Korean J Orthod.
2012 Apr;42(2):87-93. 10.4041/kjod.2012.42.2.87.
The effect of silver ion-releasing elastomers on mutans streptococci in dental plaque
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, Graduate School of Clinical Dentistry, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Dentistry, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. yonklim@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Oral Microbiology, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2273261
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2012.42.2.87
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the antimicrobial effect of silverized elastomers on mutans streptococci in dental plaque.
METHODS
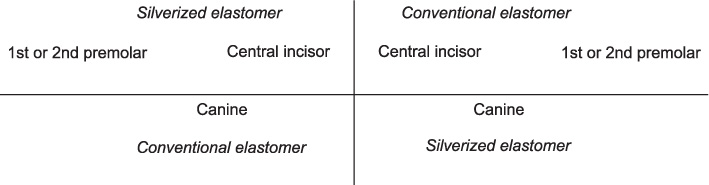
Forty patients undergoing orthodontic treatment were randomly placed into 1 of 2 groups. We examined the maxillary right and left central incisors and premolars, and the mandibular right and left canines of all participants. We ligated the right maxillary and left mandibular teeth of the participants in group 1 with silverized elastomers and ligated their contralateral teeth with conventional elastomers. We ligated the left maxillary teeth and right mandibular teeth of group 2 participants with silverized elastomers. Each participant visited the clinic 4 times at 3-week intervals. We applied the elastomers to the teeth on one side of each patient's mouth during their first visit. During the second visit, the elastomers were removed for microbiological analysis and replaced with steel ligatures. During the third visit, we used silverized elastomers to ligate the teeth contralateral to those treated on the first visit. The elastomers were removed during the fourth visit, and microbiological analyses were performed. We compared the quantity of bacteria on silverized and conventional elastomers at the 0.05 level of significance.
RESULTS
The percentage of mutans streptococci was not significantly different in cultures of dental plaque from the silverized and the conventional elastomers (p > 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
There was no significant difference between the antimicrobial effect of the silverized elastomers and that of the conventional elastomers.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Scheie AA, Arneberg P, Krogstad O. Effect of orthodontic treatment on prevalence of Streptococcus mutans in plaque and saliva. Scand J Dent Res. 1984. 92:211–217.
Article2. Rosenbloom RG, Tinanoff N. Salivary Streptococcus mutans levels in patients before, during, and after orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1991. 100:35–37.
Article3. Ogaard B. Prevalence of white spot lesions in 19-year-olds: a study on untreated and orthodontically treated persons 5 years after treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1989. 96:423–427.4. Bowden GH. Effects of fluoride on the microbial ecology of dental plaque. J Dent Res. 1990. 69:653–659.
Article5. Wiegand A, Buchalla W, Attin T. Review on fluoride-releasing restorative materials--fluoride release and uptake characteristics, antibacterial activity and influence on caries formation. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:343–362.
Article6. Forsberg CM, Brattström V, Malmberg E, Nord CE. Ligature wires and elastomeric rings: two methods of ligation, and their association with microbial colonization of Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli. Eur J Orthod. 1991. 13:416–420.
Article7. Benson PE, Douglas CW, Martin MV. Fluoridated elastomers: effect on the microbiology of plaque. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004. 126:325–330.
Article8. Lansdown AB, Sampson B, Laupattarakasem P, Vuttivirojana A. Silver aids healing in the sterile skin wound: experimental studies in the laboratory rat. Br J Dermatol. 1997. 137:728–735.
Article9. Yamamoto K, Ohashi S, Aono M, Kokubo T, Yamada I, Yamauchi J. Antibacterial activity of silver ions implanted in SiO2 filler on oral streptococci. Dent Mater. 1996. 12:227–229.
Article10. Yoshida K, Tanagawa M, Matsumoto S, Yamada T, Atsuta M. Antibacterial activity of resin composites with silver-containing materials. Eur J Oral Sci. 1999. 107:290–296.
Article11. Uchida M. Antimicrobial zeolite and its application. Chem Ind. 1995. 46:48–54.12. Hotta M, Nakajima H, Yamamoto K, Aono M. Antibacterial temporary filling materials: the effect of adding various ratios of Ag-Zn-Zeolite. J Oral Rehabil. 1998. 25:485–489.
Article13. Morishita M, Miyagi M, Yamasaki Y, Tsuruda K, Kawahara K, Iwamoto Y. Pilot study on the effect of a mouthrinse containing silver zeolite on plaque formation. J Clin Dent. 1998. 9:94–96.14. Greene JC, Vermillion JR. The simplified oral hygiene index. J Am Dent Assoc. 1964. 68:7–13.
Article15. Berger TJ, Spadaro JA, Bierman R, Chapin SE, Becker RO. Antifungal properties of electrically generated metallic ions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976. 10:856–860.
Article16. Russell AD, Hugo WB. Antimicrobial activity and action of silver. Prog Med Chem. 1994. 31:351–370.17. Im K, Takasaki Y, Endo A, Kuriyama M. Antibacterial activity of A-type zeolite supporting silver ions in deionized distilled water. J Antibact Antifung Agents. 1996. 24:269–274.18. Kourai H, Manabe Y, Yamada Y. Mode of bactericidal action of zirconium phosphate ceramics containing silver ions in the crystal structure. J Antibact Antifung Agents. 1994. 22:595–601.19. Kawahara K, Tsuruda K, Morishita M, Uchida M. Antibacterial effect of silver-zeolite on oral bacteria under anaerobic conditions. Dent Mater. 2000. 16:452–455.
Article20. Matsumura Y, Yoshikata K, Kunisaki S, Tsuchido T. Mode of bactericidal action of silver zeolite and its comparison with that of silver nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. 69:4278–4281.
Article21. Casemiro LA, Gomes Martins CH, Pires-de-Souza Fde C, Panzeri H. Antimicrobial and mechanical properties of acrylic resins with incorporated silver-zinc zeolite - part I. Gerodontology. 2008. 25:187–194.
Article22. Ahn JS, Hwang EJ, Lee DY, Lim YK. Evaluation of silver ion release from silver-containing elastomers in artificial saliva. J Korea Res Soc Dent Mater. 2010. 37:297–304.23. Won YA. The antibacterial activities of silver ion releasing elastomers on oral pathogenic microbes [MSc thesis]. 2010. Seoul: Korea University.24. Tanagawa M, Yoshida K, Matsumoto S, Yamada T, Atsuta M. Inhibitory effect of antibacterial resin composite against Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1999. 33:366–371.
Article25. Breck DW. Zeolite molecular sieve: structure, chemistry and use. Ion exchange reactions in zeolites. 1973. New York: Wiley.26. Uchida T, Maru N, Furuhata M, Fujino A, Muramoto S, Ishibashi A, et al. Anti-bacterial zeolite balloon catheter and its potential for urinary tract infection control. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1992. 38:973–978.27. Shannon IL, Suddick RP, Dowd FJ Jr. Saliva: composition and secretion. Monogr Oral Sci. 1974. 2:1–103.28. Schierholz JM, Lucas LJ, Rump A, Pulverer G. Efficacy of silver-coated medical devices. J Hosp Infect. 1998. 40:257–262.
Article29. Wiltshire WA. In vitro and in vivo fluoride release from orthodontic elastomeric ligature ties. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1999. 115:288–292.
Article30. Ahn SJ, Lee SJ, Kook JK, Lim BS. Experimental antimicrobial orthodontic adhesives using nanofillers and silver nanoparticles. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:206–213.
Article31. Magno AF, Enoki C, Ito IY, Matsumoto MA, Faria G, Nelson-Filho P. In-vivo evaluation of the contamination of Super Slick elastomeric rings by Streptococcus mutans in orthodontic patients. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008. 133:4 Suppl. S104–S109.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antibiotic susceptibility in mutans streptococci and Streptococcus anginosus isolated from dental plaque
- Frequency of Species and Biotypes of Mutans Streptococci Isolated from Dental Plaque in the Adolescents and Adults
- Identification of Mutans Streptococci isolated from dental plaque between the bracket and tooth surface in orthodontic patients
- Effect of Leaf-Extract from Camellia sinensis and Seed-Extract from Casia tora on Viability of Mutans Streptococci isolated from the interface between orthodontic brackets and tooth surfaces
- Spectrophotometric analysis of feldspathic porcelain with silver ion