Cancer Res Treat.
2006 Apr;38(2):72-77.
A Phase II Study of Irinotecan, 5-Fluorouracil and Leucovorin for Treatment in Patients with Previously Untreated Advanced Colorectal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mdnslee@hosp.sch.ac.kr
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We prospectively conducted a non-randomized phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combination irinotecan, leucovorin (LV) and 5-fluorouracil (FU) as a first-line regimen for treating patients with previously untreated advanced colorectal cancer (CRC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
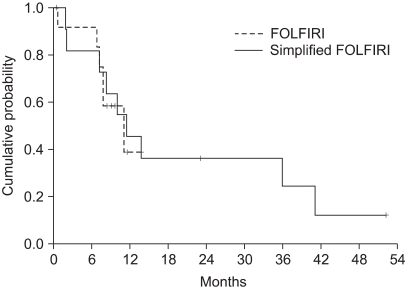
Twenty-six previously untreated patients with advanced, recurrent or metastatic CRC were enrolled in this study. The patients received either irinotecan 180 mg/m2 on day 1 with LV bolus of 200 mg/m2 and FU bolus of 400 mg/m2, and this was followed by FU continuous infusion of 600 mg/m2 on day 1 and day 2 (the FOLFIRI regimen), or they were treated with LV bolus of 400 mg/m2 and FU bolus of 400 mg/m2 followed by FU continuous infusion of 2,400 mg/m2 for 46 hours (the simplified FOLFIRI regimen), and these treatments were repeated every 2 weeks until disease progression.
RESULTS
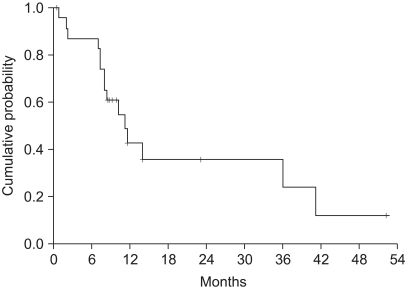
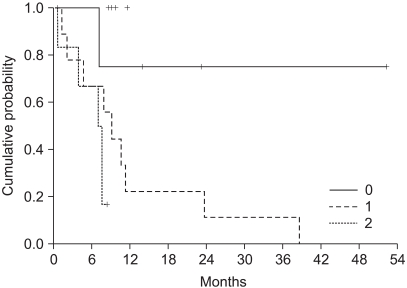
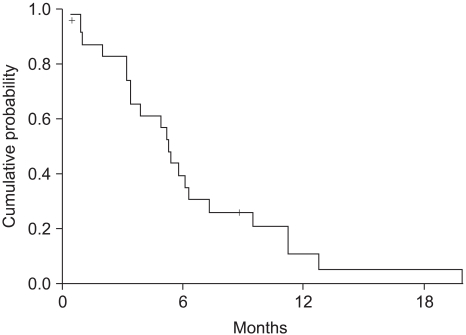
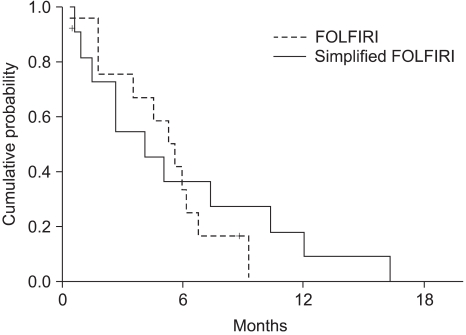
The objective response rate was 23.1% (6/26) respectively, for both treatments. The median time to progression was 5.3 months (range: 0.4~19.9), and the overall survival was 11.2 months (range: 0.5~52.3). The prognostic factor for longer survival was the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS). The non-hematological toxicities were similar for both treatment groups, with more frequent grade > or =3 neutropenia being noted for the simplified FOLFIRI regimen.
CONCLUSION
The biweekly irinotecan based regimen was demonstrated to have a moderate antitumor activity with acceptable toxicity profiles, and the ECOG PS was the independent prognostic factor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. 2002 Annual report of the Korea Central Cancer Registry (based on registered data from 139 hospitals). 2003. Ministry of Health and Welfare Republic of Korea.2. 2004 Annual report on the cause of death statistics. 2004. Korea National Statistical Office.3. Ragnhammar P, Hafstrom L, Nygren P, Glimelius B. A systematic overview of chemotherapy effects in colorectal cancer. Acta Oncol. 2001; 40:282–308. PMID: 11441937.
Article4. Modulation of fluorouracil by leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: evidence in terms of response rate. Advanced Colorectal Cancer Meta-Analysis Project. J Clin Oncol. 1992; 10:896–903. PMID: 1534121.5. de Gramont A, Bosset JF, Milan C, Rougier P, Bouche O, Etienne PL, et al. Randomized trial comparing monthly low-dose leucovorin and fluorouracil bolus with bimonthly high-dose leucovorin and fluorouracil bolus plus continuous infusion for advanced colorectal cancer: a French intergroup study. J Clin Oncol. 1997; 15:808–815. PMID: 9053508.
Article6. Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, Navarro M, James RD, Karasek P, et al. Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2000; 355:1041–1047. PMID: 10744089.
Article7. Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, Fuchs CS, Ramanathan RK, Williamson SK, et al. A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:23–30. PMID: 14665611.
Article8. Tournigand C, Andre T, Achille E, Lledo G, Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, et al. FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:229–237. PMID: 14657227.
Article9. de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:2938–2947. PMID: 10944126.
Article10. Kwon HC, Kim SH, Kim JS, Kim HJ. Irinotecan combined with bolus fluorouracil, continuous infusion fluorouracil, and low-dose leucovorin every two weeks in patients with oxaliplatin pretreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2003; 35:135–140.
Article11. Won YW, Lim YH, Park HY, Oh HS, Choi JH, Lee YY, et al. Phase II study of irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil, and leucovorin in relapsed or metastatic colorectal cancer as first-line therapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2004; 36:235–239.
Article12. Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:205–216. PMID: 10655437.13. Kaplan EL, Meier P. Non parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958; 53:457–481.14. Cox DR. Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc. 1972; 34B:187–220.
Article15. Sobrero AF, Aschele C, Bertino JR. Fluorouracil in colorectal cancer--a tale of two drugs: implications for biochemical modulation. J Clin Oncol. 1997; 15:368–381. PMID: 8996164.
Article16. Meta-analysis Group In Cancer. Efficacy of intravenous continuous infusion of fluorouracil compared with bolus administration in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998; 16:301–308. PMID: 9440757.17. de Gramont A, Andre T, Demuynck B, Garcia M, Carola E, Krulik M. A simplified bimonthly regimen with leucovorin (LV) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) for metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC). Feasibility study Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 1997; 16(289a):abstr 1019.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combination chemotherapy of irinotecan combined with bolus 5-fluorouracil, continuous infusion 5-fluorouracil, and high dose leucovorin every two weeks in recurrent or metastatic colorectal cancer
- 5-fluorouracil and low dose leucovorin in advanced colorectal carcinoma
- 5-fluorouracil and low dose leucovorin in advanced colorectal carcinoma
- The Role of Targeted Therapy in the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- Phase II Study of Irinotecan, 5-Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin in Relapsed or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer as First-line Therapy