Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2014 Mar;7(1):63-65.
Aggravation of Relapsing Polychondritis due to the Infection and Its Manifestation on a Nasal Tip Graft
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Daejin Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea. renalcho@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Dermatology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
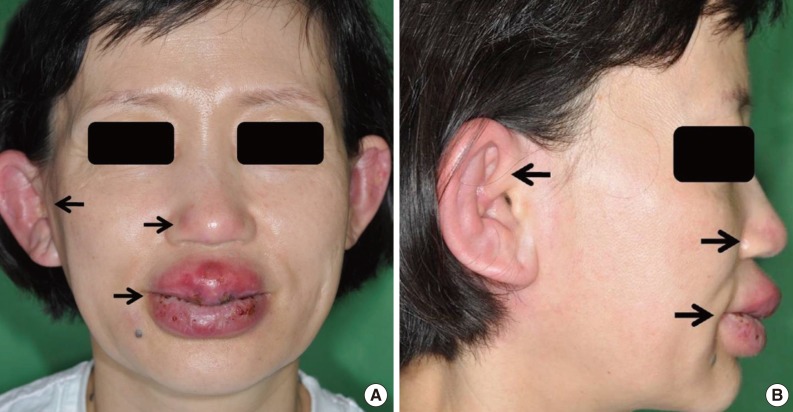
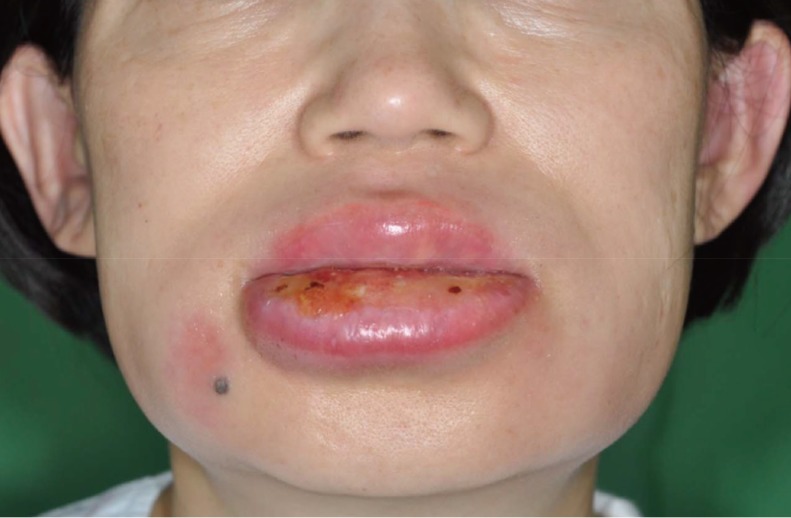
- Relapsing polychondritis (RP) is an uncommon systemic disease that is characterized by episodic and progressive inflammation of the cartilaginous structures, which can be very debilitating and in some instances life-threatening. The pathogenic pathways of RP are largely unknown. However, several hypothesis have been suggested. We had an interesting case of aggravation of RP due to the infection. Graft cartilage on the nasal tip was affected by RP also. This case can give a clue of revealing the pathogenesis of RP. We introduce a case with a review of the literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yamaoka K, Saito K, Hanami K, Nakayamada S, Nawata M, Iwata S, et al. A case of life-threatening refractory polychondritis successfully treated with combined intensive immunosuppressive therapy with methotrexate. Mod Rheumatol. 2007; 17(2):144–147. PMID: 17437170.
Article2. McAdam LP, O'Hanlan MA, Bluestone R, Pearson CM. Relapsing polychondritis: prospective study of 23 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1976; 5. 55(3):193–215. PMID: 775252.3. Dolan DL, Lemmon GB Jr, Teitelbaum SL. Relapsing polychondritis: analytical literature review and studies on pathogenesis. Am J Med. 1966; 8. 41(2):285–299. PMID: 4223687.4. Sokka T, Toloza S, Cutolo M, Kautiainen H, Makinen H, Gogus F, et al. Women, men, and rheumatoid arthritis: analyses of disease activity, disease characteristics, and treatments in the QUEST-RA study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11(1):R7. PMID: 19144159.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Relapsing Polychondritis Associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Relapsing polychondritis involving trancheobronchial tree: CT finding and differential diagnosis
- A Case of Relapsing Polychondritis
- Reconstructive rhinoplasty with costal cartilage grafting: A case report of relapsing polychondritis
- A Case of Relapsing Polychondritis Presenting As a Diffuse Tracheobronchial Tree Involvement