Factors Affecting Acceptance of Smartphone Application for Management of Obesity
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. hapark@snu.ac.kr
- 2Systems Biomedical Informatics Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Research Institute of Nursing Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2284610
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2015.21.2.74
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
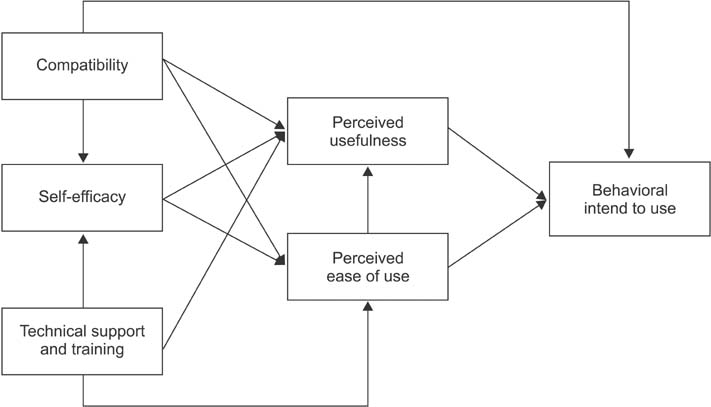
The factors affecting the acceptance of mobile obesity-management applications (apps) by the public were analyzed using a mobile healthcare system (MHS) technology acceptance model (TAM).
METHODS
The subjects who participated in this study were Android smartphone users who had an intent to manage their weight. They used the obesity-management app for two weeks, and then completed an 18-item survey designed to determine the factors influencing the acceptance of the app. Three questions were asked pertaining to each of the following six factors: compatibility, self-efficacy, technical support and training, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and behavior regarding intention to use. Cronbach's alpha was used to assess the reliability of the scales. Pathway analysis was also performed to evaluate the MHS acceptance model.
RESULTS
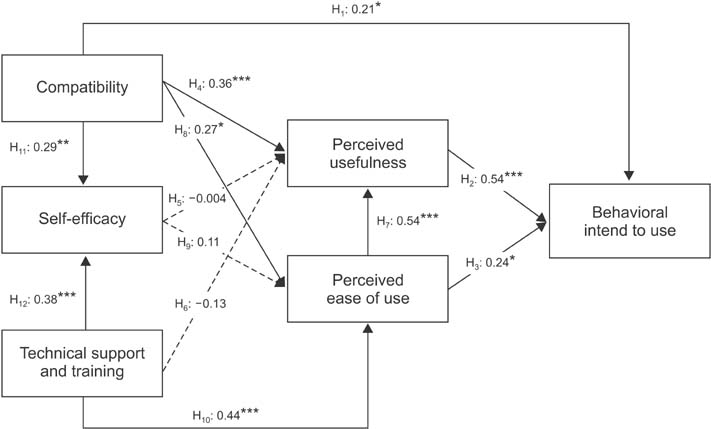
A total of 94 subjects participated in this study. The results indicate that compatibility, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease of use significantly affected the behavioral intention to use the mobile obesity-management app. Technical support and training also significantly affected the perceived ease of use; however, the hypotheses that self-efficacy affects perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use were not supported in this study.
CONCLUSIONS
This is the first attempt to analyze the factors influencing mobile obesity-management app acceptance using a TAM. Further studies should cover not only obesity but also other chronic diseases and should analyze the factors affecting the acceptance of apps among healthcare consumers in general.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Are Currently Available Wearable Devices for Activity Tracking and Heart Rate Monitoring Accurate, Precise, and Medically Beneficial?
Fatema El-Amrawy, Mohamed Ismail Nounou
Healthc Inform Res. 2015;21(4):315-320. doi: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.4.315.Development of Child-Teen Obesity Treatment Service Platform
Kahyun Lim, Byung Mun Lee, Youngho Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2016;22(3):243-249. doi: 10.4258/hir.2016.22.3.243.Medical Representatives' Intention to Use Information Technology in Pharmaceutical Marketing
Eun-Seon Kwak, Hyejung Chang
Healthc Inform Res. 2016;22(4):342-350. doi: 10.4258/hir.2016.22.4.342.Effective Validation Model and Use of Mobile-Health Applications for the Elderly
Leonardo Juan Ramirez Lopez, Edward Paul Guillen Pinto, Carlos Omar Ramos Linares
Healthc Inform Res. 2018;24(4):276-282. doi: 10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.276.
Reference
-
1. Patrick K, Griswold WG, Raab F, Intille SS. Health and the mobile phone. Am J Prev Med. 2008; 35(2):177–181.
Article2. Haux R. Health information systems - past, present, future. Int J Med Inform. 2006; 75(3-4):268–281.
Article3. Berg M. Patient care information systems and health care work: a sociotechnical approach. Int J Med Inform. 1999; 55(2):87–101.
Article4. Short D, Frischer M, Bashford J. Barriers to the adoption of computerised decision support systems in general practice consultations: a qualitative study of GPs perspectives. Int J Med Inform. 2004; 73(4):357–362.
Article5. Johnson JD, Meyer M, Woodworth M, Ethington C, Stengle W. Information technologies within the cancer information service: factors related to innovation adoption. Prev Med. 1998; 27(5 Pt 2):S71–S83.
Article6. Wu JH, Wang SC, Lin LM. Mobile computing acceptance factors in the healthcare industry: a structural equation model. Int J Med Inform. 2007; 76(1):66–77.
Article7. Zhang H, Cocosila M, Archer N. Factors of adoption of mobile information technology by homecare nurses: a technology acceptance model 2 approach. Comput Inform Nurs. 2010; 28(1):49–56.
Article8. Lee J, Rho MJ. Perception of influencing factors on acceptance of mobile health monitoring service: a comparison between users and non-users. Healthc Inform Res. 2013; 19(3):167–176.
Article9. Korea Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination. Seoul: Korea Ministry of Health and Welfare;2011.10. Goessens BM, Visseren FL, de Nooijer J, van den Borne HW, Algra A, Wierdsma J, et al. A pilot-study to identify the feasibility of an Internet-based coaching programme for changing the vascular risk profile of high-risk patients. Patient Educ Couns. 2008; 73(1):67–72.
Article11. Jeon HO, Kim O. The effects of an internet based coaching program for obesity management in hypertensive patients. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2011; 23(2):146–159.12. Breton ER, Fuemmeler BF, Abroms LC. Weight loss-there is an app for that! But does it adhere to evidenceinformed practices? Transl Behav Med. 2011; 1(4):523–529.
Article13. Jeon E, Park HA, Min YH, Kim HY. Analysis of the information quality of Korean obesity-management smartphone applications. Healthc Inform Res. 2014; 20(1):23–29.
Article14. Research2guidance. Mobile health market report 2011-2016. Berlin: Research2guidance;2012.15. Jeon E, Park HA. Development of a smartphone application for clinical-guideline-based obesity management. Healthc Inform Res. 2015; 21(1):10–20.
Article16. Venkatesh V, Davis FD. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies. Manag Sci. 2000; 46(2):186–204.
Article17. Rogers EM. Diffusion of innovations. 5th ed. New York(NY): Simon & Schuster Inc;2003.18. Compeau DR, Higgins CA. Computer self-efficacy: development of a measure and initial test. MIS Q. 1995; 19(2):189–211.
Article19. Igbaria M, Zinatelli N, Cragg P, Cavaye AL. Personal computing acceptance factors in small firms: a structural equation model. MIS Q. 1997; 21(3):279–305.
Article20. Davis FD. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989; 13(3):319–340.
Article21. Van Slyke C, Lou H, Day J. The impact of perceived innovation characteristics on intention to use groupware. Inf Resour Manag J. 2002; 15(1):1–12.
Article22. Jelekäinen P. GSM-PKI solution enabling secure mobile communications. Int J Med Inform. 2004; 73(3):317–320.
Article23. Kim K. AMOS 18.0 structural equation modeling analysis. Korean edition. Seoul, Korea: Hannarae Publishing;2010.24. Chau PY, Hu PJ. Investigating healthcare professionals' decisions to accept telemedicine technology: an empirical test of competing theories. Inf Manag. 2002; 39(4):297–311.
Article25. Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD. User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003; 27(3):425–478.
Article26. Chapman DW, Carter JF. Translation procedures for the cross cultural use of measurement instruments. Educ Eval Policy Anal. 1979; 1(3):71–76.
Article27. Hair JF Jr, Anderson RE, Tatham RL. Multivariate data analysis with readings. 2nd ed. New York (NY): Macmillan Publishing;1986.28. Ruder Finn Inc. mHealth report. New York (NY): Ruder Finn Inc.;2012.29. Hasan B. Delineating the effects of general and system-specific computer self-efficacy beliefs on IS acceptance. Inf Manag. 2006; 43(5):565–571.
Article30. Kim J, Park HA. Development of a health information technology acceptance model using consumers' health behavior intention. J Med Internet Res. 2012; 14(5):e133.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of the Factors Affecting Consumer Acceptance of Accredited Online Health Information
- Analysis of the Information Quality of Korean Obesity-Management Smartphone Applications
- Development of a Smartphone Application Prototype for Child Obesity Prevention: Rationale and Study Design of Acceptability and Feasibility Tests
- Comparison of Gender Factors Affecting Middle School Students' Smartphone Addiction
- The Development and Application Effects of a Fatigue Self-Care Smartphone Application for Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy