Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Aug;37(4):523-533. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.523.
Changes in Balancing Ability of Athletes With Chronic Ankle Instability After Foot Orthotics Application and Rehabilitation Exercises
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea. klpark21@naver.com
- 2Institute of Sports Rehabilitation, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, CHA University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2266608
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.523
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare the effect of foot orthotics and rehabilitation exercises by assessing balancing ability and joint proprioception in athletes who have chronic ankle instability.
METHODS
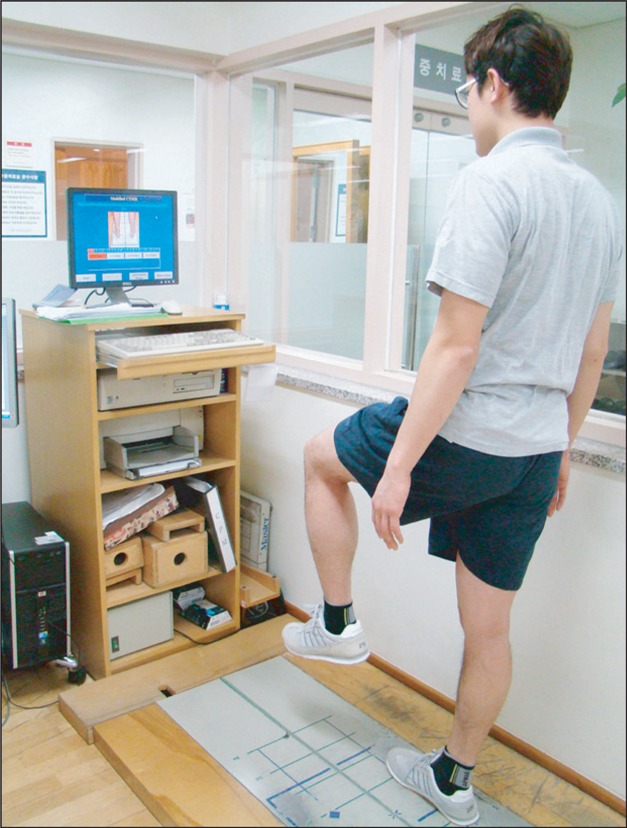
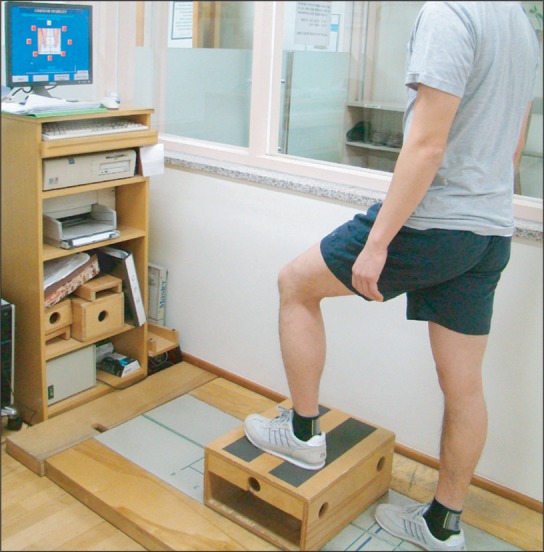
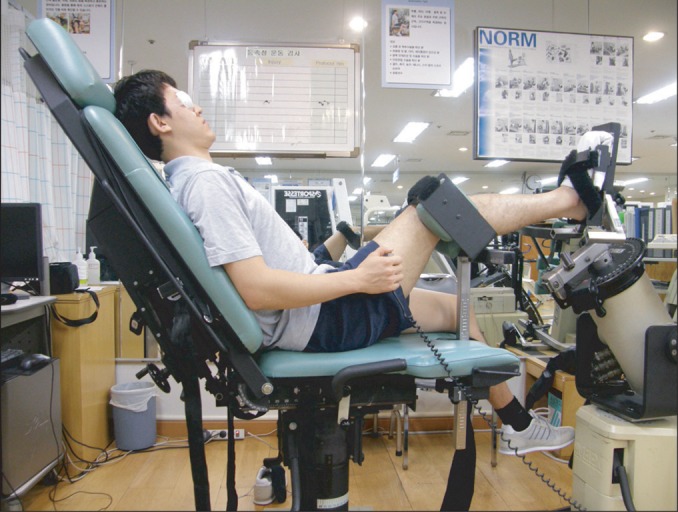
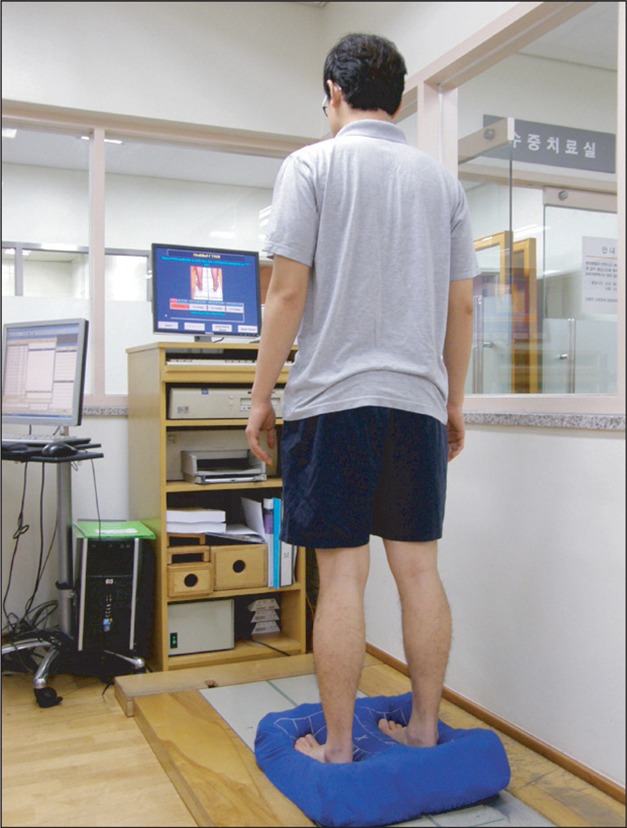
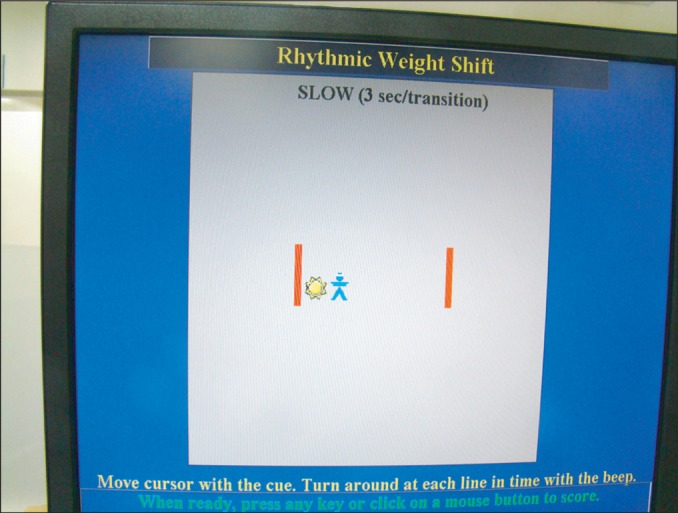
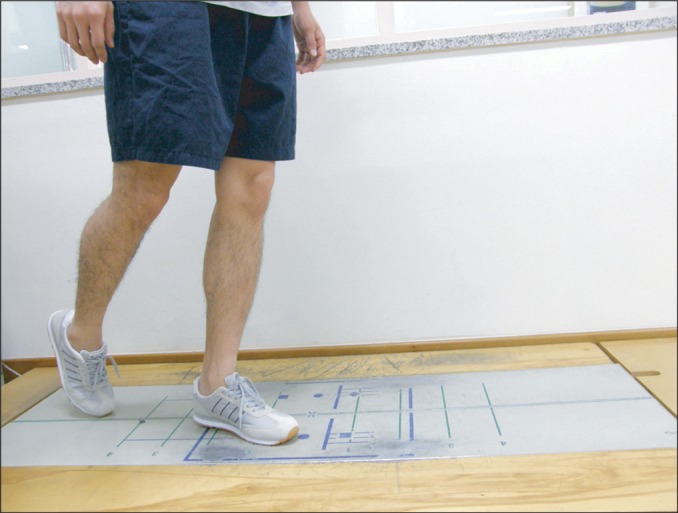
Forty-one athletes who visited hospitals due to chronic ankle instability were randomly assigned to two groups. One group had ankle rehabilitation exercises while the other group had the same rehabilitation exercises as well as foot orthotics. Joint position sense of the ankle joint was examined by using an isokinetic exercise machine. Balancing abilities categorized into static, dynamic and functional balance abilities were evaluated by using computerized posturography. We tested the subjects before and after the four-week rehabilitation program.
RESULTS
After the four-week treatment, for joint reposition sense evaluation, external 75% angle evaluation was done, revealing that the group with the application of foot orthotics improved by -1.07+/-1.64 on average, showing no significant difference between the two groups (p>0.05). Static, dynamic and functional balancing abilities using balance masters were evaluated, revealing that the two groups improved in some items, but showing no significant difference between them (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
This study found that athletes with chronic ankle instability who had foot orthotics applied for four weeks improved their proprioceptive and balancing abilities, but did not show additional treatment effects compared with rehabilitation exercise treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Balduini FC, Vegso JJ, Torg JS, Torg E. Management and rehabilitation of ligamentous injuries to the ankle. Sports Med. 1987; 4:364–380. PMID: 3313619.
Article2. Colville MR. Surgical treatment of the unstable ankle. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1998; 6:368–377. PMID: 9826420.
Article3. Colville MR. Reconstruction of the lateral ankle ligaments. Instr Course Lect. 1995; 44:341–348. PMID: 7797872.
Article4. Hertel JN, Guskiewicz KM, Kahler DM, Perrin DH. Effect of lateral ankle joint anesthesia on center of balance, postural sway, and joint position sense. J Sport Rehabil. 1996; 5:111–119.
Article5. Berlet G, Anderson RB, Davis W. Chronic lateral ankle instability. Foot Ankle Clin. 1999; 4:713–728.6. Hertel J, Denegar CR, Monroe MM, Stokes WL. Talocrural and subtalar joint instability after lateral ankle sprain. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999; 31:1501–1508. PMID: 10589849.
Article7. Freeman MA. Instability of the foot after injuries to the lateral ligament of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965; 47:669–677. PMID: 5846766.8. Wikstrom EA, Naik S, Lodha N, Cauraugh JH. Bilateral balance impairments after lateral ankle trauma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gait Posture. 2010; 31:407–414. PMID: 20303759.
Article9. Sesma AR, Mattacola CG, Uhl TL, Nitz AJ, McKeon PO. Effect of foot orthotics on single- and double-limb dynamic balance tasks in patients with chronic ankle instability. Foot Ankle Spec. 2008; 1:330–337. PMID: 19825736.
Article10. Garn SN, Newton RA. Kinesthetic awareness in subjects with multiple ankle sprains. Phys Ther. 1988; 68:1667–1671. PMID: 3186791.
Article11. Jerosch J, Bischof M. Proprioceptive capabilities of the ankle in stable and unstable joints. Sports Exerc Inj. 1996; 2:167–171.12. Boyle J, Negus V. Joint position sense in the recurrently sprained ankle. Aust J Physiother. 1998; 44:159–163. PMID: 11676729.
Article13. Gross MT. Effects of recurrent lateral ankle sprains on active and passive judgements of joint position. Phys Ther. 1987; 67:1505–1509. PMID: 3659134.14. Feuerbach JW, Grabiner MD, Koh TJ, Weiker GG. Effect of an ankle orthosis and ankle ligament anesthesia on ankle joint proprioception. Am J Sports Med. 1994; 22:223–229. PMID: 8198191.
Article15. Refshauge KM, Kilbreath SL, Raymond J. The effect of recurrent ankle inversion sprain and taping on proprioception at the ankle. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000; 32:10–15. PMID: 10647523.
Article16. McKeon PO, Ingersoll CD, Kerrigan DC, Saliba E, Bennett BC, Hertel J. Balance training improves function and postural control in those with chronic ankle instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008; 40:1810–1819. PMID: 18799992.
Article17. O'Driscoll J, Kerin F, Delahunt E. Effect of a 6-week dynamic neuromuscular training programme on ankle joint function: a case report. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2011; 3:13. PMID: 21658224.18. Chan KW, Ding BC, Mroczek KJ. Acute and chronic lateral ankle instability in the athlete. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2011; 69:17–26. PMID: 21332435.19. Richie DH Jr. Effects of foot orthoses on patients with chronic ankle instability. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2007; 97:19–30. PMID: 17218622.
Article20. Nester CJ, van der Linden ML, Bowker P. Effect of foot orthoses on the kinematics and kinetics of normal walking gait. Gait Posture. 2003; 17:180–187. PMID: 12633779.
Article21. Lee H, Na YM, Lim KB. Biomechanical characteristics of lower extremities and pelvis in Korean soccer players who complain of chronic lower back pain. Korean J Sports Med. 2004; 22:59–66.22. Lim EC, Tan MH. Side-to-side difference in joint position sense and kinesthesia in unilateral functional ankle instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2009; 30:1011–1017. PMID: 19796597.
Article23. Guskiewicz KM, Perrin DH. Effect of orthotics on postural sway following inversion ankle sprain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1996; 23:326–331. PMID: 8728531.
Article24. Stude DE, Brink DK. Effects of nine holes of simulated golf and orthotic intervention on balance and proprioception in experienced golfers. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1997; 20:590–601. PMID: 9436144.25. Cobb SC, Tis LL, Johnson JT. The effect of 6 weeks of custom-molded foot orthosis intervention on postural stability in participants with >or=7 degrees of forefoot varus. Clin J Sport Med. 2006; 16:316–322. PMID: 16858215.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correction: Changes in Balancing Ability of Athletes With Chronic Ankle Instability After Foot Orthotics Application and Rehabilitation Exercises
- Diagnosis and Comorbidity of Chronic Ankle Instability
- Arthroscopic Procedure in the Treatment of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability
- Ligament Repair in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability: Efficacy and Technique of Broström Procedures