Korean J Pain.
2014 Jan;27(1):49-53. 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.49.
Intradermal Therapy (Mesotherapy) for the Treatment of Acute Pain in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Preliminary Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Emergency Department, Central General Hospital, Bolzano-Bozen, Italy. stefano.corra@asbz.it
- 2Neurology Department, Central General Hospital, Bolzano-Bozen, Italy.
- KMID: 2278202
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.49
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common cause of severe hand pain. In this study we treated acute pain in CTS patients by means of local intradermal injections of anti-inflammatory drugs (mesotherapy).
METHODS
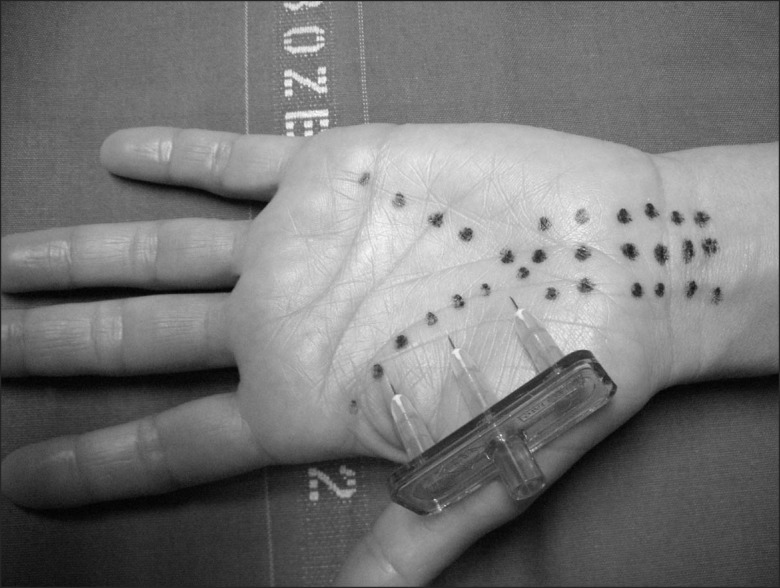
In twenty-five patients (forty-five hands), CTS diagnosis was confirmed by clinical and neurophysiological examination prior to mesotherapy. A mixture containing lidocaine 10 mg, ketoprophen lysine-acetylsalycilate 80 mg, xantinol nicotinate 100 mg, cyanocobalamine 1,000 mcg plus injectable water was used. Sites of injection were three parallel lines above the transverse carpal ligament and two v-shaped lines, one at the base of the thenar eminence, and the other at the base of the hypothenar eminence.
RESULTS
The day after the treatment, all but four patients reported a significant reduction in pain and paresthesias. After 12 months, 17 patients had a complete pain relief, eight patients reported recurrence of pain and sensory symptoms and four out of them underwent surgical treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
With the obvious limits of a small-size open-label study, our results suggest that mesotherapy can temporary relieve pain and paresthesias in most CTS patients and in some cases its effect seems to be long-lasting. Further controlled studies are needed to confirm our preliminary findings and to compare mesotherapy to conventional approaches for the treatment of CTS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for pillar pain after open carpal tunnel release: a double-blind, randomized, sham-controlled study
Mehmet Cenk Turgut, Gonca Saglam, Serdar Toy
Korean J Pain. 2021;34(3):315-321. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2021.34.3.315.
Reference
-
1. de Krom MC, Knipschild PG, Kester AD, Thijs CT, Boekkooi PF, Spaans F. Carpal tunnel syndrome: prevalence in the general population. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992; 45:373–376. PMID: 1569433.
Article2. Atroshi I, Gummesson C, Johnsson R, Ornstein E, Ranstam J, Rosén I. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population. JAMA. 1999; 282:153–158. PMID: 10411196.
Article3. Gelberman RH, Hergenroeder PT, Hargens AR, Lundborg GN, Akeson WH. The carpal tunnel syndrome. A study of carpal canal pressures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:380–383. PMID: 7204435.
Article4. You H, Simmons Z, Freivalds A, Kothari MJ, Naidu SH. Relationships between clinical symptom severity scales and nerve conduction measures in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22:497–501. PMID: 10204785.
Article5. Boyd KU, Gan BS, Ross DC, Richards RS, Roth JH, MacDermid JC. Outcomes in carpal tunnel syndrome: symptom severity, conservative management and progression to surgery. Clin Invest Med. 2005; 28:254–260. PMID: 16265997.6. Falkenburg SA. Choosing hand splints to aid carpal tunnel syndrome recovery. Occup Health Saf. 1987; 56:6063–64. PMID: 3587813.7. Muller M, Tsui D, Schnurr R, Biddulph-Deisroth L, Hard J, MacDermid JC. Effectiveness of hand therapy interventions in primary management of carpal tunnel syndrome: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2004; 17:210–228. PMID: 15162107.
Article8. Shi Q, MacDermid JC. Is surgical intervention more effective than non-surgical treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome? A systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011; 6:17. PMID: 21477381.
Article9. Chang MH, Chiang HT, Lee SS, Ger LP, Lo YK. Oral drug of choice in carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurology. 1998; 51:390–393. PMID: 9710008.
Article10. Semple JC, Cargill AO. Carpal-tunnel syndrome. Results of surgical decompression. Lancet. 1969; 1:918–919. PMID: 4180898.11. Shum C, Parisien M, Strauch RJ, Rosenwasser MP. The role of flexor tenosynovectomy in the operative treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A:221–225. PMID: 11861728.
Article12. Rohrich RJ. Mesotherapy: what is it? Does it work? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 115:1425. PMID: 15809612.
Article13. Bessis D, Guilhou JJ, Guillot B. Localized urticaria pigmentosa triggered by mesotherapy. Dermatology. 2004; 209:343–344. PMID: 15539904.
Article14. Brandão C, Fernandes N, Mesquita N, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Silva R, Lomba Viana H, et al. Abdominal haematoma--a mesotherapy complication. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005; 85:446. PMID: 16159740.15. Di Cesare A, Giombini A, Di Cesare M, Ripani M, Vulpiani MC, Saraceni VM. Comparison between the effects of trigger point mesotherapy versus acupuncture points mesotherapy in the treatment of chronic low back pain: a short term randomized controlled trial. Complement Ther Med. 2011; 19:19–26. PMID: 21296263.
Article16. Costantino C, Marangio E, Coruzzi G. Mesotherapy versus systemic therapy in the treatment of acute low back pain: a randomized trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011; 2011:317183. PMID: 20953425.
Article17. Cacchio A, De Blasis E, Desiati P, Spacca G, Santilli V, De Paulis F. Effectiveness of treatment of calcific tendinitis of the shoulder by disodium EDTA. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 61:84–91. PMID: 19116968.
Article18. Mammucari M, Gatti A, Maggiori S, Sabato AF. Role of mesotherapy in musculoskeletal pain: opinions from the italian society of mesotherapy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012:436959. PMID: 22654954.
Article19. Mammucari M, Gatti A, Maggiori S, Bartoletti CA, Sabato AF. Mesotherapy, definition, rationale and clinical role: a consensus report from the Italian Society of Mesotherapy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011; 15:682–694. PMID: 21796873.20. Navarte DA, Rosset-Llobet J. Safety of subcutaneous microinjections (mesotherapy) in musicians. Med Probl Perform Art. 2011; 26:79–83. PMID: 21695355.
Article21. Freynhagen R, Baron R, Tölle T, Stemmler E, Gockel U, Stevens M, et al. Screening of neuropathic pain components in patients with chronic back pain associated with nerve root compression: a prospective observational pilot study (MIPORT). Curr Med Res Opin. 2006; 22:529–537. PMID: 16574036.
Article22. Simovic D, Weinberg DH, Allam G, Hayes MT. A quantitative clinical scale for the carpal tunnel syndrome. 50th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology (AAN). Minneapolis, 25 April-2 May 1998, Poster 05.119. Neurology. 1998; 50:5119.23. Jablecki CK, Andary MT, Floeter MK, Miller RG, Quartly CA, Vennix MJ, et al. Practice parameter: electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. Report of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, American Academy of Neurology, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2002; 58:1589–1592. PMID: 12058083.
Article24. Kimura J. Electrodiagnosis in diseases of nerve and muscle: principles and practice. 2nd ed. Philadelphia (PA): Oxford University Press;1989. p. 501–511.25. Cioni R, Passero S, Paradiso C, Giannini F, Battistini N, Rushworth G. Diagnostic specificity of sensory and motor nerve conduction variables in early detection of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Neurol. 1989; 236:208–213. PMID: 2760633.
Article26. Uncini A, Lange DJ, Solomon M, Soliven B, Meer J, Lovelace RE. Ring finger testing in carpal tunnel syndrome: a comparative study of diagnostic utility. Muscle Nerve. 1989; 12:735–741. PMID: 2641997.
Article27. Padua L, Lo Monaco M, Valente EM, Tonali PA. A useful electrophysiologic parameter for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1996; 19:48–53. PMID: 8538669.
Article28. Hsu CC, Kuo HC, Hsu CT, Gu Q. Abdominal mesotherapy injection extended the absorption of follicle-stimulating hormone. Fertil Steril. 2011; 95:2134–2136. 2136.e1PMID: 21208615.
Article29. Andreu JL, Ly-Pen D. A randomized controlled trial of surgery vs steroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurology. 2006; 66:955–956. PMID: 16567731.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Hydrodissection for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Median Nerve Block for Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Report of 5 cases
- Usefulness of Ultrasound for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Proven in Meta-Analysis Studies
- The Current Concepts for the Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Current Approaches for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome