Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Jun;36(3):386-393. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.386.
Effect of Lower Limb Strength on Falls and Balance of the Elderly
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 301-721, Korea. yjsjk214@cnuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2266745
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.386
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
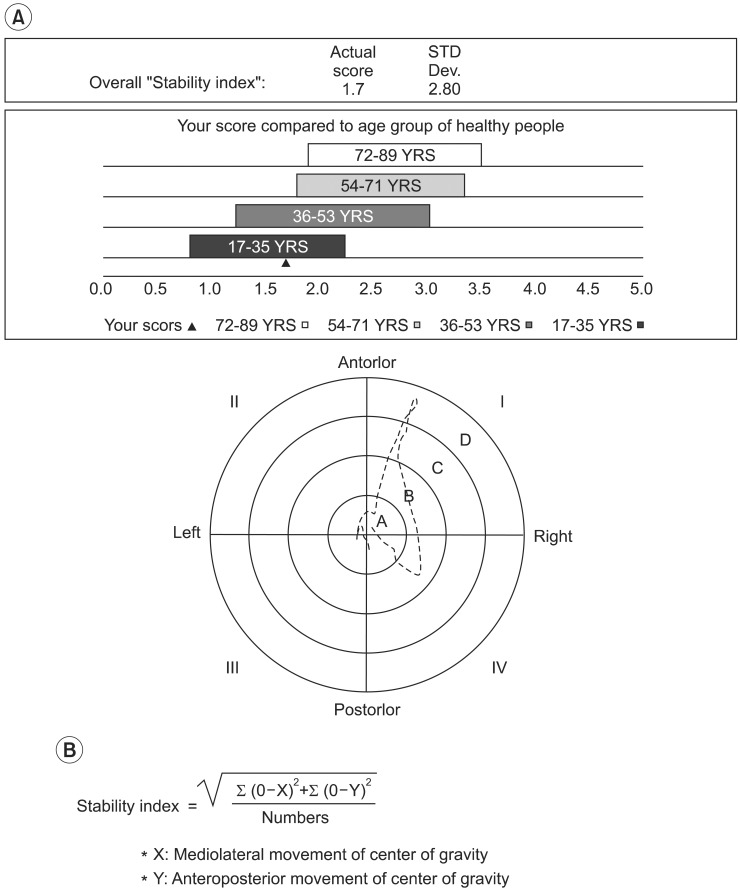
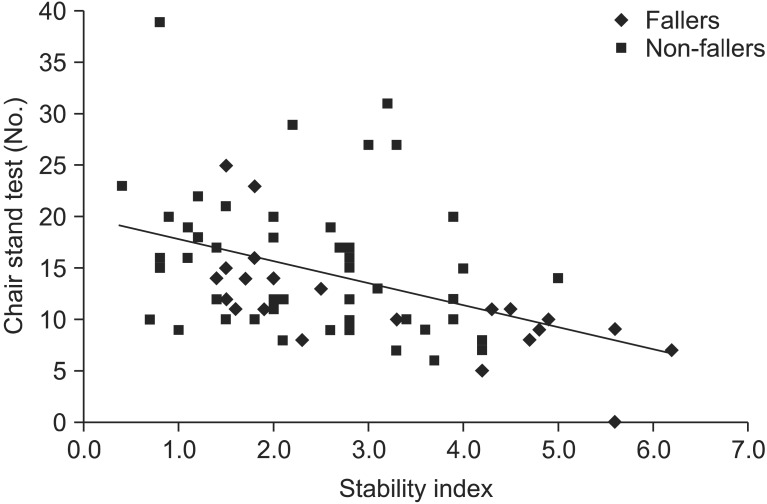
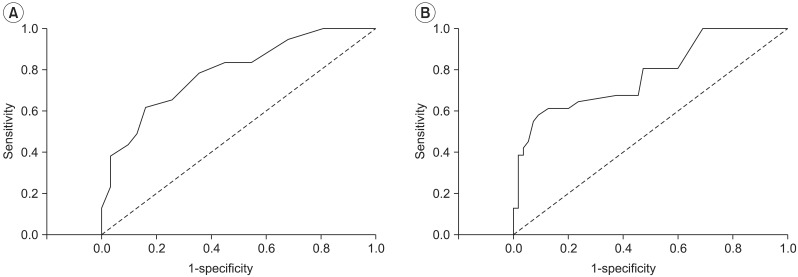
To assess the effect of lower limb strength on falls and balance in community-dwelling elderly persons by a health status questionnaire, evaluation of lower limb strength and balance. METHOD: A total of 86 subjects (age 69.8+/-5.3) were categorized into one of two groups, "Fallers" and "Non-fallers". Thirty one participants who had reported the experience of having fallen unexpectedly at least once in the past year were assigned into the group "Fallers", and the remaining 55 subjects having no fall history in the past year, "Non-fallers". A self-assessment questionnaire was taken. Lower limb strength was measured by a "Chair stand test". Balance was measured by the stability index of the fall risk test protocol of Balance System SD(R) (Biodex, New York, USA). The differences between the two groups were compared and the correlation between lower limb strength and balance were analyzed.
RESULTS
The questionnaire demonstrated no significant differences between two groups. The "Chair stand test" showed a significantly less for the "Fallers" (p<0.05). The stability index was significantly greater in the "Fallers" group (p<0.05). There was a moderate negative correlation between the "Chair stand test" and the "Stability index" (R=-0.576, p<0.01).
CONCLUSION
This study suggests that the "Chair stand test" is a useful screening process for lower limb strength which correlates to risk for falls and balance in the elderly.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Antigravity Treadmill Gait Training on Gait Function and Fall Risk in Stroke Patients
Kyungrok Oh, Namgyu Im, Young Lee, Nana Lim, Taehwan Cho, Sura Ryu, Seora Yoon
Ann Rehabil Med. 2022;46(3):114-121. doi: 10.5535/arm.22034.
Reference
-
1. Sattin RW, Lambert Huber DA, Devito CA, Rodriguez JG, Ros A, Bacehelli S, Stevens JA, Waxweiler RJ. The incidence of fall injury events among the elderly in a defined population. Am J Epidemiol. 1990; 131:1028–1037. PMID: 2343855.
Article2. Tinetti ME, Williams CS. Falls, injuries due to falls, and the risk of admission to a nursing home. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:1279–1284. PMID: 9345078.
Article3. Sterling DA, O'Connor JA, Bonadies J. Geriatric falls: injury severity is high and disproportionate to mechanism. J Trauma. 2001; 50:116–119. PMID: 11231681.
Article4. Tinetti ME, Speechly M. Prevention of falls among the elderly. N Engl J Med. 1989; 320:1055–1059. PMID: 2648154.
Article5. Tinetti ME, Speechly M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:1701–1707. PMID: 3205267.
Article6. Campbell AJ, Borries MJ, Spears GF. Risk factors for falls in a community-based prospective study of people 70 years and older. J Gerontol. 1989; 44:M112–M117. PMID: 2738307.
Article7. Podsiadlo D, Richardson S. The timed "Up & Go": a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991; 39:142–148. PMID: 1991946.8. Guideline for the prevention of falls in older persons. American Geriatrics Society, British Geriatrics Society, and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Panel on Falls Prevention. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001; 49:664–672. PMID: 11380764.9. Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community-residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999; 70:113–119. PMID: 10380242.
Article10. Finn JA, Alvarez MM, Jett RE, Axtell RS, Kemler DS. Stability performance assessment among subjects of disparate balancing abilities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999; 31:S252.
Article11. Ware JE Jr, Scherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992; 30:473–483. PMID: 1593914.12. Melzer I, Benzuya N, Kaplanski J. Postural stability in the elderly: a comparison between fallers and non-fallers. Age Ageing. 2004; 33:602–607. PMID: 15501837.
Article13. Melzer I, Kurz I, Oddsson LI. A retrospective analysis of balance control parameters in elderly fallers and non-fallers. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010; 25:984–988.
Article14. Caterino JM, Karaman R, Arora V, Martin JL, Hiestand BC. Comparision of balance assessment modalities in emergency department elders: a pilot cross-sectional observational study. BMC Emerg Med. 2009; 9:19–25. PMID: 19785763.
Article15. Maki BE, Holliday PJ, Topper AK. A prospective study of postural balance and risk of falling in an ambulatory and independent elderly population. J Gerontol. 1994; 49:M72–M84. PMID: 8126355.
Article16. Skelton DA, Kennedy J, Rutherford OM. Explosive power and asymmetry in leg muscle function in frequent fallers and non-fallers aged over 65. Age Ageing. 2002; 31:119–125. PMID: 11937474.
Article17. Wolfson L, Judge J, Whipple R, King M. Strength is a major factor in balance, gait, and the occurrence of falls. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1995; 50:64–67. PMID: 7493221.18. Whipple RH, Wolfson LI, Amerman PM. The relationship of knee and ankle weakness to falls in nursing home residents: an isokinetic study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1987; 35:13–20. PMID: 3794141.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Review of Exercise Interventions for Fall Prevention in the Elderly
- Effect of Seniorobic Program on Physical Function and Fall in Elderly
- The Mediating Effect of Depression in the Relationship between Muscle Strength of Extremities and Falls among Community-Dwelling Elderly
- Common Disorders Causing Balance Problems
- Comparison of Walking, Muscle Strength, Balance, and Fear of Falling Between Repeated Fall Group, One-time Fall Group, and Nonfall Group of the Elderly Receiving Home Care Service