Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Apr;5(Suppl 1):S99-S102.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss after Failure from Oral and Intratympanic Corticosteroid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Otorhinolaryngology, Burapha University Faculty of Medicine, Chon Buri, Thailand. drthanarath@gmail.com
- 2Division of Preventive Medicine, Abhakornkiattiwong Hospital, Sattahip Naval Base, Chon Buri, Thailand.
- 3Department of Otolaryngology, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand.
Abstract
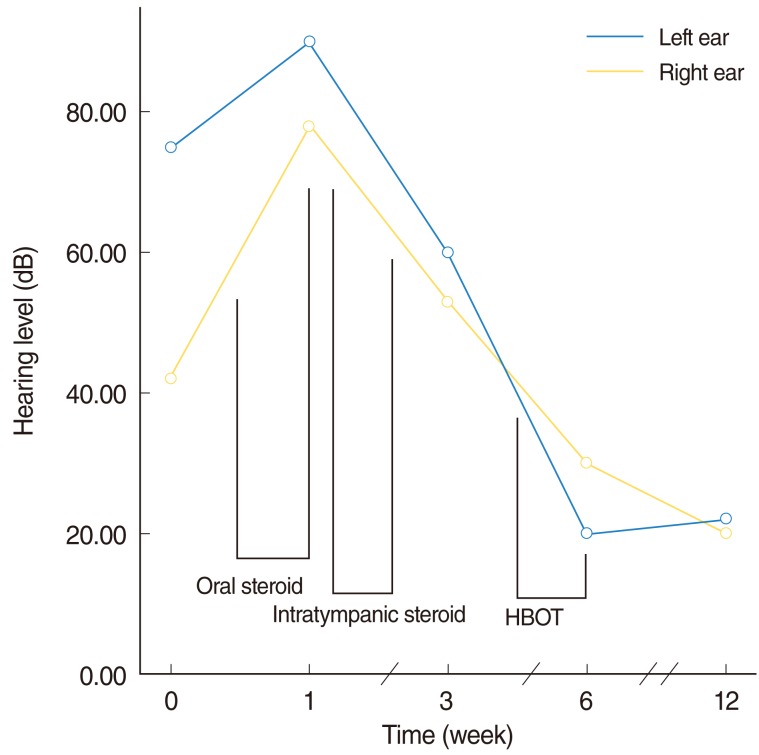
- Systemic and intratympanic steroids are most widely used for treating idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Other treatments include vasodilator, immunosuppressant and antiviral medication. However, only 61% of patients achieve full recovery, and controversies about the standard treatment still exist. In this case report, we present a patient with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss who failed to respond to systemic and intratympanic steroid treatments but subsequently recovered after undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hughes GB, Freedman MA, Haberkamp TJ, Guay ME. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1996; 6. 29(3):393–405. PMID: 8743339.
Article2. Rauch SD. Clinical practice: idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. N Engl J Med. 2008; 8. 21. 359(8):833–840. PMID: 18716300.3. Conlin AE, Parnes LS. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: I. a systematic review. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 6. 133(6):573–581. PMID: 17576908.4. Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss: a double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol. 1980; 12. 106(12):772–776. PMID: 7002129.
Article5. Fujimura T, Suzuki H, Shiomori T, Udaka T, Mori T. Hyperbaric oxygen and steroid therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 8. 264(8):861–866. PMID: 17340130.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Application of Hyperbaric Oxygen in Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Comparison of Steroid Treatment with and without Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Intratympanic Steroid Therapy for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Clinical Characteristics and Management of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- The First Cases of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Post Coronavirus Disease in Children