Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2013 Dec;6(4):231-236.
Learning Curve of Septoplasty with Radiofrequency Volume Reduction of the Inferior Turbinate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. profsookim@gmail.com
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Since few studies on surgical training and learning curves have been performed, majority of inexperienced surgeons are anxious about performing operations. We aimed to access the results and learning curve of septoplasty with radiofrequency volume reduction (RFVR) of the inferior turbinate.
METHODS
We included 270 patients who underwent septoplasty with RFVR of the inferior turbinate by 6 inexperienced surgeons between January 2009 and July 2011. We analyzed success score, cases of revision, cases of complication, operation time, and acoustic rhinometry.
RESULTS
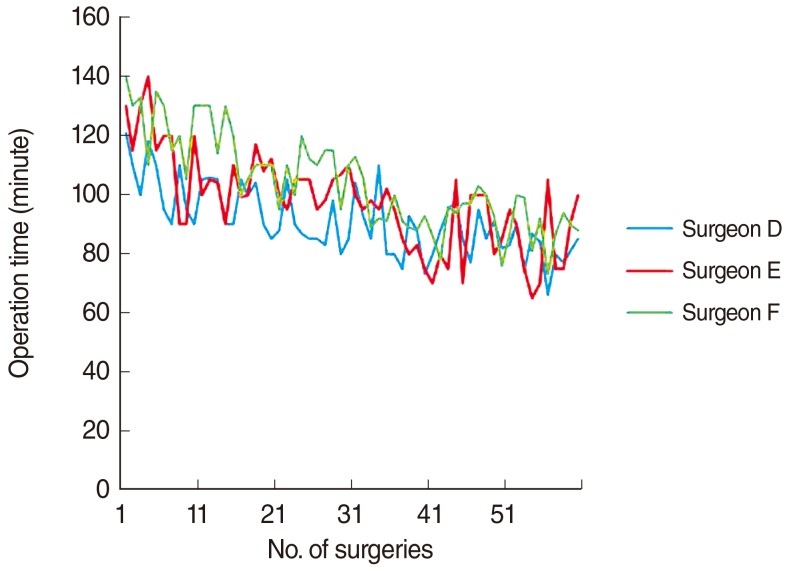
Success score was relatively high and every surgeon had few cases of revision and complication. No significant difference was found in success score, revision, complication case, or acoustic rhinometry values between early cases and later cases. Operation time decreased according to increase in experience. However, there was no significant difference in the operation time after more than 30 cases.
CONCLUSION
We can conclude that 30 cases are needed to develop mature surgical skills for septoplasty with RFVR of the inferior turbinate and that training surgeons do not need to be anxious about performing this operation in the unskilled state.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Babineau TJ, Becker J, Gibbons G, Sentovich S, Hess D, Robertson S, et al. The "cost" of operative training for surgical residents. Arch Surg. 2004; 4. 139(4):366–369. PMID: 15078701.
Article2. Bridges M, Diamond DL. The financial impact of teaching surgical residents in the operating room. Am J Surg. 1999; 1. 177(1):28–32. PMID: 10037304.
Article3. Koperna T. How long do we need teaching in the operating room? The true costs of achieving surgical routine. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2004; 6. 389(3):204–208. PMID: 14557883.
Article4. Wang MC, Yu EC, Shiao AS, Liao WH, Liu CY. The costs and quality of operative training for residents in tympanoplasty type I. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009; 5. 129(5):512–514. PMID: 18720069.
Article5. Bokhari AR, Davies MA, Diamond T. Endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: a single surgeon experience and the learning curve. Br J Neurosurg. 2013; 2. 27(1):44–49. PMID: 22900510.
Article6. Marks SC. Learning curve in endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999; 2. 120(2):215–218. PMID: 9949355.
Article7. Uribe JI, Ralph WM Jr, Glaser AY, Fried MP. Learning curves, acquisition, and retention of skills trained with the endoscopic sinus surgery simulator. Am J Rhinol. 2004; Mar-Apr. 18(2):87–92. PMID: 15152873.8. Liu CY, Yu EC, Lin SH, Wang YP, Wang MC. Learning curve of septomeatoplasty. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2009; 12. 36(6):661–664. PMID: 19414230.
Article9. D'Ascanio L, Manzini M. Quick septoplasty: surgical technique and learning curve. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2009; 11. 33(6):814–818. PMID: 19582504.10. Jin HR, Lee JY, Jung WJ. New description method and classification system for septal deviation. J Rhinol. 2007; 5. 14(1):27–31.11. Dobratz EJ, Park SS. Septoplasty pearls. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2009; 6. 42(3):527–537. PMID: 19486747.
Article12. Fettman N, Sanford T, Sindwani R. Surgical management of the deviated septum: techniques in septoplasty. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2009; 4. 42(2):241–252. PMID: 19328889.
Article13. Smith SJ, Eralil G, Woon K, Sama A, Dow G, Robertson I. Light at the end of the tunnel: the learning curve associated with endoscopic transsphenoidal skull base surgery. Skull Base. 2010; 3. 20(2):69–74. PMID: 20808530.
Article14. Soot SJ, Eshraghi N, Farahmand M, Sheppard BC, Deveney CW. Transition from open to laparoscopic fundoplication: the learning curve. Arch Surg. 1999; 3. 134(3):278–281. PMID: 10088568.15. Patel N, Shelton C. The surgical learning curve in aural atresia surgery. Laryngoscope. 2007; 1. 117(1):67–73. PMID: 17202933.
Article16. Luers JC, Damm M, Klussmann JP, Beutner D. The learning curve of sialendoscopy with modular sialendoscopes: a single surgeon's experience. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 8. 136(8):762–765. PMID: 20566901.17. Cakmak O, Tarhan E, Coskun M, Cankurtaran M, Celik H. Acoustic rhinometry: accuracy and ability to detect changes in passage area at different locations in the nasal cavity. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005; 12. 114(12):949–957. PMID: 16425563.
Article18. Roithmann R, Cole P, Chapnik J, Barreto SM, Szalai JP, Zamel N. Acoustic rhinometry, rhinomanometry, and the sensation of nasal patency: a correlative study. J Otolaryngol. 1994; 12. 23(6):454–458. PMID: 7897780.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coblation Turbinate Reduction in Patient with Nasal Obstruction
- Septoplasty and Turbinoplasty ; Current Concept and Technique
- Effectiveness of the Turbinoplasty in the Patient with Deviated Septum of Nose
- Surgical treatment for allergic rhinitis
- The Evaluation of Olfactory Function in Patients with Septal and Turbinate Surgery