Healthc Inform Res.
2015 Jan;21(1):56-60. 10.4258/hir.2015.21.1.56.
SMART Careplan System for Continuum of Care
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Medical Information and Technology, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Office of Quality Improvement, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Nursing, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. SEMEKIM@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2284599
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2015.21.1.56
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This paper describes the integrated Careplan system, designed to manage and utilize the existing Electronic Medical Record (EMR) system; the system also defines key items for interdisciplinary communication and continuity of patient care.
METHODS
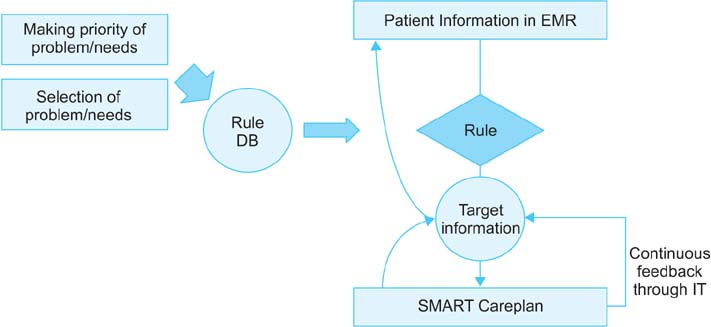
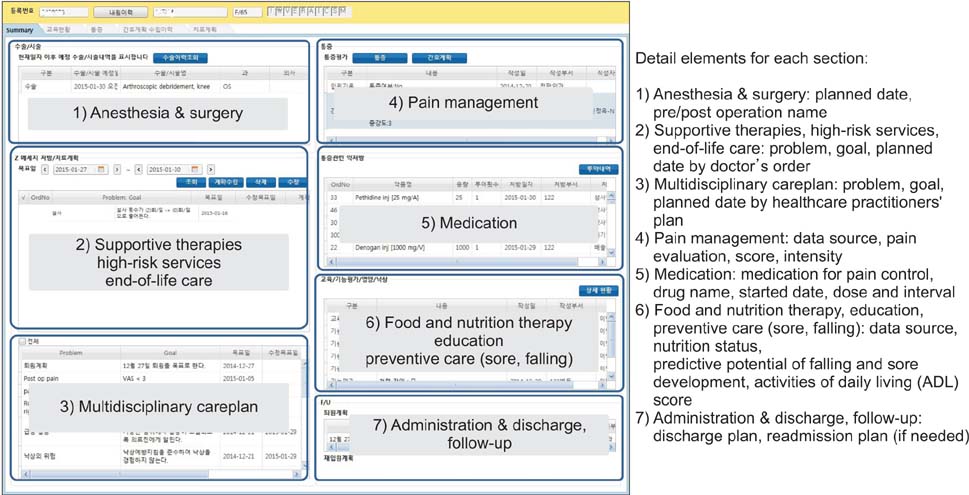
We structured the Careplan system to provide effective interdisciplinary communication for healthcare services. The design of the Careplan system architecture proceeded in four steps-defining target datasets; construction of conceptual framework and architecture; screen layout and storyboard creation; screen user interface (UI) design and development, and pilot test and step-by-step deployment. This Careplan system architecture consists of two parts, a server-side and client-side area. On the server-side, it performs the roles of data retrieval and storage from target EMRs. Furthermore, it performs the role of sending push notifications to the client depending on the careplan series. Also, the Careplan system provides various convenient modules to easily enter an individual careplan.
RESULTS
Currently, Severance Hospital operates the Careplan system and provides a stable service dealing with dynamic changes (e.g., domestic medical certification, the Joint Commission International guideline) of EMR.
CONCLUSIONS
The Careplan system should go hand in hand with key items for strengthening interdisciplinary communication and information sharing within the EMR environment. A well-designed Careplan system can enhance user satisfaction and completed performance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality [Internet]. Washington (DC): US Department of Health and Human Service;2014. 2015 Jan 15. Available from: http://www.ahrq.gov/.2. Institute of Medicine. Health IT and patient safety: building safer systems for better care. Washington (DC): National Academies Press;2011.3. Joint Commission International. Joint Commission International accreditation standards for hospitals. 4th ed. Oakbrook Terrace (IL): Joint Commission Resources;2011.4. Meterko M, Mohr DC, Young GJ. Teamwork culture and patient satisfaction in hospitals. Med Care. 2004; 42(5):492–498.
Article5. Gaylin DS, Moiduddin A, Mohamoud S, Lundeen K, Kelly JA. Public attitudes about health information technology, and its relationship to health care quality, costs, and privacy. Health Serv Res. 2011; 46(3):920–938.
Article6. Kim SH. Patient safety: achieving a new standard for care. Hosp Line. 2006; 35(5):87–96.7. Park CS, Koh SH. A review of hospital information system quality evaluation from the viewpoint of software usability. Inf Syst Rev. 2007; 9(2):169–187.8. Ryu I, Kim M. An empirical study on the success factors and performance model of hospital information systems. J MIS Res. 2002; 12(1):45–65.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of excretion care with a smart automatic defecation treatment system on skin humidity, incontinence-associated dermatitis, and pressure ulcers of patients with incontinence residing in long-term care facilities: Non-equivalent control group non-synchronized design
- Developing a Smart Phone Application for the OMAHA System Guidelines
- Integrated Information System for Early Detection of Maternal Risk Factors Based on Continuum of Care Approach of Mother and Toddler Cohorts
- Evaluation of the i-Smart 30 Point-of-Care Analyzer for Use in Clinical Laboratory Settings
- Effects of smart-care services program for breast cancer survivors