Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Mar;5(1):34-38.
Long-term Study of Sialodochoplasty for Preventing Submandibular Sialolithiasis Recurrence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. lsw0922@schmc.ac.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The transoral removal of stones by sialodochoplasty has been popularized in the treatment of submandibular sialolithiasis. However, the effectiveness of sialodochoplasty is controversial, and there are no reports on the long-term outcomes of this procedure. The purpose of this study was to assess the effectiveness and long-term outcomes of sialodochoplasty in patients with submandibular sialolithiasis.
METHODS
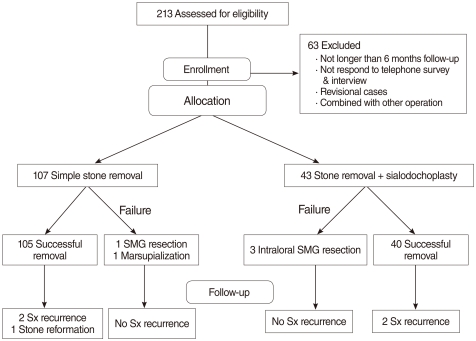
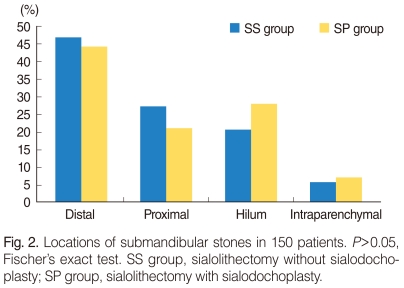
We conducted a cross-sectional study that included retrospective chart reviews and prospective telephone or interview surveys of 150 patients treated for submandibular sialolithiasis from March 2001 to January 2008. The patients were treated with two different procedures by two different surgeons. One surgeon performed a transoral sialolithectomy without sialodochoplasty in 107 patients (SS group), and the other surgeon performed a transoral sialolithectomy with sialodochoplasty in 43 patients (SP group).
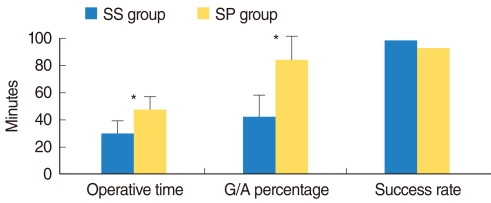
RESULTS
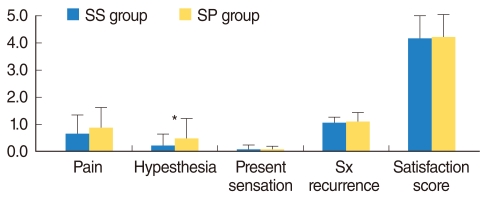
The success rate of transoral sialolithectomy was 98.1% in the SS group and 93% in the SP group. The recurrence rates of symptoms or stones were 1.9% and 4.7% in the SS and SP groups, respectively. The incidence of postoperative transient hypoesthesia was 13.1% in the SS group and 34.9% in the SP group. The mean operating times were 29.79 and 47.44 minutes in the SS and SP groups, respectively. The mean percentage of general anesthesia was 42.1% in the SS group and 83.7% in the SP group.
CONCLUSION
Sialodochoplasty in addition to transoral sialolithectomy for submandibular sialolithiasis did not affect the rate of symptom or stone recurrence, but did increase the postoperative hypoesthesia incidence and general anesthesia percentage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zenk J, Constantinidis J, Al-Kadah B, Iro H. Transoral removal of submandibular stones. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; 4. 127(4):432–436. PMID: 11296054.
Article2. Zenk J, Benzel W, Iro H. New modalities in the management of human sialolithiasis. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 1994; 3(5):275–284.
Article3. Isacsson G, Ahlner B, Lundquist PG. Chronic sialadenitis of the submandibular gland: a retrospective study of 108 case. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1981; 232(1):91–100. PMID: 7271582.4. Marchal F, Kurt AM, Dulguerov P, Becker M, Oedman M, Lehmann W. Histopathology of submandibular glands removed for sialolithiasis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001; 5. 110(5 Pt 1):464–469. PMID: 11372932.
Article5. van den Akker HP, Busemann-Sokole E. Submandibular gland function following transoral sialolithectomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983; 10. 56(4):351–356. PMID: 6579472.
Article6. Nishi M, Mimura T, Marutani K, Noikura T. Evaluation of submandibular gland function by sialo-scintigraphy following sialolithectomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1987; 7. 45(7):567–571. PMID: 3037049.
Article7. Epker BN. Obstructive and inflammatory diseases of the major salivary glands. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1972; 1. 33(1):2–27. PMID: 4332075.
Article8. Roh JL, Park CI. Transoral removal of submandibular hilar stone and sialodochoplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 8. 139(2):235–239. PMID: 18656721.
Article9. Rontal M, Rontal E. The use of sialodochoplasty in the treatment of benign inflammatory obstructive submandibular gland disease. Laryngoscope. 1987; 12. 97(12):1417–1421. PMID: 3683054.
Article10. Roh JL, Kim AY. Application of mitomycin C after transoral removal of submandibular stones and sialodochoplasty. Laryngoscope. 2005; 5. 115(5):915–918. PMID: 15867666.
Article11. Wilkie TF. The surgical treatment of drooling: a follow-up report of five years' experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1970; 6. 45(6):549–554. PMID: 5444670.12. Sobol S, Spector GJ. Sialodochotomy and sialolithectomy for acute calculous submaxillary sialadenitis. Laryngoscope. 1979; 11. 89(11):1864–1866. PMID: 502708.13. Makdissi J, Escudier MP, Brown JE, Osailan S, Drage N, McGurk M. Glandular function after intraoral removal of salivary calculi from the hilum of the submandibular gland. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 12. 42(6):538–541. PMID: 15544884.
Article14. McGurk M, Makdissi J, Brown JE. Intra-oral removal of stones from the hilum of the submandibular gland: report of technique and morbidity. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 10. 33(7):683–686. PMID: 15337182.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recurrent Sialolithiasis on Remnant Wharton's Duct Following Submandibular Gland Resection
- A Case of Unilateral Absence of the Submandibular Gland Secondary to Sialolithiasis
- Sialolithiasis Mimicking Metastatic Thyroid Cancer
- A case report of the sialolithiasis on the submandibular gland
- Giant sialolithiasis of the submandibular gland: a case report