Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Apr;36(2):282-286. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.2.282.
Back Pain Secondary to Brucella Spondylitis in the Lumbar Region
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Ilsanpaik Hospital, Goyang 411-706, Korea. killingstar@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Ilsanpaik Hospital, Goyang 411-706, Korea.
- KMID: 2266770
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.2.282
Abstract
- Brucellosis is a systemic, infectious disease caused by the bacterial genus Brucella and a common zoonosis that still remains a major health problem in certain parts of the world such as the Mediterranean region, the Middle East, and Latin America. It may involve multiple organs and tissues. Osteoarticular involvement is the most frequent complication of brucellosis, in which the diagnosis of brucellar spondylitis is often difficult since the clinical presentation may be obscured by many other conditions. There are only a few reports on brucellar spondylitis in Korea. Here, we report a case of spondylitis due to brucella in an elderly male.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
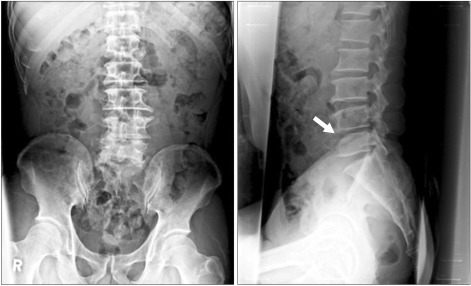
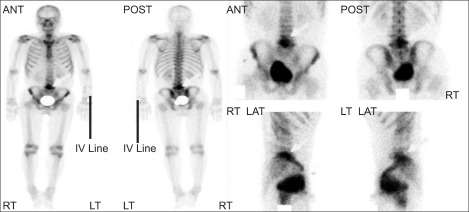
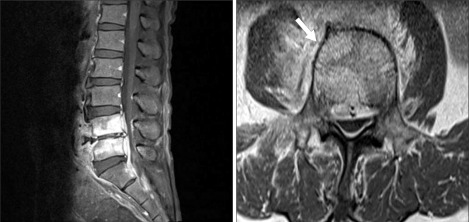
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aydin G, Tosun A, Keles I, Ayaslioglu E, Tosun O, Orkun S. Brucellar spondylodiscitis: a case report. Int J Clin Pract. 2006; 60:1502–1505. PMID: 16669838.
Article2. Lee HJ, Hur JW, Lee JW, Lee SR. Brucellar spondylitis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 44:277–279. PMID: 19096693.
Article3. Madkour MM. Braunwald E, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL, Fauci AS, editors. Brucellosis. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2001. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional;p. 969–971.4. Cobbaert K, Pieters A, Devinck M, Devos M, Goethals I, Mielants H. Brucellar spondylodiscitis: case report. Acta Clin Belg. 2007; 62:304–307. PMID: 18229463.
Article5. Ugarriza LF, Porras LF, Lorenzana LM, Rodríguez-Sánchez JA, García-Yagüe LM, Cabezudo JM. Brucellar spinal epidural abscesses. Analaysis of eleven cases. Br J Neurosurg. 2005; 19:235–240. PMID: 16455524.6. Lim HS, Song YG, Yoo HS, Park MY, Kim JW. Brucellosis: an overview. Korean J Epidemiol. 2005; 27:26–36.7. Solera J, Lozano E, Martínez-Alfaro E, Espinosa A, Castillejos ML, Abad L. Brucellar spondylitis: review of 35 cases and literature survey. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 29:1440–1449. PMID: 10585793.
Article8. Yilmaz E, Parlak M, Akalin H, Heper Y, Ozakin C, Mistik R, Oral B, Helvaci S, Töre O. Brucellar spondylitis: review of 25 cases. J Clin Rheumatol. 2004; 10:300–307. PMID: 17043537.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute low back pain revealed as pyogenic spondylitis: A report of 2 cases
- Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Aseptic Spondylitis Following Lumbar Disk Surgery
- A case of brucella endocarditis with spondylitis in a patient with multiple myeloma
- A case of back pain caused by Salmonella spondylitis: A case report