Diabetes Metab J.
2011 Feb;35(1):80-85. 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.1.80.
Autoimmune Hypoglycemia in a Patient with Characterization of Insulin Receptor Autoantibodies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. orqwic@chol.com
- 2Research Institute of Endocrinology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2281496
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.1.80
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
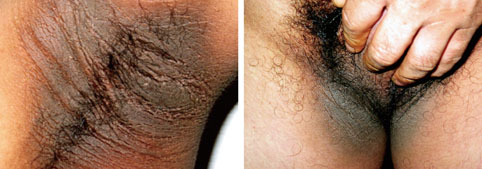
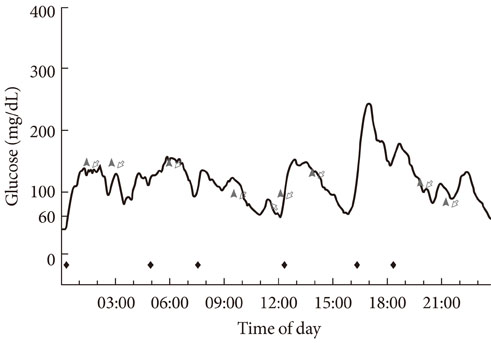
Type B insulin resistance syndrome is a manifestation of autoantibodies to the insulin receptor that results in severe hyperglycemia and acanthosis nigricans. However, the mechanisms by which these autoantibodies induce hypoglycemia are largely unknown. In this paper, we report the case of patient with type B insulin resistance syndrome who presented with frequent severe fasting hypoglycemia and acanthosis nigricans.
METHODS
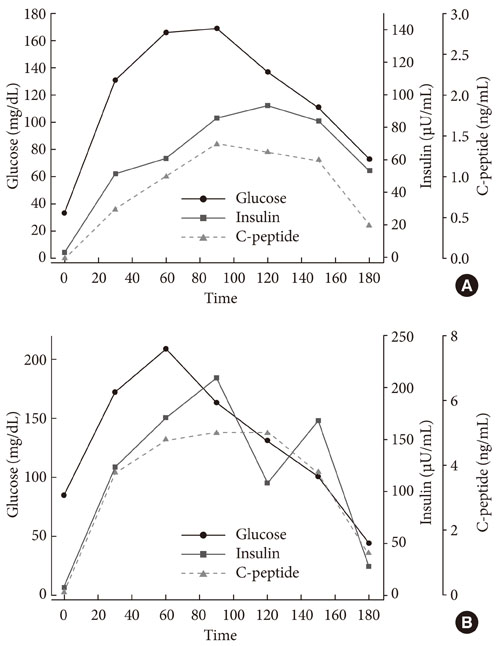
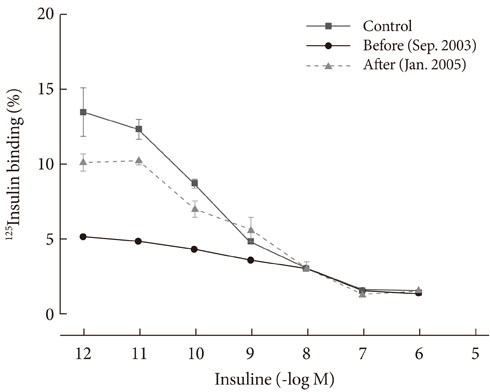
To evaluate the mechanism of hypoglycemia, we measured the inhibition of insulin binding to erythrocytes and IM9 lymphocytes in a sample of the patient's dialyzed serum before and after immunosuppressive therapy.
RESULTS
In the patient's pre-treatment serum IgG, the binding of 125I-insulin to erythrocytes was markedly inhibited in a dose-dependent manner until the cold insulin level reached 10-9 mol/L. We also observed dose-dependent inhibition of insulin binding to IM9 lymphocytes, which reached approximately 82% inhibition and persisted even when diluted 1:20. After treatment with glucocorticoids, insulin-erythrocyte binding activity returned to between 70% and 80% of normal, while the inhibition of insulin-lymphocyte binding was reduced by 17%.
CONCLUSION
We treated a patient with type B insulin resistance syndrome showing recurrent fasting hypoglycemia with steroids and azathioprine. We characterized the patient's insulin receptor antibodies by measuring the inhibition of insulin binding.
MeSH Terms
-
Acanthosis Nigricans
Antibodies
Autoantibodies
Azathioprine
Cold Temperature
Erythrocytes
Glucocorticoids
Humans
Hyperglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Immunoglobulin G
Insulin
Insulin Resistance
Lymphocytes
Receptor, Insulin
Steroids
Antibodies
Autoantibodies
Azathioprine
Glucocorticoids
Immunoglobulin G
Insulin
Receptor, Insulin
Steroids
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cruz PD Jr, Hud JA Jr. Excess insulin binding to insulin-like growth factor receptors: proposed mechanism for acanthosis nigricans. J Invest Dermatol. 1992. 98:6 Suppl. 82S–85S.2. Hirata Y, Uchigata Y. Insulin autoimmune syndrome in Japan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1994. 24:Suppl. S153–S157.3. Flier JS, Kahn CR, Roth J, Bar RS. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975. 190:63–65.4. Braund WJ, Naylor BA, Williamson DH, Buley ID, Clark A, Chapel HM, Turner RC. Autoimmunity to insulin receptor and hypoglycaemia in patient with Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1987. 1:237–240.5. Taylor SI, Grunberger G, Marcus-Samuels B, Underhill LH, Dons RF, Ryan J, Roddam RF, Rupe CE, Gorden P. Hypoglycemia associated with antibodies to the insulin receptor. N Engl J Med. 1982. 307:1422–1426.6. Rodriguez O, Collier E, Arakaki R, Gorden P. Characterization of purified autoantibodies to the insulin receptor from six patients with type B insulin resistance. Metabolism. 1992. 41:325–331.7. Dozio N, Micossi P, Galimberti G, Sartori S, Pozza G, Dosio F, Savi A, Gerundini PG, Fazio F, Chiumello G, et al. In vivo demonstration of insulin-receptor defect with 123I-labeled insulin and scintigraphic scanning in severe insulin resistance. Diabetes Care. 1992. 15:651–656.8. Gambhir KK, Archer JA, Carter L. Insulin radioreceptor assay for human erythrocytes. Clin Chem. 1977. 23:1590–1595.9. Kahn CR, Flier JS, Bar RS, Archer JA, Gorden P, Martin MM, Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976. 294:739–745.10. Flier JS, Eastman RC, Minaker KL, Matteson D, Rowe JW. Acanthosis nigricans in obese women with hyperandrogenism. Characterization of an insulin-resistant state distinct from the type A and B syndromes. Diabetes. 1985. 34:101–107.11. Taylor SI, Dons RF, Hernandez E, Roth J, Gorden P. Insulin resistance associated with androgen excess in women with autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Ann Intern Med. 1982. 97:851–855.12. Accili D, Barbetti F, Cama A, Kadowaki H, Kadowaki T, Imano E, Levy-Toledano R, Taylor SI. Mutations in the insulin receptor gene in patients with genetic syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. J Invest Dermatol. 1992. 98:6 Suppl. 77S–81S.13. Cama A, de la Luz Sierra M, Ottini L, Kadowaki T, Gorden P, Imperato-McGinley J, Taylor SI. A mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor associated with insulin resistance in an obese woman. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991. 73:894–901.14. De Pirro R, Roth RA, Rossetti L, Goldfine ID. Characterization of the serum from a patient with insulin resistance and hypoglycemia. Evidence for multiple populations of insulin receptor antibodies with different receptor binding and insulin-mimicking activities. Diabetes. 1984. 33:301–304.15. Dons RF, Havlik R, Taylor SI, Baird KL, Chernick SS, Gorden P. Clinical disorders associated with autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Simulation by passive transfer of immunoglobulins to rats. J Clin Invest. 1983. 72:1072–1080.16. Tsushima T, Omori Y, Murakami H, Hirata Y, Shizume K. Demonstration of heterogeneity of autoantibodies to insulin receptors in type B insulin resistance by isoelectric focusing. Diabetes. 1989. 38:1090–1096.17. Pedersen O, Hjollund E, Beck-Nielsen H, Kromann H. Diabetes mellitus caused by insulin-receptor blockade and impaired sensitivity to insulin. N Engl J Med. 1981. 304:1085–1088.18. Di Paolo S, Giorgino R. Insulin resistance and hypoglycemia in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: description of antiinsulin receptor antibodies that enhance insulin binding and inhibit insulin action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991. 73:650–657.19. Yamasaki H, Yamaguchi Y, Fujita N, Kato C, Kuwahara H, Yamauchi MD, Yamakawa K, Abe T, Ozaki M, Sera Y, Uotani S, Kawasaki E, Takino H, Eguchi K. Anti-insulin receptor autoantibodies in a patient with type B insulin resistance and fasting hypoglycemia. Acta Diabetol. 2000. 37:189–196.20. Arioglu E, Andewelt A, Diabo C, Bell M, Taylor SI, Gorden P. Clinical course of the syndrome of autoantibodies to the insulin receptor (type B insulin resistance): a 28-year perspective. Medicine (Baltimore). 2002. 81:87–100.21. Malek R, Chong AY, Lupsa BC, Lungu AO, Cochran EK, Soos MA, Semple RK, Balow JE, Gorden P. Treatment of type B insulin resistance: a novel approach to reduce insulin receptor autoantibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. 95:3641–3647.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of insulin autoimmune syndrome
- Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome with Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome in a Patient with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- A Case of Autoimmune Hypoglycemia due to Insulin Antibody in Patient with End Stage Renal Disease
- Insulin autoimmune syndrome associated with alpha-lipoic acid in a young woman with no concomitant disease