J Adv Prosthodont.
2012 Feb;4(1):24-29. 10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.24.
Comparative evaluation of sodium hypochlorite and microwave disinfection on dimensional stability of denture bases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Sharad Pawar Dental College and Hospital, Maharashtra, India. rutuja_phutane@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2284780
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.24
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the effect of sodium hypochlorite and microwave disinfection on the dimensional stability of denture bases without and with relining.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
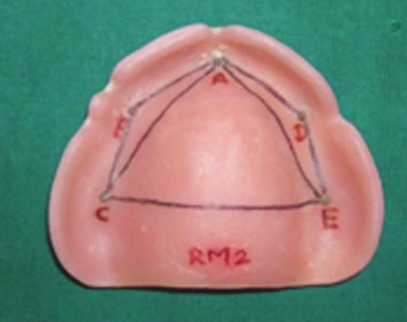
A brass die was prepared by simulating an edentulous maxillary arch. It was used to fabricate 1.5 mm and 3 mm of thickness denture bases (n = 40). The 1.5 mm of thickness-specimens (n = 20) were relined with 1.5 mm of autopolymerizing relining resin. Five holes were prepared over crest of ridge of brass die with intimately fitting stainless steel pins which were transferred to the intaglio surface of specimens during fabrication of denture bases. For calculation of dimensional changes in denture bases, differences between the baseline area before and after disinfection of the specimens were used. The denture bases without and with relining were divided into 2 groups (each n = 20). Data were analyzed using student paired 't' and unpaired 't' test.
RESULTS
Microwave disinfection produces significant shrinkage in both denture bases without relining (t = 17.16; P<.001) and with relining (t = 14.9; P<.001). Denture bases without relining showed more shrinkage when compared with relined denture bases after microwave disinfection (t = 6.09; P<.001). The changes in dimensional stability after sodium hypochlorite disinfection were not significant for both denture bases without relining (t = 2.19; P=.056) and denture bases with relining (t = 2.17; P=.058).
CONCLUSION
Microwave disinfection leads to increased shrinkage of denture bases without and with relining. Chemical disinfection with sodium hypochlorite seems to be a safer method of disinfection with regards to physical properties such as changes in dimensional stability.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Asad T, Watkinson AC, Huggett R. The effects of various disinfectant solutions on the surface hardness of an acrylic resin denture base material. Int J Prosthodont. 1993. 6:9–12.2. Vig RG. Reducing laboratory aerosol contamination. J Prosthet Dent. 1969. 22:156–157.3. Katberg JW Jr. Cross-contamination via the prosthodontic laboratory. J Prosthet Dent. 1974. 32:412–419.4. Shen C, Javid NS, Colaizzi FA. The effect of glutaraldehyde base disinfectants on denture base resins. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 61:583–589.5. Sartori EA, Schmidt CB, Walber LF, Shinkai RS. Effect of microwave disinfection on denture base adaptation and resin surface roughness. Braz Dent J. 2006. 17:195–200.6. Pavan S, Arioli Filho JN, Dos Santos PH, Mollo Fde A Jr. Effect of microwave treatments on dimensional accuracy of maxillary acrylic resin denture base. Braz Dent J. 2005. 16:119–123.7. Seo RS, Vergani CE, Pavarina AC, Compagnoni MA, Machado AL. Influence of microwave disinfection on the dimensional stability of intact and relined acrylic resin denture bases. J Prosthet Dent. 2007. 98:216–223.8. Hussen AM, Rejab LT, Abbood LN. The effect of microwave disinfection on the dimensional change of acrylic resins. Al-Rafidain Dent J. 2008. 8:38–43.9. Rohrer MD, Bulard RA. Microwave sterilization. J Am Dent Assoc. 1985. 110:194–198.10. Burns DR, Kazanoglu A, Moon PC, Gunsolley JC. Dimensional stability of acrylic resin materials after microwave sterilization. Int J Prosthodont. 1990. 3:489–493.11. Polyzois GL, Zissis AJ, Yannikakis SA. The effect of glutaraldehyde and microwave disinfection on some properties of acrylic denture resin. Int J Prosthodont. 1995. 8:150–154.12. Consani RL, Iwasaki RY, Mesquita MF, Mendes WB, Consani S. Effect of repeated simulated disinfections by microwave energy on the complete denture base adaptation. Open Dent J. 2008. 2:61–66.13. Council on Dental Therapeutics. Council on Prosthetic Services and Dental Laboratory Relations. Guidelines for infection control in the dental office and the commercial dental laboratory. J Am Dent Assoc. 1985. 110:969–972.14. Neppelenbroek KH, Pavarina AC, Spolidorio DM, Vergani CE, Mima EG, Machado AL. Effectiveness of microwave sterilization on three hard chairside reline resins. Int J Prosthodont. 2003. 16:616–620.15. Huggett R, Zissis A, Harrison A, Dennis A. Dimensional accuracy and stability of acrylic resin denture bases. J Prosthet Dent. 1992. 68:634–640.16. Polychronakis N, Yannikakis S, Zissis A. A clinical 5-year longitudinal study on the dimensional changes of complete maxillary dentures. Int J Prosthodont. 2003. 16:78–81.17. Craig RC. Prosthetic applications of polymers in Restorative dental materials. 1997. 12th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;513–547.18. Thomas CJ, Webb BC. Microwaving of acrylic resin dentures. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 1995. 3:179–182.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A simple and effective method for addition silicone impression disinfection
- A STUDY ON DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF IMPRESSION MATERIALS FOLLOWING IMMERSION DISINFECTION
- Precipitate from a combination of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine
- A comparative study on the dimensional change of the different denture bases
- A comparative study on the accuracies of resin denture bases and metal denture bases