Cancer Res Treat.
2010 Sep;42(3):157-162.
Bcl-2 as a Predictive Factor for Biochemical Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy: An Interim Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Center for Prostate Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. uroonco@ncc.re.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Center for Prostate Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The objective of this study was to determine Bcl-2 expression in localized prostate cancer and its potential role as a predictive factor for biochemical recurrence (BCR).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
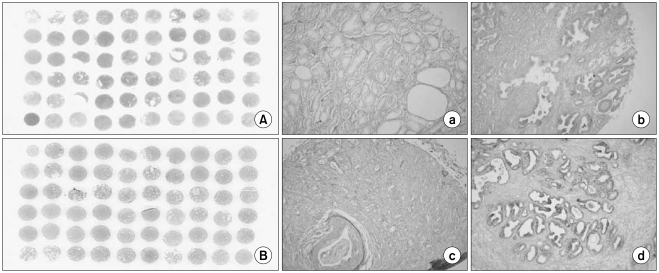
This study included 171 Korean patients with newly diagnosed adenocarcinoma of the prostate who underwent radical prostatectomy (RP) without neoadjuvant therapy at a single center between February 2005 and May 2009. RP specimens obtained from these patients were analyzed for the expression of Bcl-2 using tissue microarray. The values of Bcl-2 and other clinicopathologic factors were evaluated. Statistical analysis was performed with contingency table analysis, chi-square tests, and a Cox proportional hazard model.
RESULTS
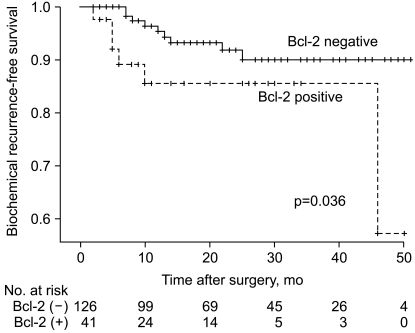
Bcl-2 expression was immunohistologically-confirmed in 42 patients (24.6%). Bcl-2 expression was not associated with conventional clinicopathologic factors. Bcl-2 negative patients had a significantly longer mean BCR-free survival than Bcl-2-positive patients (p=0.036). Among several variables, a high Gleason score in the RP specimen (> or =8), extraprostatic extension, seminal vesicle invasion (SVI), lymphovascular invasion (LVI), and Bcl-2 expression were significant predictors of BCR based on univariate analysis. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis revealed that BCR was significantly associated with a high prostate specific antigen level (p=0.047), SVI (p<0.001), a positive surgical margin (p=0.004) and Bcl-2 expression (p=0.012).
CONCLUSION
Bcl-2 expression in RP specimens is associated with a significantly worse outcome, suggesting a potential clinical role for Bcl-2. Post-operative Bcl-2 could be a significant predictor of outcome after RP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kattan MW, Eastham JA, Stapleton AM, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT. A preoperative nomogram for disease recurrence following radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998; 90:766–771. PMID: 9605647.
Article2. Kattan MW, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT. Postoperative nomogram for disease recurrence after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:1499–1507. PMID: 10334537.
Article3. Epstein JI, Partin AW, Sauvageot J, Walsh PC. Prediction of progression following radical prostatectomy: a multivariate analysis of 721 men with long-term follow-up. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996; 20:286–292. PMID: 8772781.4. D'Amico AV, Chen MH, Roehl KA, Catalona WJ. Identifying patients at risk for significant versus clinically insignificant postoperative prostate-specific antigen failure. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:4975–4979. PMID: 16051949.5. Ross JS, Sheehan CE, Dolen EM, Kallakury BV. Morphologic and molecular prognostic markers in prostate cancer. Adv Anat Pathol. 2002; 9:115–128. PMID: 11917165.
Article6. Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2: an antidote to programmed cell death. Cancer Surv. 1992; 15:105–118. PMID: 1451107.7. Colombel M, Symmans F, Gil S, O'Toole KM, Chopin D, Benson M, et al. Detection of the apoptosis-suppressing oncoprotein bc1-2 in hormone-refractory human prostate cancers. Am J Pathol. 1993; 143:390–400. PMID: 7688182.8. Villuendas R, Piris MA, Orradre JL, Mollejo M, Rodriguez R, Morente M. Different bcl-2 protein expression in high-grade B-cell lymphomas derived from lymph node or mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Am J Pathol. 1991; 139:989–993. PMID: 1951637.9. Hur DS, Lee SW, Kim KH, Cho YS, Joo KJ, Park HJ, et al. Significance of expressions of bcl-2 and p53 protein as the prognostic factor in metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. Korean J Urol. 2001; 42:1265–1269.10. Berges RR, Furuya Y, Remington L, English HF, Jacks T, Isaacs JT. Cell proliferation, DNA repair, and p53 function are not required for programmed death of prostatic glandular cells induced by androgen ablation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993; 90:8910–8914. PMID: 8415631.
Article11. Bauer JJ, Sesterhenn IA, Mostofi FK, McLeod DG, Srivastava S, Moul JW. Elevated levels of apoptosis regulator proteins p53 and bcl-2 are independent prognostic biomarkers in surgically treated clinically localized prostate cancer. J Urol. 1996; 156:1511–1516. PMID: 8808919.
Article12. de la Taille A, Buttyan R, Benson MC, Katz AE. The role of tumor biomarkers as predictors of serum PSA recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Semin Urol Oncol. 1998; 16:137–144. PMID: 9741418.13. McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM, Logothetis C, Chung LW, Hsieh JT, et al. Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1992; 52:6940–6944. PMID: 1458483.14. Westin P, Stattin P, Damber JE, Bergh A. Castration therapy rapidly induces apoptosis in a minority and decreases cell proliferation in a majority of human prostatic tumors. Am J Pathol. 1995; 146:1368–1375. PMID: 7778676.15. Raffo AJ, Perlman H, Chen MW, Day ML, Streitman JS, Buttyan R. Overexpression of bcl-2 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:4438–4445. PMID: 7671257.16. Wu TT, Hsu YS, Wang JS, Lee YH, Huang JK. The role of p53, bcl-2 and E-cadherin expression in predicting biochemical relapse for organ confined prostate cancer in Taiwan. J Urol. 2003; 170:78–81. PMID: 12796649.
Article17. Stackhouse GB, Sesterhenn IA, Bauer JJ, Mostofi FK, Connelly RR, Srivastava SK, et al. p53 and bcl-2 immunohistochemistry in pretreatment prostate needle biopsies to predict recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 1999; 162:2040–2045. PMID: 10569564.
Article18. Merseburger AS, Kuczyk MA, Serth J, Bokemeyer C, Young DY, Sun L, et al. Limitations of tissue microarrays in the evaluation of focal alterations of bcl-2and p53 in whole mount derived prostate tissues. Oncol Rep. 2003; 10:223–228. PMID: 12469173.19. Amirghofran Z, Monabati A, Gholijani N. Apoptosis in prostate cancer: bax correlation with stage. Int J Urol. 2005; 12:340–345. PMID: 15948719.
Article20. Moul JW. Angiogenesis, p53, bcl-2 and Ki-67 in the progression of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 1999; 35:399–407. PMID: 10325496.21. Bubendorf L, Tapia C, Gasser TC, Casella R, Grunder B, Moch H, et al. Ki67 labeling index in core needle biopsies independently predicts tumor-specific survival in prostate cancer. Hum Pathol. 1998; 29:949–954. PMID: 9744310.
Article22. Oxley JD, Winkler MH, Parry K, Brewster S, Abbott C, Gillatt DA. p53 and bcl-2 immunohistochemistry in preoperative biopsies as predictors of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2002; 89:27–32. PMID: 11849156.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Impact of Positive Surgical Margins on Biochemical Recurrence after Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy
- CORRIGENDUM: Correction of the Figure. Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy has lower biochemical recurrence than laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Cribriform Pattern at the Surgical Margin is Highly Predictive of Biochemical Recurrence in Patients Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy
- The Effect of Tumor-Prostate Ratio on Biochemical Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy
- Biochemical Recurrence-Free and Cancer-Specific Survival after Radical Prostatectomy at a Single Institution