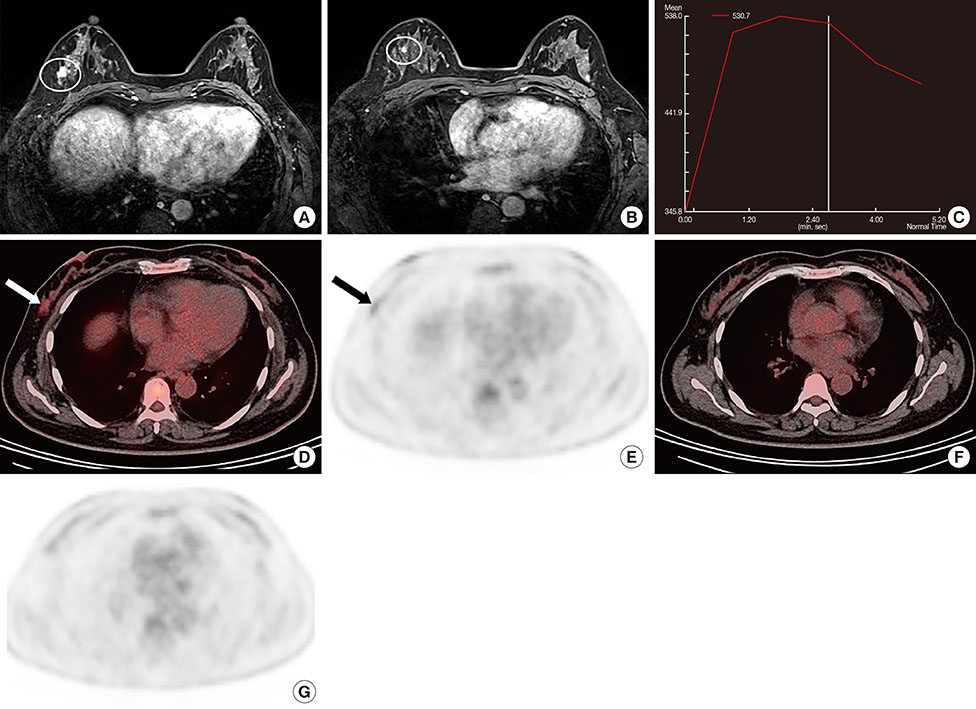
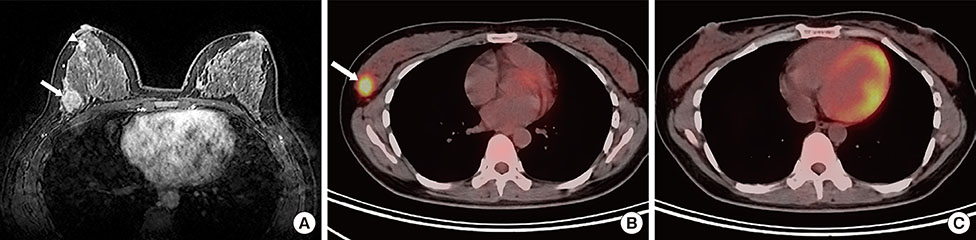
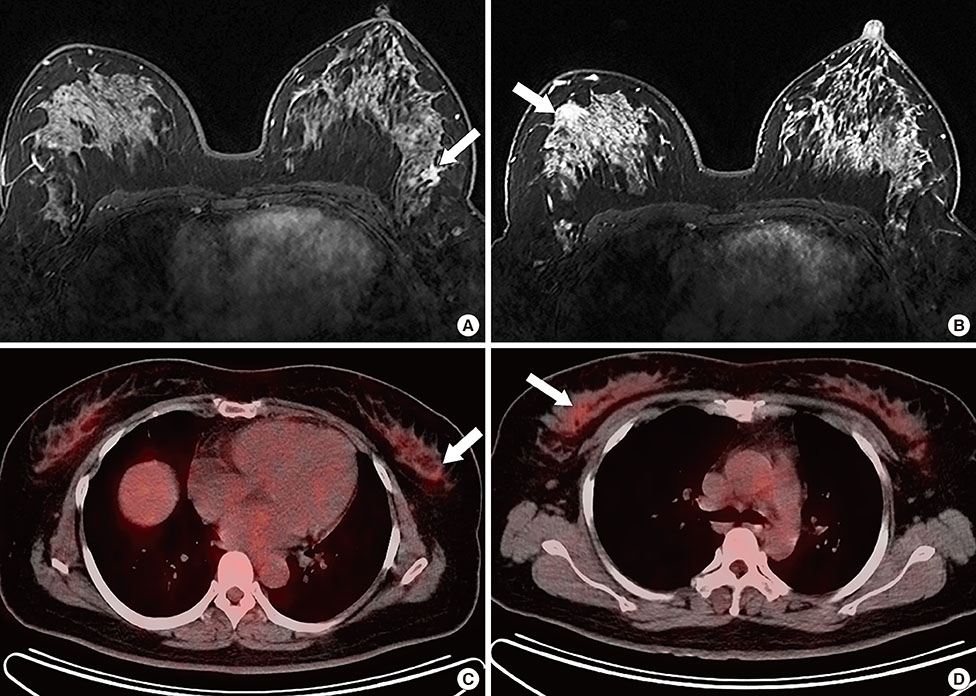
Primary ILCs were greater in size, but demonstrated lower maximum standardized uptake values than IDCs. All primary masses were detected on MRI. The detection rate for ILCs (75.0%) was lower than that for IDCs (83.6%) on 18F-FDG PET/CT, but the difference was not significant. For additional ipsilateral lesion(s), the sensitivities and specificities of MRI were 87.5% and 58.3% for ILC and 100.0% and 66.7% for IDC, respectively; whereas the sensitivities and specificities of 18F-FDG PET/CT were 0% and 91.7% for ILC and 37.5% and 94.7% for IDC, respectively. The sensitivity of 18F-FDG PET/CT for ipsilateral lesion(s) was significantly lower in the ILC group than the IDC group. The sensitivity for ipsilateral lesion(s) was significantly higher with MRI; however, specificity was higher with 18F-FDG PET/CT in both tumor groups. There was no significant difference in the diagnostic performance for additional contralateral lesion(s) or axillary lymph node metastasis on MRI or 18F-FDG PET/CT for ILC versus IDC.
CONCLUSION
The MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT detection rates for the primary cancer do not differ between the ILC and IDC groups. Although 18F-FDG PET/CT demonstrates lower sensitivity for primary and additional ipsilateral lesions, it shows higher specificity for additional ipsilateral lesions, and could play a complementary role in the staging of ILC as well as IDC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stivalet A, Luciani A, Pigneur F, Dao TH, Beaussart P, Merabet Z, et al. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: MRI pathological correlation following bilateral total mastectomy. Acta Radiol. 2012; 53:367–375.
Article2. Boetes C, Veltman J, van Die L, Bult P, Wobbes T, Barentsz JO. The role of MRI in invasive lobular carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004; 86:31–37.
Article3. Mann RM, Hoogeveen YL, Blickman JG, Boetes C. MRI compared to conventional diagnostic work-up in the detection and evaluation of invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: a review of existing literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008; 107:1–14.
Article4. Li CI, Anderson BO, Daling JR, Moe RE. Trends in incidence rates of invasive lobular and ductal breast carcinoma. JAMA. 2003; 289:1421–1424.
Article5. Veltman J, Boetes C, van Die L, Bult P, Blickman JG, Barentsz JO. Mammographic detection and staging of invasive lobular carcinoma. Clin Imaging. 2006; 30:94–98.
Article6. Hilleren DJ, Andersson IT, Lindholm K, Linnell FS. Invasive lobular carcinoma: mammographic findings in a 10-year experience. Radiology. 1991; 178:149–154.
Article7. Skaane P, Skjørten F. Ultrasonographic evaluation of invasive lobular carcinoma. Acta Radiol. 1999; 40:369–375.
Article8. Watermann DO, Tempfer C, Hefler LA, Parat C, Stickeler E. Ultrasound morphology of invasive lobular breast cancer is different compared with other types of breast cancer. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2005; 31:167–174.
Article9. Rodenko GN, Harms SE, Pruneda JM, Farrell RS Jr, Evans WP, Copit DS, et al. MR imaging in the management before surgery of lobular carcinoma of the breast: correlation with pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 167:1415–1419.
Article10. Kim SH, Cha ES, Park CS, Kang BJ, Whang IY, Lee AW, et al. Imaging features of invasive lobular carcinoma: comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma. Jpn J Radiol. 2011; 29:475–482.
Article11. Liberman L, Morris EA, Kim CM, Kaplan JB, Abramson AF, Menell JH, et al. MR imaging findings in the contralateral breast of women with recently diagnosed breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:333–341.
Article12. Mameri CS, Kemp C, Goldman SM, Sobral LA, Ajzen S. Impact of breast MRI on surgical treatment, axillary approach, and systemic therapy for breast cancer. Breast J. 2008; 14:236–244.
Article13. Lau B, Romero LM. Does preoperative magnetic resonance imaging beneficially alter surgical management of invasive lobular carcinoma. Am Surg. 2011; 77:1368–1371.
Article14. Choi YJ, Shin YD, Kang YH, Lee MS, Lee MK, Cho BS, et al. The effects of preoperative (18)F-FDG PET/CT in breast cancer patients in comparison to the conventional imaging study. J Breast Cancer. 2012; 15:441–448.
Article15. Groves AM, Shastry M, Ben-Haim S, Kayani I, Malhotra A, Davidson T, et al. Defining the role of PET-CT in staging early breast cancer. Oncologist. 2012; 17:613–619.
Article16. Avril N, Rosé CA, Schelling M, Dose J, Kuhn W, Bense S, et al. Breast imaging with positron emission tomography and fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose: use and limitations. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:3495–3502.
Article17. Buck AK, Schirrmeister H, Mattfeldt T, Reske SN. Biological characterisation of breast cancer by means of PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004; 31:Suppl 1. S80–S87.
Article18. American College of Radiology. ACR BI-RADS Breast Imaging and Reporting Data System: Breast Imaging Atlas. 4th ed. Reston: American College of Radiology;2003.19. Liberman L, Morris EA, Dershaw DD, Abramson AF, Tan LK. MR imaging of the ipsilateral breast in women with percutaneously proven breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:901–910.
Article20. Liberman L, Morris EA, Lee MJ, Kaplan JB, LaTrenta LR, Menell JH, et al. Breast lesions detected on MR imaging: features and positive predictive value. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:171–178.
Article21. Arpino G, Bardou VJ, Clark GM, Elledge RM. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: tumor characteristics and clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res. 2004; 6:R149–R156.
Article22. Bos R, van Der Hoeven JJ, van Der Wall E, van Der Groep P, van Diest PJ, Comans EF, et al. Biologic correlates of (18)fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in human breast cancer measured by positron emission tomography. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:379–387.
Article23. Vandorpe T, Smeets A, Van Calster B, Van Hoorde K, Leunen K, Amant F, et al. Lobular and non-lobular breast cancers differ regarding axillary lymph node metastasis: a cross-sectional study on 4,292 consecutive patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 128:429–435.
Article24. Kneeshaw PJ, Turnbull LW, Smith A, Drew PJ. Dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging aids the surgical management of invasive lobular breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2003; 29:32–37.
Article25. McGhan LJ, Wasif N, Gray RJ, Giurescu ME, Pizzitola VJ, Lorans R, et al. Use of preoperative magnetic resonance imaging for invasive lobular cancer: good, better, but maybe not the best? Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:Suppl 3. 255–262.
Article26. Sardanelli F, Giuseppetti GM, Panizza P, Bazzocchi M, Fausto A, Simonetti G, et al. Sensitivity of MRI versus mammography for detecting foci of multifocal, multicentric breast cancer in fatty and dense breasts using the whole-breast pathologic examination as a gold standard. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:1149–1157.
Article27. Mann RM, Loo CE, Wobbes T, Bult P, Barentsz JO, Gilhuijs KG, et al. The impact of preoperative breast MRI on the re-excision rate in invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 119:415–422.
Article28. Pediconi F, Catalano C, Roselli A, Padula S, Altomari F, Moriconi E, et al. Contrast-enhanced MR mammography for evaluation of the contralateral breast in patients with diagnosed unilateral breast cancer or high-risk lesions. Radiology. 2007; 243:670–680.
Article29. Fehr MK, Hornung R, Varga Z, Burger D, Hess T, Haller U, et al. Axillary staging using positron emission tomography in breast cancer patients qualifying for sentinel lymph node biopsy. Breast J. 2004; 10:89–93.
Article30. Heusner TA, Kuemmel S, Hahn S, Koeninger A, Otterbach F, Hamami ME, et al. Diagnostic value of full-dose FDG PET/CT for axillary lymph node staging in breast cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009; 36:1543–1550.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Associated with Mixed Lobular and Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: A Case Report
- Random Synchronous Malignancy in Male Breast: A Case Report
- 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/CT Scan Findings for Ductal Carcinomas of Breast: Association of Standardized Uptake Value and Histological Findings
- F18-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography and computed tomography is not accurate in preoperative staging of gastric cancer
- Nodular Metastatic Carcinoma from Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer