Korean J Pain.
2014 Jul;27(3):266-270. 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.266.
Variations in Entrance of Vertebral Artery in Korean Cervical Spine: MDCT-based Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Pohang Stroke and Spine Hospital, Pohang, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea. solafide5@yahoo.co.kr
- 4Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2278238
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.266
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Knowledge of the anatomical variation of the vertebral artery has clinical importance not only for the performance of interventional or surgical procedures itself but also to ensure their safety. We conducted a study of the anatomical variation by reviewing multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) images of the cervical spine from 460 Korean patients.
METHODS
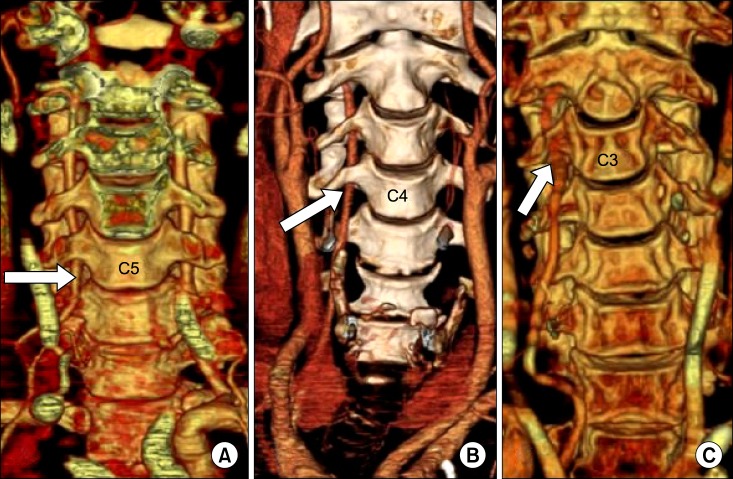
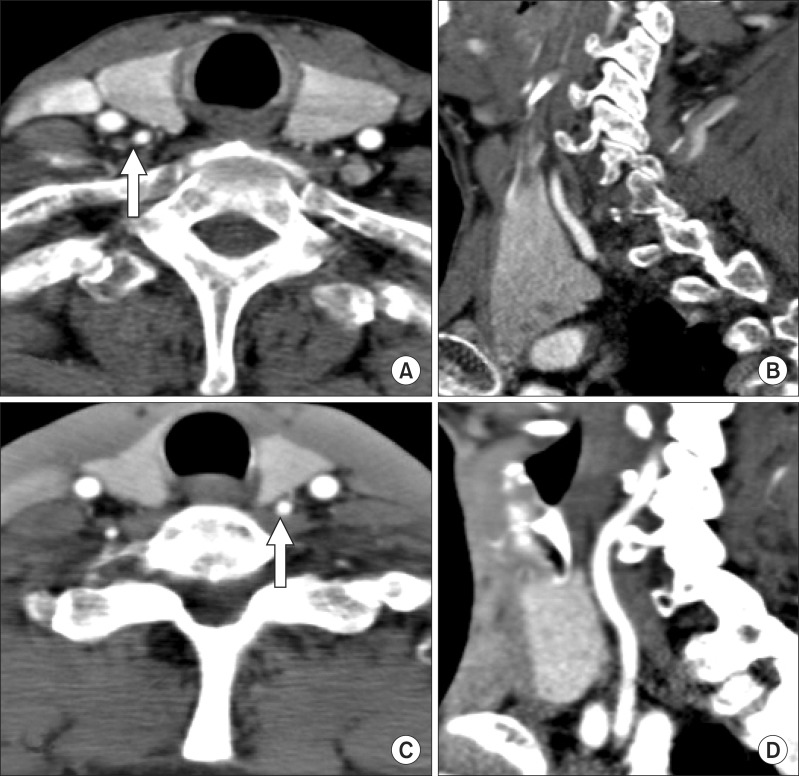
16-row MDCT data from 460 patients were used in this study. We observed 920 vertebral arteries. Examination points included level of entrance of the artery into the transverse foramen of the cervical vertebra, origin site of the vertebral artery, course of a vertebral artery with aberrant entrance. RESULT: The vertebral artery in 2 (0.2%) cases in this study entered into the transverse foramen of the 7th cervical vertebra from the left. In 45 (4.9%) cases, the vertebral artery entered into the transverse foramen of the 5th cervical vertebra. Of these, the entrance was on the right in 15 (1.6%) and on the left in 30 (3.3%). We found 17 (1.8%) cases in which the artery entered into the transverse foramen of the 4th cervical vertebra, 10 (1.1%) on the right and 7 (0.7%) on the left side. As is commonly acknowledged, the 6th cervical vertebra was the most common site of entry; the vertebral artery entered the transverse foramen of the 6th cervical vertebra in the remaining 855 (93.0%) cases, on the right in 434 (47.2%) and on the left in 421 (45.8%).
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, the possibility of an atypical course of the vertebral artery in segments V1 and V2 should be evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or CT images before carrying out procedures involving the anterior cervical vertebrae.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park HK, Jho HD. The management of vertebral artery injury in anterior cervical spine operation: a systematic review of published cases. Eur Spine J. 2012; 21:2475–2485. PMID: 22790563.
Article2. Rozin L, Rozin R, Koehler SA, Shakir A, Ladham S, Barmada M, et al. Death during transforaminal epidural steroid nerve root block (C7) due to perforation of the left vertebral artery. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2003; 24:351–355. PMID: 14634474.
Article3. Wallace MA, Fukui MB, Williams RL, Ku A, Baghai P. Complications of cervical selective nerve root blocks performed with fluoroscopic guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:1218–1221. PMID: 17449763.
Article4. Inamasu J, Guiot BH. Iatrogenic vertebral artery injury. Acta Neurol Scand. 2005; 112:349–357. PMID: 16281916.
Article5. Jung H, Lim JA, Park KB, Hong SW, Kwak KH, Park JM. Computed tomography-guided cervical selective transforaminal epidural block for a patient with bilateral anatomical variations of vertebral artery -a case report-. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013; 65:468–472. PMID: 24363853.
Article6. Hong JT, Park DK, Lee MJ, Kim SW, An HS. Anatomical variations of the vertebral artery segment in the lower cervical spine: analysis by three-dimensional computed tomography angiography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:2422–2426. PMID: 18923317.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vertebral Artery Injury during Anterior Cervical Spine Surgery: Report of Two Cases
- Vertebral Artery Injury Following Blunt Trauma to the Cervical Spine Case Report and Literature Review
- Radiologic Characteristics of Vertebral Artery Injury in the Cervical Spine Fracture
- Occlusion of Vertebral Artery and Cerebral Infarction after Cervical Spine Fracture: A Case Report
- Endovascular Management of Iatrogenic Vertebral Artery Pseudoaneurysm: A Case Report