Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Aug;37(4):567-571. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.567.
Multiorgan With Renal Infarction Following Treatment of Cerebral Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Institute of Wonkwang Medical Science, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. mcjoo68@wonkwang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2266614
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.567
Abstract
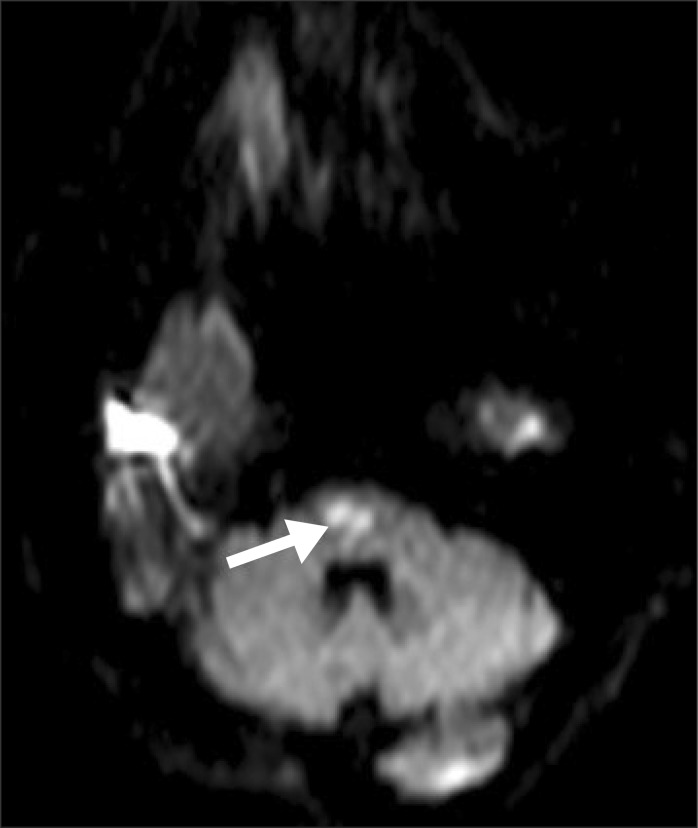
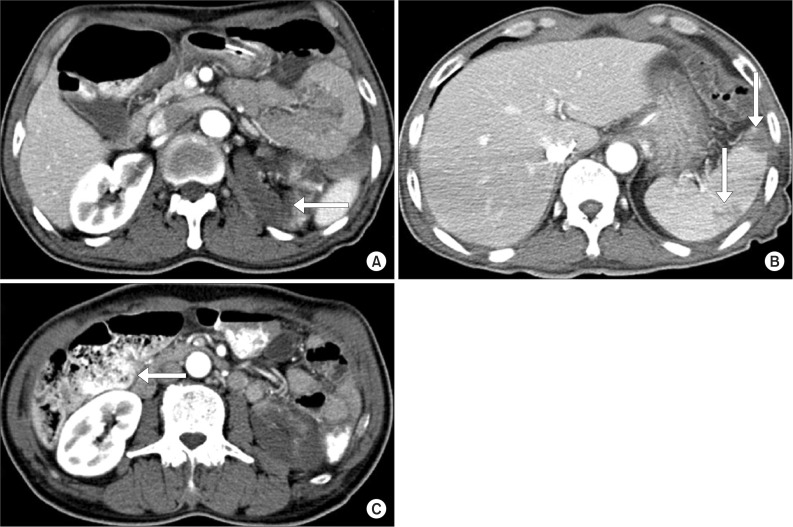
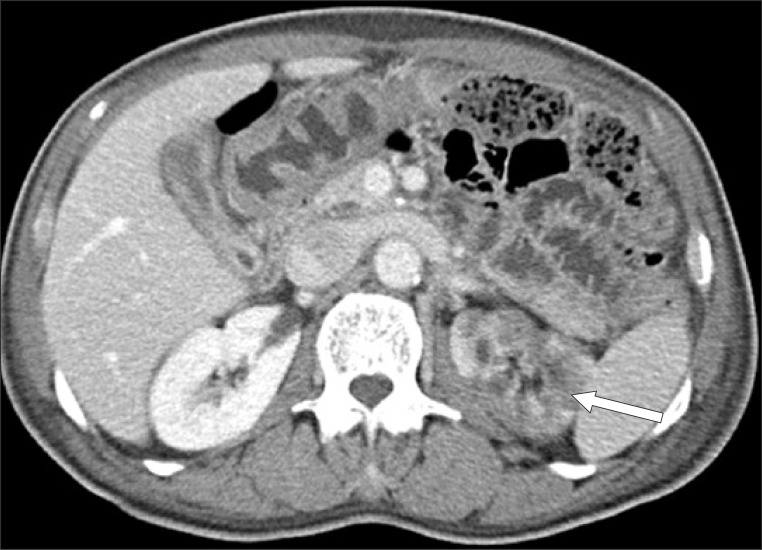
- Acute renal infarction is a rare disease and it is often difficult to make a clinical diagnosis due to the non-specific clinical presentations and lack of the physicians' awarenesses. We experienced a case of a 72-year-old man who was diagnosed as multiorgan with renal infarction during the bridge therapy of cerebral infarction with atrial fibrillation. Computed tomogram (CT) with intravenous contrast of the abdomen and pelvis revealed left renal infarction with renal artery occlusion, multifocal splenic infarction, and ischemic colitis on rectum and sigmoid colon. The patient was treated with low molecular weight heparin for 10 days, his symptoms were improved and laboratory findings were normalized. Follow-up CT was performed on the 43th day, there were persisted left renal infarction with atrophic change shown and the splenic perfusion was improved.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tsai SH, Chu SJ, Chen SJ, Fan YM, Chang WC, Wu CP, et al. Acute renal infarction: a 10-year experience. Int J Clin Pract. 2007; 61:62–67. PMID: 17229180.
Article2. Menke J, Luthje L, Kastrup A, Larsen J. Thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2010; 105:502–510. PMID: 20152245.
Article3. Abboud H, Labreuche J, Gongora-Riverra F, Jaramillo A, Duyckaerts C, Steg PG, et al. Prevalence and determinants of subdiaphragmatic visceral infarction in patients with fatal stroke. Stroke. 2007; 38:1442–1446. PMID: 17379822.
Article4. Korzets Z, Plotkin E, Bernheim J, Zissin R. The clinical spectrum of acute renal infarction. Isr Med Assoc J. 2002; 4:781–784. PMID: 12389340.5. Kim JS, Lee SY, Kim JH, Kwon EH, Song SH, Lee DW, et al. Acute renal infarction: clinical features in 23 cases. Korean J Med. 2006; 70:543–550.6. Salih SB, Al Durihim H, Al Jizeeri A, Al Maziad G. Acute renal infarction secondary to atrial fibrillation: mimicking renal stone picture. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2006; 17:208–212. PMID: 16903629.7. Spyropoulos AC, Turpie AG, Dunn AS, Spandorfer J, Douketis J, Jacobson A, et al. Clinical outcomes with unfractionated heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin as bridging therapy in patients on long-term oral anticoagulants: the REGIMEN registry. J Thromb Haemost. 2006; 4:1246–1252. PMID: 16706967.8. Gage BF, Waterman AD, Shannon W, Boechler M, Rich MW, Radford MJ. Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA. 2001; 285:2864–2870. PMID: 11401607.
Article9. Hazanov N, Somin M, Attali M, Beilinson N, Thaler M, Mouallem M, et al. Acute renal embolism: forty-four cases of renal infarction in patients with atrial fibrillation. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004; 83:292–299. PMID: 15342973.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple Cerebral infarction Associated with Heat Stroke
- Cardioembolic Stroke and Bilateral Renal Infarction in a Patient with Atrial Fibrillation
- Bilateral Anterior Cerebral Artery Infarction Associated with Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome
- A Case of the Thrombi in Left Atrial Appendage Confirmed by Transesophageal Echocardiography(TEE) in A Patient with Acute Myocardial Infarction Accompanied by Cerebral Infarction
- Acute Cerebral Infarction in Carbon Monoxide Poisoning