Korean J Perinatol.
2014 Sep;25(3):178-183. 10.14734/kjp.2014.25.3.178.
A Huge Umbilical Vein Aneurysm: Case Report and a Brief Review of Literatures Describing Umbilical Vessel Aneurysm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Severance Hospital, Institute of Women's Medical Life Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. YHKIM522@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2280993
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2014.25.3.178
Abstract
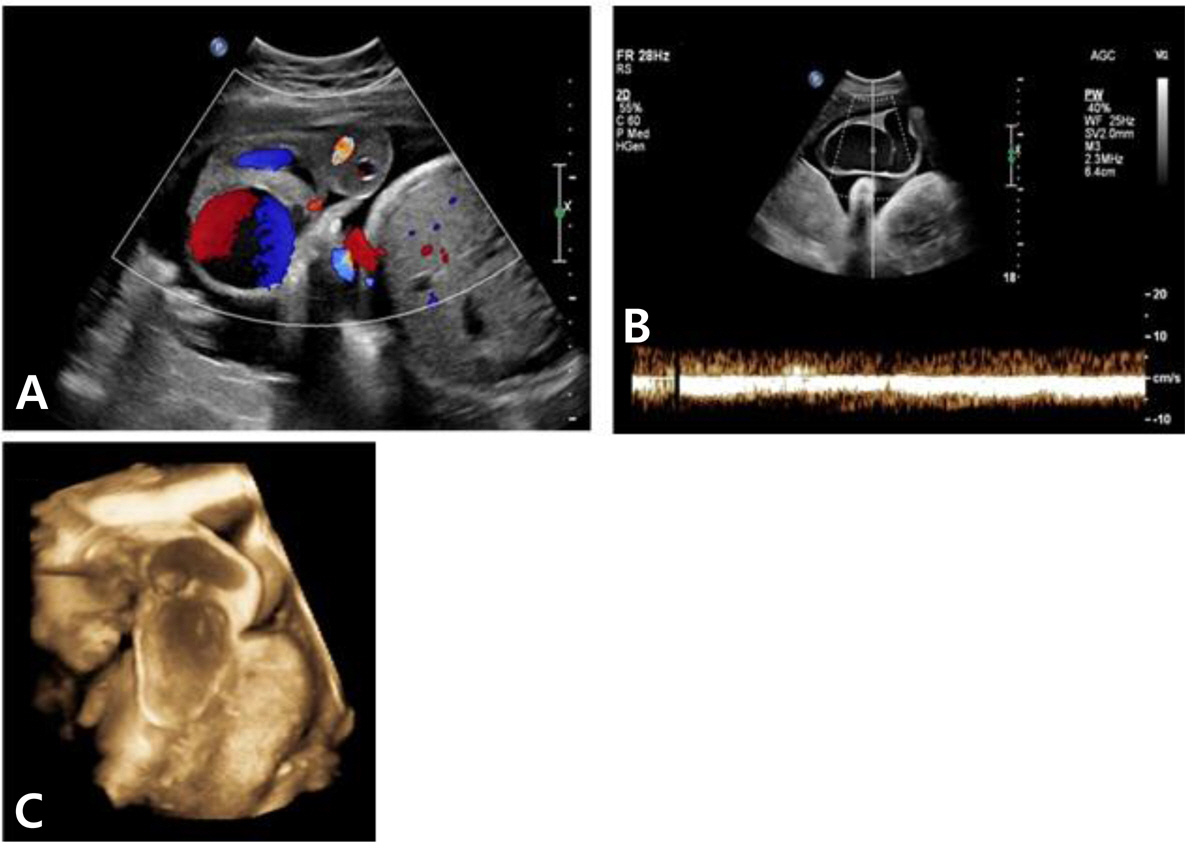
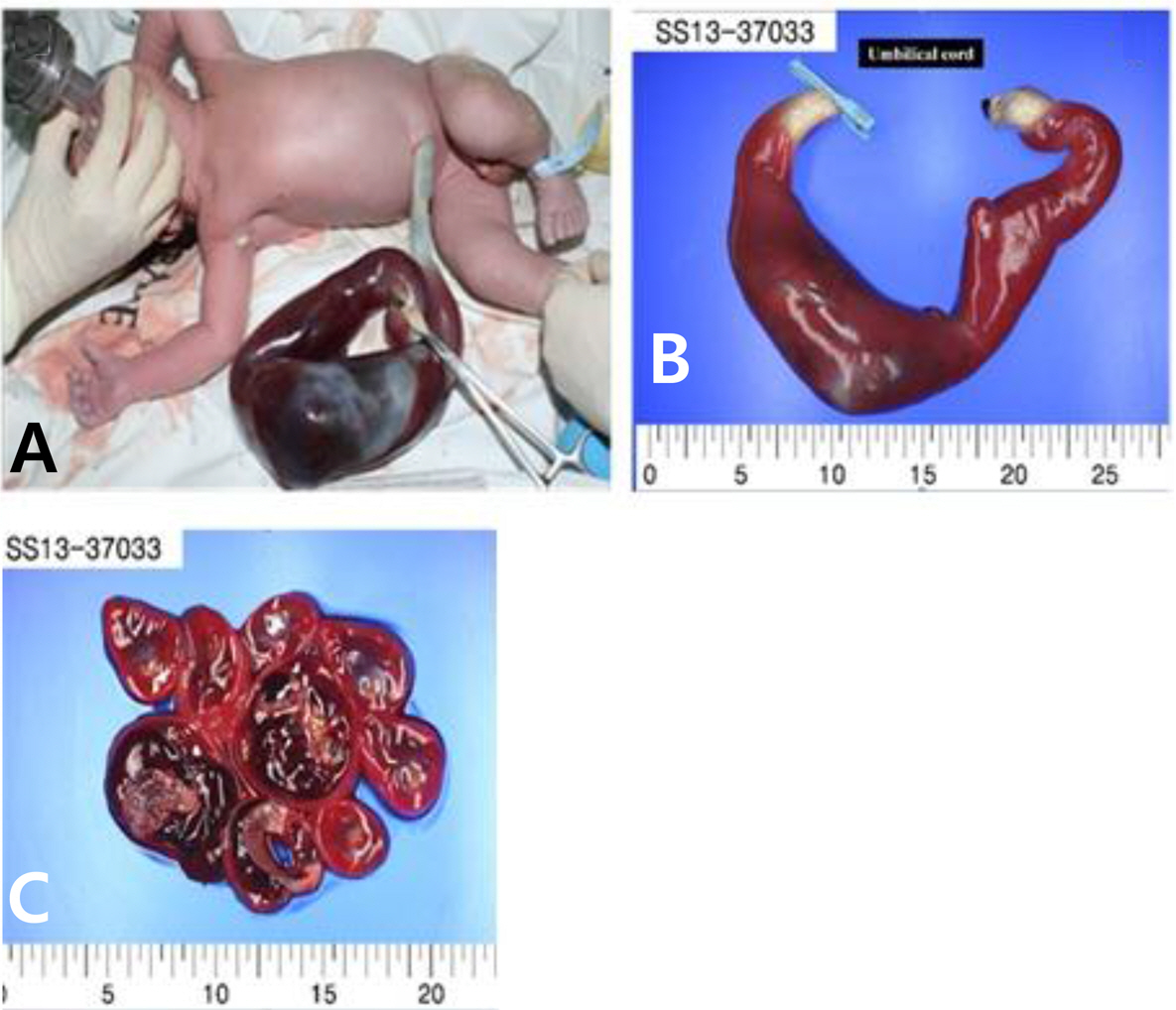
- An umbilical vein aneurysm is rare, but appears to be associated with fetal morbidity and mortality. There are no specific guidelines for pregnancy with umbilical vein aneurysm and the management is substantially up to the clinician. We report a case of intra-amniotic umbilical vein aneurysm diagnosed at 35 gestational weeks by ultrasound. Because the aneurysm was growing rapidly, prompt cesarean delivery was conducted. After delivery, a huge fusiform umbilical cord was noted, which was confirmed to be umbilical vein aneurysm by pathological examination. We also reviewed previous reported cases and summarized the management strategies of prenatally detected umbilical vein aneurysms. In addition, the umbilical vein in this case report had the largest size ever reported.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Kumar, Abbas, Aster. Robbins Basic Pathology. 9th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders co;2012. p. 344.2.Fung TY., Leung TN., Leung TY., Lau TK. Fetal intra-abdominal umbilical vein varix: what is the clinical significance? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005. 25:149–54.
Article3.Beraud E., Rozel C., Milon J., Darnault P. Umbilical vein varix: Importance of ante- and post-natal monitoring by ultrasound.4.Berg C., Giepel A., Germer U., Gloeckner-Hofmann K., Gem-bruch U. Prenatal diagnosis of umbilical cord aneurysm in a fetus with trisomy 18. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001. 17:79–81.
Article5.Siddiqi TA., Bendon R., Schultz DM., Miodovnik M. Umbilical artery aneurysm: prenatal diagnosis and management. Obstet Gynecol. 1992. 80:530–3.6.Lee SW., Kim MY., Kim JE., Chung JH., Lee HJ., Yoon JY. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of antenatal fetal intraabdominal umbilical vein varix detection. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2014. 57:181–6.
Article7.Challis D., Trudinger BJ., Moore L., Kennedy DS., Ryan G., Toi A, et al. Intra-abdominal varix of the umbilical vein: is it an indication for fetal karyotyping? (Abstract). Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997. 176:s93.8.Doehrman P., Derksen BJ., Perlow JH., Clewell WH., Finberg HJ. Umbilical artery aneurysm: A case report, literature review, and management recommendations. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2014. 69:159–63.9.Olog A., Thomas JT., Petersen S., Cattanach S., Lourie R., Gardener G. Large umbilical artery aneurysm with a live healthy baby delivered at 31 weeks. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2011. 29:331–3.
Article10.Schröcksnadel H., Holböck E., Mitterschiffthaler G., Tötsch M., Dapunt O. Thrombotic occlusion of an umbilical vein varix causing fetal death. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 1991. 248:213–5.
Article11.White SP., Kofinas A. Prenatal diagnosis and management of umbilical vein varix of the intra-amniotic portion of the umbilical vein. J Ultrasound Med. 1994. 13:992–4.
Article12.Shipp TD., Bromley B., Benacerraf BR. Sonographically detected abnormalities of the umbilical cord. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1995. 48:179–85.
Article13.Babay ZA., Lange IR., Elliott PD., Hwang WS. A case of varix dilatation of the umbilical vein and review of the literature. Fetal Diagn Ther. 1996. 11:221–3.
Article14.Vandevijver N., Hermans RH., Schrander-Stumpel CC., Arends JW., Peeters LL., Moerman PL. Aneurysm of the umbilical vein: case report and review of literature. Eur J Obstet Gy-necol Reprod Biol. 2000. 89:85–7.
Article15.Cruise K., Rouse G. Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber Syndrome complicated by extrafetal umbilical vein varix. J Diagn Med Sonogr. 2002. 18:317–20.
Article16.Zachariah M., Vyjayanthi S., Bell-Thomas S. Umbilical vein varix thrombosis: a rare pathology. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2004. 24:581.
Article17.Panda B., Stiller R., Iruretagoyena I., Levi A. Prenatal diagnosis of an umbilical vein aneurysm: a case report. Conn Med. 2009. 73:465–7.18.Akar M., Dilli D., Sandal G., Öncel MY., Erdeve Ö., Dilmen U. Prenatally diagnosed umbilical vein aneurysm with good prognosis. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012. 40:368–9.
Article19.Deront-Bourdin F., Blanquiot JL., Checchi C., Nataf S., Bongain A. Umbilical vein varix thrombosis. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2014. 42:448–50.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CT Findings of Portal Vein Aneurysm
- A Case Report: Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein
- A Case of Open Heart Surgery in a Patient with Huge Sinoatrial Nodal Artery Aneurysm -A case report-
- Basilar Bifurcation Aneurysm Associated with Carotid-Ophthalmic Aneurysm: A Case Report
- A Case Report of Non-surgical Removal of Fragmented Remnant of Umbilical Vein Catheter Using an Intravascular Snare