Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2014 Dec;7(4):324-328. 10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.324.
Long-Term Results of Endoscopic Dilatation for Tracheal and Subglottic Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. lsw0922@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2278375
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.324
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to assess the long-term results of endoscopic dilatation of airway stenosis and to evaluate predictive factors for favorable results.
METHODS
Fifty-four patients with tracheal and subglottic stenosis who underwent endoscopic dilatation with at least 12 months follow-up were enrolled in this study. We evaluated predictive factors for final treatment outcome such as stenosis length, location, characteristics, procedure type, and the severity of stenosis.
RESULTS
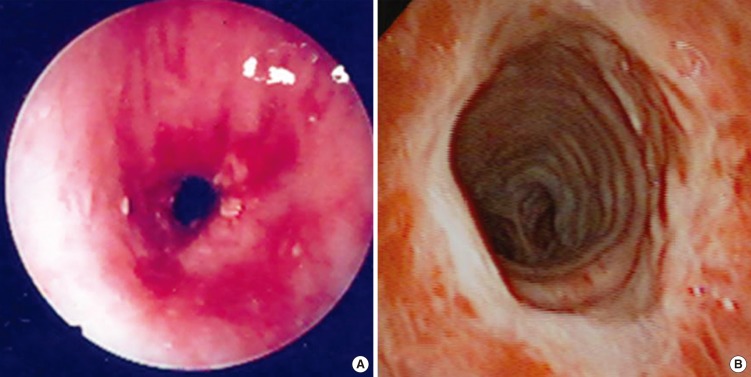
The final outcome of endoscopic dilatation showed a cure rate of 40.7%, improvement rate of 46.3%, and failure rate of 13.0%. Patients with mild stenosis or a shorter stenotic segment and those who underwent a touch-up procedure following tracheal resection with end-to-end anastomosis showed better outcomes. The cure rate of endoscopic dilatation for patients with shorter mild stenosis was 72.2%.
CONCLUSION
Endoscopic dilatation may be a primary treatment modality for patients with airway stenosis characterized by mild severity and a short stenotic segment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The applications of endoscopic surgery in department of otorhinolaryngology-head and neck surgery
Jong In Jeong, Sang Duk Hong
J Korean Med Assoc. 2015;58(6):548-554. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2015.58.6.548.
Reference
-
1. Mandour M, Remacle M, Van de Heyning P, Elwany S, Tantawy A, Gaafar A. Chronic subglottic and tracheal stenosis: endoscopic management vs. surgical reconstruction. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2003; 8. 260(7):374–380. PMID: 12682844.
Article2. Schweinfurth JM. Endoscopic treatment of severe tracheal stenosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2006; 1. 115(1):30–34. PMID: 16466097.
Article3. Yamamoto K, Kojima F, Tomiyama K, Nakamura T, Hayashino Y. Meta-analysis of therapeutic procedures for acquired subglottic stenosis in adults. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011; 6. 91(6):1747–1753. PMID: 21619972.
Article4. Shapshay SM, Beamis JF Jr, Hybels RL, Bohigian RK. Endoscopic treatment of subglottic and tracheal stenosis by radial laser incision and dilation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1987; Nov-Dec. 96(6):661–664. PMID: 3688753.
Article5. Monnier P, George M, Monod ML, Lang F. The role of the CO2 laser in the management of laryngotracheal stenosis: a survey of 100 cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; 8. 262(8):602–608. PMID: 16021463.6. Simpson CB, James JC. The efficacy of mitomycin-C in the treatment of laryngotracheal stenosis. Laryngoscope. 2006; 10. 116(10):1923–1925. PMID: 17003706.
Article7. Nouraei SA, Singh A, Patel A, Ferguson C, Howard DJ, Sandhu GS. Early endoscopic treatment of acute inflammatory airway lesions improves the outcome of postintubation airway stenosis. Laryngoscope. 2006; 8. 116(8):1417–1421. PMID: 16885746.
Article8. Cotton RT. Pediatric laryngotracheal stenosis. J Pediatr Surg. 1984; 12. 19(6):699–704. PMID: 6520674.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expandable Metallic Stent in the Treatment of Subglottic Tracheal Stenosis: Report of Long-term Failure in 4 Cases
- Ultrasound Guided Bronchoscopic Balloon Dilatation in the Management of Tracheal Stenosis: A Case Report
- Surgical Management of Idiopathic Tracheal Stenosis: Three case reports
- Endoscopic Dilatation and Mitomycin Injection of Subglottic Stenosis in Wegener's Granuolmatosis
- A Case of Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis Treated by Endoscopic Nd-YAG Laser and Balloon Catheter