Korean J Pain.
2012 Jul;25(3):151-154. 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.3.151.
Morphologic Analysis of Water-Cooled Bipolar Radiofrequency lesions on Egg White in Vitro
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmshin1@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2278148
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.3.151
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to document the optimal spacing of two cannulae to form continuous strip lesions and maximal surface area by using water-cooled bipolar radiofrequency technology.
METHODS
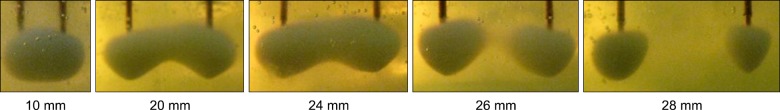
Two water-cooled needle probes (15 cm length, 18-gauge probe with 6 mm electrode tip) were placed in a parallel position 10, 20, 24, 26, and 28 mm apart and submerged in egg white. Temperatures of the probes were raised from 35degrees C to 90degrees C and the progress of lesion formation was photographed every 1 minute with the increase of the tip temperature. Approximately 30 photographs were taken. The resultant surface areas of the lesions were measured with the digital image program.
RESULTS
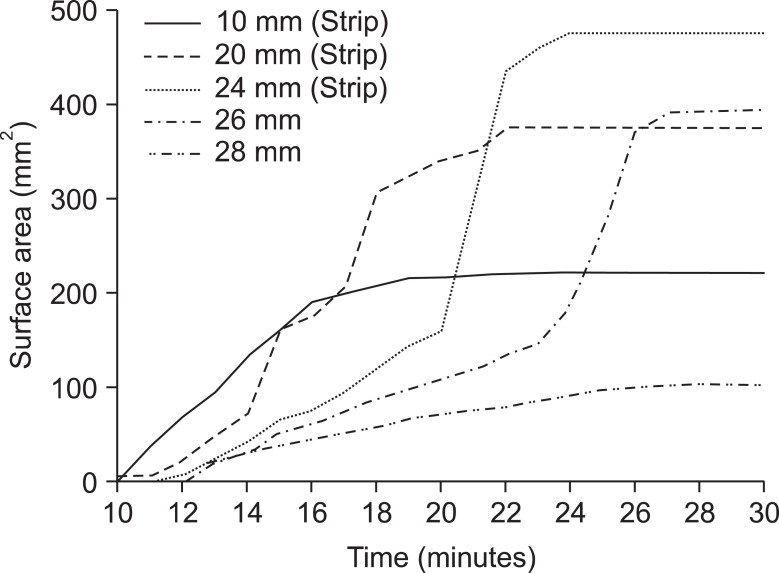
Continuous strip lesions were formed when the cannulae were spaced 24 mm or less apart; monopolar lesions around each cannula resulted if they were spaced more than 26 mm apart. Maximal surface areas through the formation of continuous strip lesion were 221 mm2, 375 mm2, and 476 mm2 in 10, 20, and 24 mm, respectively. Summations of maximal surface area of each monopolar lesions were 394 mm2 and 103 mm2 in 26 and 28 mm, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Water-cooled bipolar Radiofrequency technology creates continuous "strip" lesions proportional in size to the distance between the probes till the distance between cannulae is 24 mm or less. Spacing the cannulae 24 mm apart and treating about 80degrees C for 24 minutes maximizes the surface area of the lesion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nakada SY, Jerde TJ, Warner TF, Wright AS, Haemmerich D, Mahvi DM, et al. Bipolar radiofrequency ablation of the kidney: comparison with monopolar radiofrequency ablation. J Endourol. 2003; 17:927–933. PMID: 14744366.
Article2. Anfinsen OG, Kongsgaard E, Foerster A, Aass H, Amlie JP. Radiofrequency current ablation of porcine right atrium: increased lesion size with bipolar two catheter technique compared to unipolar application in vitro and in vivo. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1998; 21:69–78. PMID: 9474650.
Article3. Wang YG, Lu ZY, Zhao HY, Song YE, Li RL. A comparative study of radiofrequency ablation in unipolar and bipolar fashion. J Tongji Med Univ. 1995; 15:73–76. PMID: 8731956.
Article4. Watanabe I, Masaki R, Min N, Oshikawa N, Okubo K, Sugimura H, et al. Cooled-tip ablation results in increased radiofrequency power delivery and lesion size in the canine heart: importance of catheter-tip temperature monitoring for prevention of popping and impedance rise. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2002; 6:9–16. PMID: 11839878.5. Ferrante FM, King LF, Roche EA, Kim PS, Aranda M, Delaney LR, et al. Radiofrequency sacroiliac joint denervation for sacroiliac syndrome. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001; 26:137–142. PMID: 11251137.
Article6. Gauci CA. Wedley JR, Gauci CA, editors. Sacroiliac joint denervation. Handbook of clinical techniques in the management of chronic pain. 1994. Chur, Switzerland: Harwood Academic;p. 12–13.7. Ray CD. Percutaneous radiofrequency facet nerve blocks: treatment of the mechanical low back syndrome. Procedure technique series. 1982. Boston, MA: Radionics;p. 18–19.8. Pino CA, Hoeft MA, Hofsess C, Rathmell JP. Morphologic analysis of bipolar radiofrequency lesions: implications for treatment of the sacroiliac joint. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2005; 30:335–338. PMID: 16032584.
Article9. Choi EM, Shin KM, Nam SK, Cheong IY. A study about size and shape of bipolar radiofrequency lesions. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008; 54:197–200.
Article10. Kang SS, Shin KM, Jung SM, Park JH, Hong SJ. Sequential bipolar radiofrequency lumbar sympathectomy in Raynaud's disease -A case report-. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010; 59:286–289. PMID: 21057622.
Article11. Lorentzen T. A cooled needle electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation: thermodynamic aspects of improved performance compared with conventional needle design. Acad Radiol. 1996; 3:556–563. PMID: 8796717.
Article12. Sim WS, Lee AR. Radiofrequency lumbar medial branch denervation using bipolar probe in patient with facet joint syndrome. J Korean Pain Soc. 2004; 17:153–158.
Article13. Lee KH, Yun SH, Kim HJ, Jung BH, Lim SY, Shin KM, et al. A comparison of the size and shape of radiofrequency lesions produced by different temperatures using straight and curved electrodes. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2000; 39:260–264.
Article14. Lee KH, Kim KS, Lim SY, Hong SY, Won RS, Shin KM. Experimental radiofrequency lesion size utilizing Different parameters and neuropathologic correlation on the peripheral nerve. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2002; 42:368–382.
Article15. Derby R, Lee CH. The efficacy of a two needle electrode technique in percutaneous radiofrequency rhizotomy: an investigational laboratory study in an animal model. Pain Physician. 2006; 9:207–213. PMID: 16886029.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study about Size and Shape of Bipolar Radiofrequency Lesions
- Saline-Enhanced Hepatic Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Perfused-Cooled Electrode: Comparison of Dual Probe Bipolar Mode with Monopolar and Single Probe Bipolar Modes
- A Comparison of the Size and Shape of Radiofrequency Lesions Produced by Different Temperatures Using Straight and Curved Electrodes
- Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using Dual Internally Cooled Wet Electrodes: Experimental Study in Ex Vivo Bovine Liver
- Enhanced radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma post-transarterial chemoembolization: a prospective study utilizing twin internally cooled-perfusion electrodes