Korean J Pain.
2012 Jan;25(1):60-64. 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.1.60.
Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning of the Axillary and Suprascapular Nerve in Calcific Tendinitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hiitsme@snubh.org
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2278119
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.1.60
Abstract
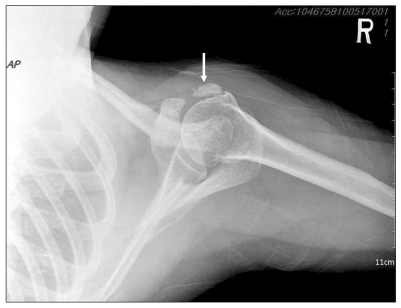
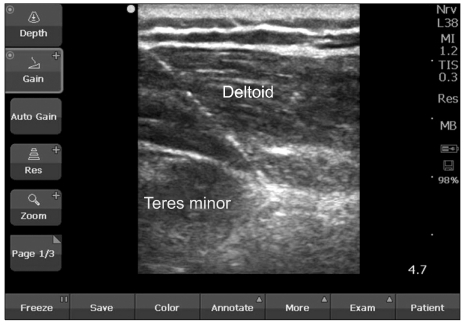
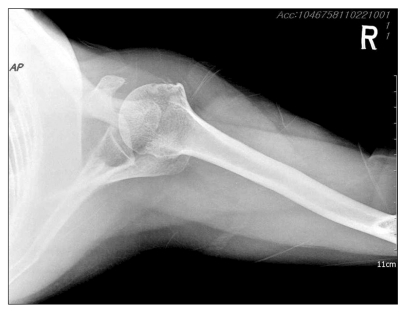
- The patient was a 45-year-female who presented with pain at right shoulder and right upper arm. The patient suffered from right shoulder and arm pain for 3 years and had pain management which was performed using medication and conservative management after she had been diagnosed with calcific tendinitis. However, substantial pain relief was not consistently achieved, and recurrence of pain was reported. Therefore, we performed right axillary nerve and suprascapular nerve block through pulsed radiofrequency. Two months after the procedure, the shoulder pain gradually subsided with the size reduction of the calcified nodule and she needed no more pain management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Accuracy of suprascapular notch cross-sectional area by MRI in the diagnosis of suprascapular nerve entrapment syndrome: a retrospective pilot study
Jiyeon Park, Min-Ying Su, Young Uk Kim
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2022;75(6):496-501. doi: 10.4097/kja.22153.
Reference
-
1. Uhthoff HK, Loehr JW. Calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1997; 5:183–191. PMID: 10797220.
Article2. Gerdesmeyer L, Wagenpfeil S, Haake M, Maier M, Loew M, Wörtler K, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic calcifying tendonitis of the rotator cuff: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003; 290:2573–2580. PMID: 14625334.
Article3. Mouzopoulos G, Stamatakos M, Mouzopoulos D, Tzurbakis M. Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for shoulder calcific tendonitis: a systematic review. Skeletal Radiol. 2007; 36:803–811. PMID: 17415561.
Article4. Aina R, Cardinal E, Bureau NJ, Aubin B, Brassard P. Calcific shoulder tendinitis: treatment with modified US-guided fine-needle technique. Radiology. 2001; 221:455–461. PMID: 11687690.
Article5. Kang KN, Park IK, Suh JH, Leem JG, Shin JW. Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency lesioning of the phrenic nerve in a patient with intractable hiccup. Korean J Pain. 2010; 23:198–201. PMID: 20830266.
Article6. Lee JS, Yoon KB, Kim IK, Yoon DM. Pulsed radiofrequency treatment of pain relieving point in a soft tissue. Korean J Pain. 2011; 24:57–60. PMID: 21390181.
Article7. Van Zundert J, de Louw AJ, Joosten EA, Kessels AG, Honig W, Dederen PJ, et al. Pulsed and continuous radiofrequency current adjacent to the cervical dorsal root ganglion of the rat induces late cellular activity in the dorsal horn. Anesthesiology. 2005; 102:125–131. PMID: 15618796.
Article8. Bosworth BM. Calcium deposits in the shoulder and subacromial bursitis: a survey of 12,122 shoulders. JAMA. 1941; 116:2477–2482.
Article9. McKendry RJ, Uhthoff HK, Sarkar K, Hyslop PS. Calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder: prognostic value of clinical, histologic, and radiologic features in 57 surgically treated cases. J Rheumatol. 1982; 9:75–80. PMID: 7086781.10. Rathbun JB, Macnab I. The microvascular pattern of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970; 52:540–553. PMID: 5455089.
Article11. Chard MD, Cawston TE, Riley GP, Gresham GA, Hazleman BL. Rotator cuff degeneration and lateral epicondylitis: a comparative histological study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994; 53:30–34. PMID: 8311552.
Article12. Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Takeshima N, Noguchi T. Mechanisms of analgesic action of pulsed radiofrequency on adjuvant-induced pain in the rat: roles of descending adrenergic and serotonergic systems. Eur J Pain. 2009; 13:249–252. PMID: 18539061.
Article13. Nitz AJ. Physical therapy management of the shoulder. Phys Ther. 1986; 66:1912–1919. PMID: 3491371.
Article14. Gorkiewicz R. Ultrasound for subacromial bursitis. A case report. Phys Ther. 1984; 64:46–47. PMID: 6691053.15. Aszmann OC, Dellon AL, Birely BT, McFarland EG. Innervation of the human shoulder joint and its implications for surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (330):202–207. PMID: 8804294.
Article16. Ebraheim NA, Whitehead JL, Alla SR, Moral MZ, Castillo S, McCollough AL, et al. The suprascapular nerve and its articular branch to the acromioclavicular joint: an anatomic study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20:e13–e17. PMID: 21194975.
Article17. de Sèze MP, Rezzouk J, de Sèze M, Uzel M, Lavignolle B, Midy D, et al. Does the motor branch of the long head of the triceps brachii arise from the radial nerve? An anatomic and electromyographic study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004; 26:459–461. PMID: 15365769.
Article18. Shah RV, Racz GB. Pulsed mode radiofrequency lesioning of the suprascapular nerve for the treatment of chronic shoulder pain. Pain Physician. 2003; 6:503–506. PMID: 16871304.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning of the Suprascapular Nerve for Referred Shoulder Pain due to Metastatic Liver Cancer: A case report
- Isolated Infraspinatus Tear and Suprascapular Nerve Neuropathy after Barbotage and Steroid Injection of Calcific Tendinitis
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning of Supraorbital and Supratrochlear Nerve in Postherpetic Neuralgia: A report of 2 cases
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment of the Supraorbital and Supratrochlear Nerve in a Case of Trigeminal Neuralgia: A case report
- Pulsed radiofrequency lesioning of the median nerve in a patient with bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome: A case report