Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2010 Apr;53(4):330-338. 10.5468/kjog.2010.53.4.330.
MyD88 expression and anti-apoptotic signals of paclitaxel in epithelial ovarian cancer cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. ghkim@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 2273860
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/kjog.2010.53.4.330
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The objectives of this study was to evaluate the correlation between myeloid differentiation protein 88 (MyD88) expression and paclitaxel effects on epithelial ovarian cancer cells and to evaluate whether paclitaxel had anti-apoptotic signals.
METHODS
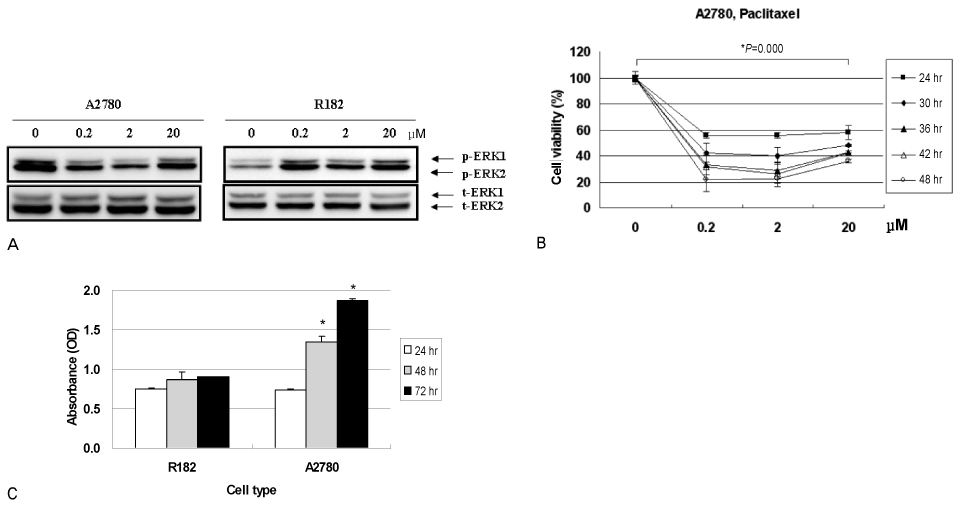
Epithelial ovarian cancer cells isolated from ascites and established cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations of paclitaxel (0.2 to 20 microM) for 24 and 48 hours and cell viability was determined using the CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay. Cytokine profiling was performed from culture supernatants using the Luminex 200 system. Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity was determined using a Luciferase reporter system. Levels of phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK) were measured by Western blot analysis.
RESULTS
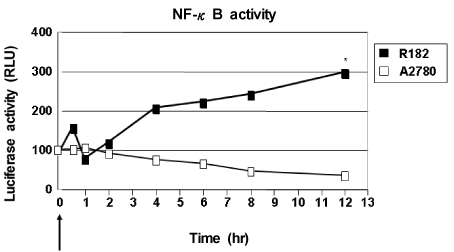
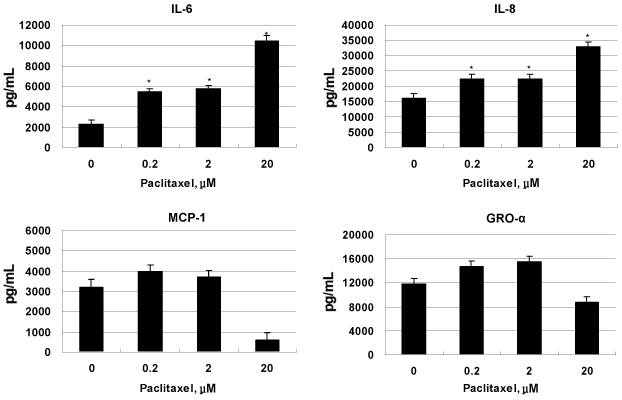
A strong signal for MyD88 expression was observed in R182, 01-19b and SKOV3 cells (MyD88-positive). A2780, R454 and 01-28 cells showed low levels of MyD88 (MyD88-negative). Paclitaxel effectively decreased cell viability in MyD88-negative A2780, R454, 01-28 cells after 24 and 48 hours (57%, 49%, 42% and 35%, 28%, 29%, respectively). MyD88-positive cells were resistant to paclitaxel. There was a significant increase in caspase-3/7 activity following paclitaxel treatment in MyD88-negative cells. No significant change in caspase-3/7 activity was detected in MyD88-positive cells. Paclitaxel induced NF-kappaB activation and enhanced the secretion of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-8 in a dose dependent manner and induced ERK phosphorylation on MyD88-positive cells.
CONCLUSION
Paclitaxel treatment for MyD88-positive ovarian cancer could have detrimental effects due to the paclitaxel-induced enhancement of NF-kappaB, ERK activities and pro-inflammatory cytokine production, which promote chemoresistance and tumor progression.
MeSH Terms
-
Ascites
Blotting, Western
Cell Line
Cell Proliferation
Cell Survival
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Luciferases
Myeloid Differentiation Factor 88
Neoplasms, Glandular and Epithelial
NF-kappa B
Ovarian Neoplasms
Paclitaxel
Phosphorylation
Phosphotransferases
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Luciferases
Myeloid Differentiation Factor 88
NF-kappa B
Neoplasms, Glandular and Epithelial
Ovarian Neoplasms
Paclitaxel
Phosphotransferases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aletti GD, Gallenberg MM, Cliby WA, Jatoi A, Hartmann LC. Current management strategies for ovarian cancer. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007. 82:751–770.
Article2. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008. 58:71–96.
Article3. Crown J, O'Leary M. The taxanes: an update. Lancet. 2000. 355:1176–1178.
Article4. Okano J, Rustgi AK. Paclitaxel induces prolonged activation of the Ras/MEK/ERK pathway independently of activating the programmed cell death machinery. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:19555–19564.
Article5. Lee M, Jeon YJ. Paclitaxel-induced immune suppression is associated with NF-kappaB activation via conventional PKC isotypes in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated 70Z/3 pre-B lymphocyte tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2001. 59:248–253.6. Taxman DJ, MacKeigan JP, Clements C, Bergstralh DT, Ting JP. Transcriptional profiling of targets for combination therapy of lung carcinoma with paclitaxel and mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:5095–5104.7. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008. 454:436–444.
Article8. Kelly MG, Alvero AB, Chen R, Silasi DA, Abrahams VM, Chan S, et al. TLR-4 signaling promotes tumor growth and paclitaxel chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2006. 66:3859–3868.
Article9. Allen LF, Sebolt-Leopold J, Meyer MB. CI-1040 (PD184352), a targeted signal transduction inhibitor of MEK (MAPKK). Semin Oncol. 2003. 30:105–116.
Article10. Zeng P, Wagoner HA, Pescovitz OH, Steinmetz R. RNA interference (RNAi) for extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) alone is sufficient to suppress cell viability in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. 4:961–967.
Article11. Hsu CY, Bristow R, Cha MS, Wang BG, Ho CL, Kurman RJ, et al. Characterization of active mitogen-activated protein kinase in ovarian serous carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:6432–6436.
Article12. Chen R, Alvero AB, Silasi DA, Steffensen KD, Mor G. Cancers take their Toll--the function and regulation of Toll-like receptors in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008. 27:225–233.
Article13. Silasi DA, Alvero AB, Illuzzi J, Kelly M, Chen R, Fu HH, et al. MyD88 predicts chemoresistance to paclitaxel in epithelial ovarian cancer. Yale J Biol Med. 2006. 79:153–163.14. Wang AC, Su QB, Wu FX, Zhang XL, Liu PS. Role of TLR4 for paclitaxel chemotherapy in human epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009. 39:157–164.
Article15. Kim KH, Xie Y, Tytler EM, Woessner R, Mor G, Alvero AB. KSP inhibitor ARRY-520 as a substitute for Paclitaxel in Type I ovarian cancer cells. J Transl Med. 2009. 7:63.
Article16. Akira S. Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:38105–38108.
Article17. Tsan MF. Toll-like receptors, inflammation and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006. 16:32–37.
Article18. Lewis TS, Shapiro PS, Ahn NG. Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res. 1998. 74:49–139.
Article19. Nakayama N, Nakayama K, Yeasmin S, Ishibashi M, Katagiri A, Iida K, et al. KRAS or BRAF mutation status is a useful predictor of sensitivity to MEK inhibition in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008. 99:2020–2028.
Article20. Hoshino R, Chatani Y, Yamori T, Tsuruo T, Oka H, Yoshida O, et al. Constitutive activation of the 41-/43-kDa mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in human tumors. Oncogene. 1999. 18:813–822.
Article21. Schmitz KJ, Wohlschlaeger J, Alakus H, Bohr J, Stauder MA, Worm K, et al. Activation of extracellular regulated kinases (ERK1/2) but not AKT predicts poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma and is associated with k-ras mutations. Virchows Arch. 2007. 450:151–159.
Article22. Fan M, Chambers TC. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the response of tumor cells to chemotherapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2001. 4:253–267.
Article23. MacKeigan JP, Collins TS, Ting JP. MEK inhibition enhances paclitaxel-induced tumor apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:38953–38956.
Article24. Seidman R, Gitelman I, Sagi O, Horwitz SB, Wolfson M. The role of ERK 1/2 and p38 MAP-kinase pathways in taxol-induced apoptosis in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2001. 268:84–92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Osteopontin on Normal and Malignant Ovarian Epithelial Cell
- Apoptotic effect of NV-196, an isofl avone derivative, in epithelial ovarian cancer cells
- Clusterin confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer
- Anti-proliferative effect in epithelial ovarian cancer cells by MEK Inhibitor AZD6244
- Weekly versus 3-weekly paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin in advanced ovarian cancer: which is the optimal adjuvant chemotherapy regimen?