Healthc Inform Res.
2010 Dec;16(4):224-230. 10.4258/hir.2010.16.4.224.
Support Vector Regression-based Model to Analyze Prognosis of Infants with Congenital Muscular Torticollis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Biomedical Information Technology Center, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Medical Informatics, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ynkim@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2284536
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2010.16.4.224
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Congenital muscular torticollis, a common disorder that refers to the shortening of the sternocleidomastoid in infants, is sensitive to correction through physical therapy when treated early. If physical therapy is unsuccessful, surgery is required. In this study, we developed a support vector regression model for congenital muscular torticollis to investigate the prognosis of the physical therapy treatent in infants.
METHODS
Fifty-nine infants with congenital muscular torticollis received physical therapy until the degree of neck tilt was less than 5degrees. After treatment, the mass diameter was reevaluated. Based on the data, a support vector regression model was applied to predict the prognoses.
RESULTS
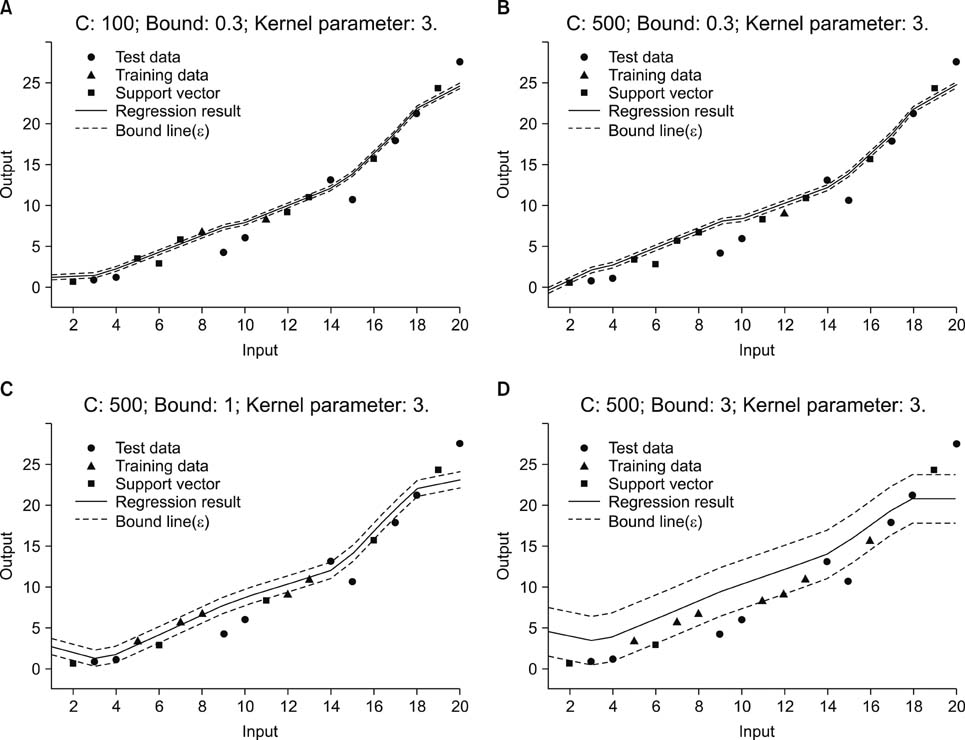
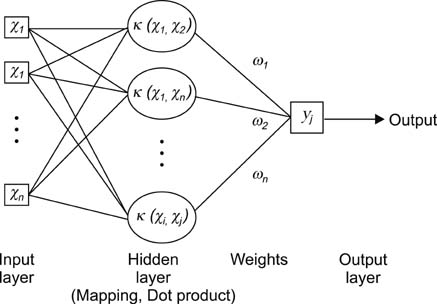
10-, 20-, and 50-fold cross-tabulation analyses for the proposed model were conducted based on support vector regression and conventional multi-regression method based on least squares. The proposed methodbased on support vector regression was robust and enabled the effective analysis of even a small amount of data containing outliers.
CONCLUSIONS
The developed support vector regression model is an effective prognostic tool for infants with congenital muscular torticollis who receive physical therapy.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Canale ST, Griffin DW, Hubbard CN. Congenital muscular torticollis: a long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982. 64:810–816.
Article2. Celayir AC. Congenital muscular torticollis: early and intensive treatment is critical. A prospective study. Pediatr Int. 2000. 42:504–507.
Article3. Binder H, Eng GD, Gaiser JF, Koch B. Congenital muscular torticollis: results of conservative management with long-term follow-up in 85 cases. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1987. 68:222–225.4. Kim HS, Vaq SG, Kim SW, Lee SK, You S, Shin JB, Chung HJ. The clinical features and outcome of therapy according to the subtypes of torticollis. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2006. 14:243–249.5. Morrison DL, MacEwen GD. Congenital muscular torticollis: observations re-garding clinical findings, associated conditions, and results of treatment. J Pediatr Orthop. 1982. 2:500–505.6. Joyce MB, de Chalain TM. Treatment of recalcitrant idiopathic muscular torticollis in infants with botulinum toxin type a. J Craniofac Surg. 2005. 16:321–327.
Article7. Oleszek JL, Chang N, Apkon SD, Wilson PE. Botulinum toxin type a in the treat-ment of children with congenital muscular torticollis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2005. 84:813–816.
Article8. Jun JE, Ryu HK, Shim JW, Shim JY, Jung HL, Park MS, Kim DS. Clinical features of congenital muscular torticollis. Korean J Pediatr. 2007. 50:241–247.
Article9. Lee IH, Shin AM, Park HJ, Kim YN, Lee KY. Development of the last mass di-ameter prediction model for congenital muscular torticollis infants provided physical therapy. J Korean Soc Phys Ther. 2009. 21:65–70.10. Jun SH. An outlier data analysis using support vector regression. J Intell Inf Syst. 2008. 18:876–880.
Article11. Myers RH. Classical and modern regression with applications. 2000. 2nd ed. Pacific Grove, CA: Duxbury.12. Smyth P. Data mining: data analysis on a grand scale? Stat Methods Med Res. 2000. 9:309–327.
Article13. Burges CJ. A tutorial on support vector machine for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Disc. 1998. 2:121–167.14. Vapnik VN. Statistical learning theory: adaptive and learning systems for signal processing, communications, and control. 1998. New York: Wiley.15. Scholkopf B, Smola AJ. Learning with kernels: support vector machines, regulari-zation, optimization, and beyond: adaptive computation and machine learning. 2002. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.16. Wennekers T. Orientation tuning properties of simple cells in area V1 derived from an approximate analysis of nonlinear neural field models. Neural Comput. 2001. 13:1721–1747.
Article17. Lee IH. The effect of manual stretching and positioning and developmental treatment in congenital muscular torticollis: randomized controlled trials. J Korean Acad Univ Trained Phys Ther. 2009. 16:34–41.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Familial Congenital Muscular Torticollis: A Case Report
- Two Cases of Sternomastoid Tumor
- Congenital Torticollis with Bilateral Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Contracture
- Unipolar Release of the Sternocleidomastoideus in Congenital Muscular Torticollis in Children
- Biterminal Sternocleidomastoid Tenotomy for the Treatment of Congenital Muscular Torticollis in Children