Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Feb;37(1):138-142. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.1.138.
Pseudo-Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome by Multiple Intramuscular Injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea. rmkdh@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan, Korea.
- KMID: 2266663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.1.138
Abstract
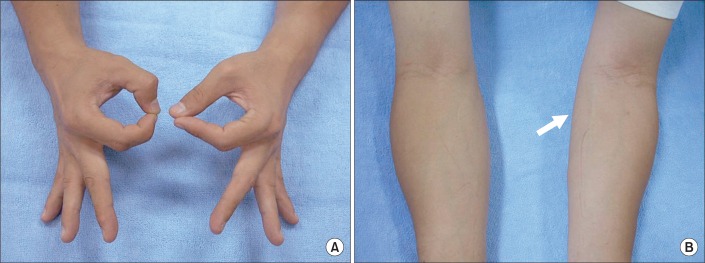
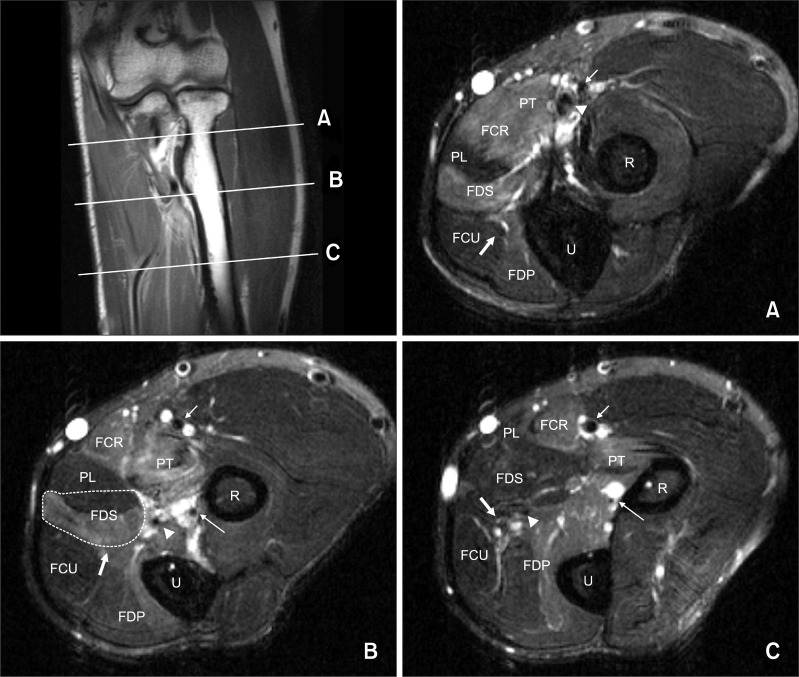
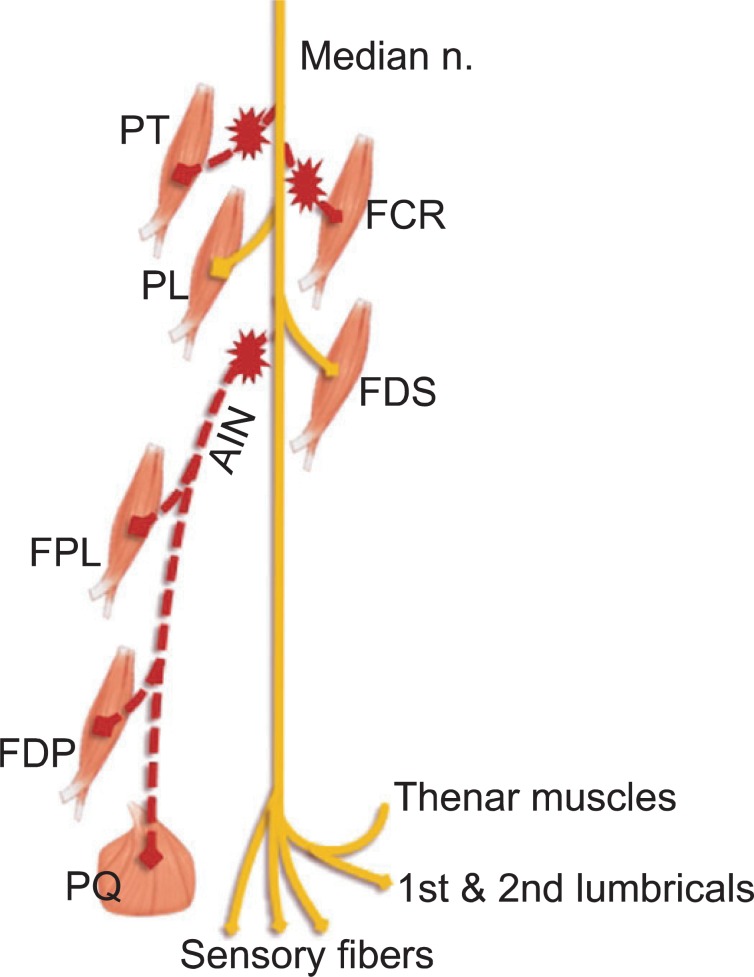
- Blind intramuscular injection might cause severe neurovascular injury if it would be performed with insufficient knowledge of anatomy around the injection area. We report a case of pseudo-anterior interosseous syndrome caused by multiple intramuscular steroid injections around the antecubital area. The patient had weakness of the 1st to 3rd digits flexion with typical OK sign. Muscle atrophy was noted on the proximal medial forearm, and sensation was intact. The electrophysiologic studies showed anterior interosseous nerve compromise, accompanying with injury of the other muscles innervated by the median nerve proximal to anterior interosseous nerve. Magnetic resonance imaging of the left proximal forearm revealed abnormally increased signal intensity of the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, proximal portion of flexor digitorum superficialis, and flexor digitorum profundus innervated by the median nerve on the T2-weighted images. This case shows the importance of knowledge about anatomic structures in considering intramuscular injection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Katirji MB. Pseudo-anterior interosseous nerve syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1986; 9:266–267. PMID: 3010104.
Article2. Seror P, Leger JM, Maisonobe T. Anterior interosseous nerve and multifocal motor neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 26:841–844. PMID: 12451612.
Article3. Puhaindran ME, Wong HP. A case of anterior interosseous nerve syndrome after peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line insertion. Singapore Med J. 2003; 44:653–655. PMID: 14770261.4. Sisco M, Dumanian GA. Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome following shoulder arthroscopy: a report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:392–395. PMID: 17272456.5. Megele R. Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome with atypical nerve course in relation to the pronator teres. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1988; 91:144–146. PMID: 3407460.
Article6. Snow DM, Reading J, Dalal R. Lateral plantar nerve injury following steroid injection for plantar fasciitis. Br J Sports Med. 2005; 39:e41. PMID: 16306487.7. Stahl S, Kaufman T. Ulnar nerve injury at the elbow after steroid injection for medial epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Br. 1997; 22:69–70. PMID: 9061530.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome
- Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome following Bowling: A case report
- Bilateral Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: A Case Report
- Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome with Varient Nerve Innervation: A Case Report
- Selective Fascicular Involvement of the Median Nerve Trunk Causing Pseudo-Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: Ultrasound and MR Imaging Features