The Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Lower Limb Spasticity in Subacute Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University Graduate School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. solioh21@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurology, Gyeongsang National University Graduate School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Samcheonpo Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2266601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.461
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) on lower limb spasticity in subacute stroke patients.
METHODS
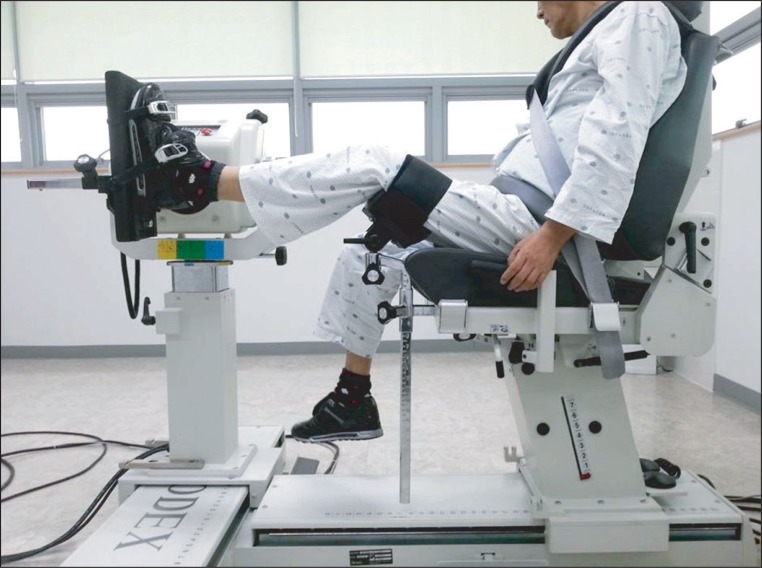
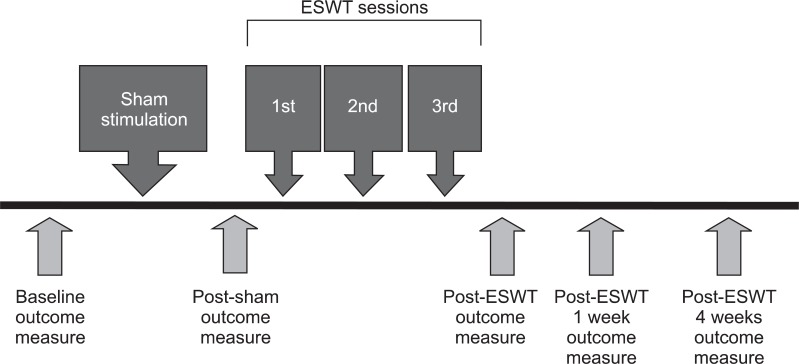
We studied thirty hemiplegic subacute stroke patients with ankle plantar flexor spasticity. ESWT was applied for 1 session/week, with a total of 3 sessions at the musculotendinous junction of medial and lateral gastrocnemius muscles. Patients were evaluated both clinically and biomechanically at baseline, after sham stimulation, and at immediately 1 week and 4 weeks after ESWT. For clinical assessment, Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS), clonus score, passive range of motion of ankle, and Fugl-Myer Assessment for the lower extremity were used. A biomechanical assessment of spasticity was conducted by an isokinetic dynamometer. Two parameters, peak eccentric torque (PET) and torque threshold angle (TTA), were analyzed at the velocities of 60degrees/sec, 180degrees/sec, and 240degrees/sec.
RESULTS
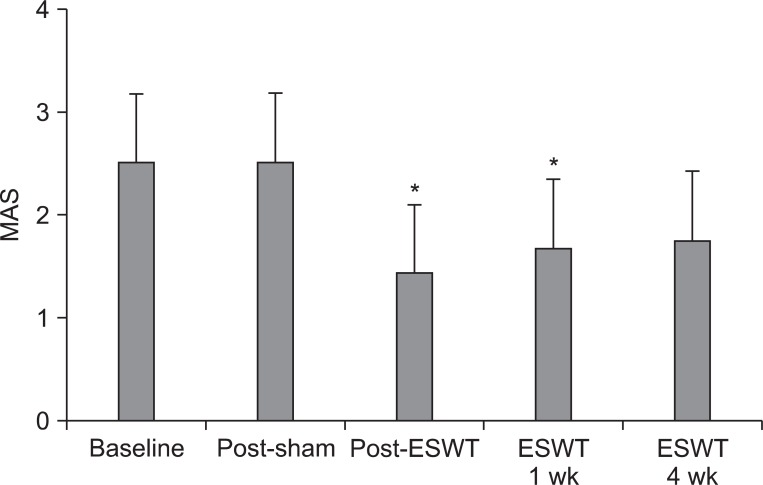
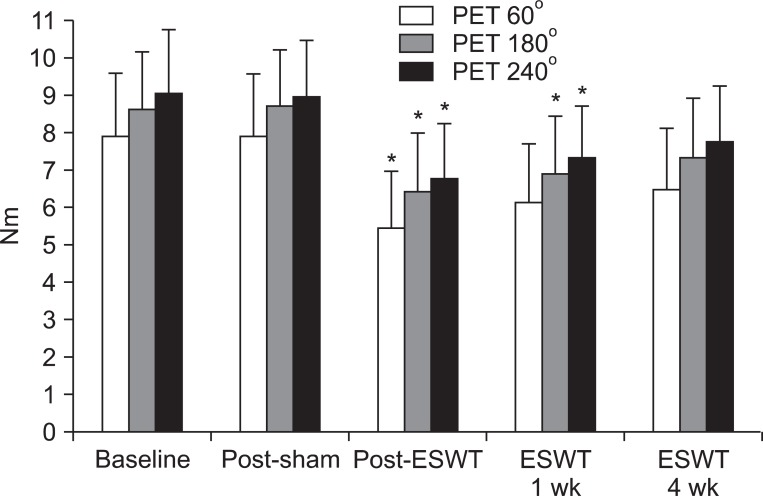
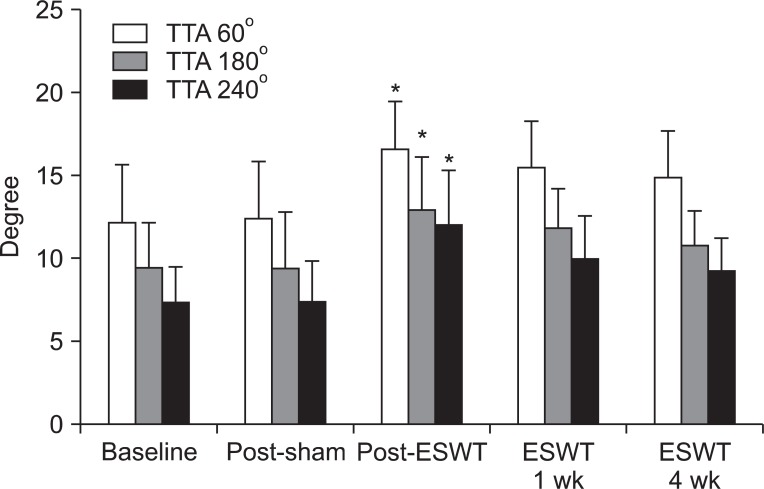
After sham stimulation, there were no significant changes between each assessment. MAS and PET (180degrees/sec and 240degrees/sec) were significantly improved immediately and 1 week after ESWT. However, these changes were not significant at 4 weeks after ESWT. PET (60degrees/sec) and TTA (60degrees/sec, 180degrees/sec, and 240degrees/sec) were significantly improved immediately after ESWT. Yet, these changes were not significant at 1 week and 4 weeks after ESWT as well.
CONCLUSION
Lower limb spasticity in subacute stroke patients was significantly improved immediately after ESWT. Although the therapeutic effect of ESWT reduced with time and therefore was not significant at 4 weeks after ESWT, the degree of spasticity was lower than that of the baseline. Future studies with a larger sample of patients are warranted in order to verify the protocols which can optimize the effect of ESWT on spasticity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Effect of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain Syndrome
Sung Hwan Kim, Kang Wook Ha, Yun Hee Kim, Pyong-Hwa Seol, Ho-Jun Kwak, Seung-Wan Park, Byung-Ju Ryu
Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(3):509-519. doi: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.3.509.Effective Site for the Application of Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Therapy on Spasticity in Chronic Stroke: Muscle Belly or Myotendinous Junction
Sang Ho Yoon, Min Kyung Shin, Eun Jung Choi, Hyo Jung Kang
Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(4):547-555. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.4.547.Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Versus Trigger Point Injection in the Treatment of Myofascial Pain Syndrome in the Quadratus Lumborum
Jin Oh Hong, Joon Sang Park, Dae Geun Jeon, Wang Hyeon Yoon, Jung Hyun Park
Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(4):582-588. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.4.582.Duration of Treatment Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave on Spasticity and Subgroup-Analysis According to Number of Shocks and Application Site: A Meta-Analysis
Jae Ho Oh, Hee Dong Park, Seung Hee Han, Ga Yang Shim, Kyung Yeul Choi
Ann Rehabil Med. 2019;43(2):163-177. doi: 10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.163.
Reference
-
2. Mori F, Koch G, Foti C, Bernardi G, Centonze D. The use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for the treatment of spasticity. Prog Brain Res. 2009; 175:429–439. PMID: 19660671.
Article3. Stevenson VL. Rehabilitation in practice: spasticity management. Clin Rehabil. 2010; 24:293–304. PMID: 20360150.
Article4. Valchanou VD, Michailov P. High energy shock waves in the treatment of delayed and nonunion of fractures. Int Orthop. 1991; 15:181–184. PMID: 1743828.
Article5. Wang CJ, Yang KD, Wang FS, Chen HH, Wang JW. Shock wave therapy for calcific tendinitis of the shoulder: a prospective clinical study with two-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2003; 31:425–430. PMID: 12750138.6. Rompe JD, Theis C, Maffulli N. Shock wave treatment for tennis elbow. Orthopade. 2005; 34:567–570. PMID: 15886855.7. Rompe JD. Shock-wave therapy for plantar fasciitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:681–682. PMID: 15786568.
Article8. Manganotti P, Amelio E. Long-term effect of shock wave therapy on upper limb hypertonia in patients affected by stroke. Stroke. 2005; 36:1967–1971. PMID: 16109905.
Article9. Sohn MK, Cho KH, Kim YJ, Hwang SL. Spasticity and electrophysiologic changes after extracorporeal shock wave therapy on gastrocnemius. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:599–604. PMID: 22506181.
Article10. Bae H, Lee JM, Lee KH. The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on spasticity in chronic stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:663–669.11. Yoo SD, Kim HS, Jung PK. The effect of shock wave therapy on upper limb spasticityin the patients with stroke. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2008; 32:406–410.12. Duncan PW, Propst M, Nelson SG. Reliability of the Fugl-Meyer assessment of sensorimotor recovery following cerebrovascular accident. Phys Ther. 1983; 63:1606–1610. PMID: 6622535.
Article13. Lee SJ, Han TR. A quantitative assessment of spasticity in hemiplegic patients using isokinetic dynamometer. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1998; 22:784–792.14. Mariotto S, Cavalieri E, Amelio E, Ciampa AR, de Prati AC, Marlinghaus E, et al. Extracorporeal shock waves: from lithotripsy to anti-inflammatory action by NO production. Nitric Oxide. 2005; 12:89–96. PMID: 15740982.
Article15. Leone JA, Kukulka CG. Effects of tendon pressure on alpha motoneuron excitability in patients with stroke. Phys Ther. 1988; 68:475–480. PMID: 3353457.
Article16. Mariotto S, de Prati AC, Cavalieri E, Amelio E, Marlinghaus E, Suzuki H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr Med Chem. 2009; 16:2366–2372. PMID: 19601786.
Article17. Mariotto S, Menegazzi M, Suzuki H. Biochemical aspects of nitric oxide. Curr Pharm Des. 2004; 10:1627–1645. PMID: 15134561.
Article18. Kenmoku T, Ochiai N, Ohtori S, Saisu T, Sasho T, Nakagawa K, et al. Degeneration and recovery of the neuromuscular junction after application of extracorporeal shock wave therapy. J Orthop Res. 2012; 30:1660–1665. PMID: 22457214.
Article19. Mirbagheri MM, Barbeau H, Ladouceur M, Kearney RE. Intrinsic and reflex stiffness in normal and spastic, spinal cord injured subjects. Exp Brain Res. 2001; 141:446–459. PMID: 11810139.20. Fellows SJ, Ross HF, Thilmann AF. The limitations of the tendon jerk as a marker of pathological stretch reflex activity in human spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993; 56:531–537. PMID: 8505646.
Article21. Given JD, Dewald JP, Rymer WZ. Joint dependent passive stiffness in paretic and contralateral limbs of spastic patients with hemiparetic stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995; 59:271–279. PMID: 7673955.
Article22. Amelio E, Manganotti P. Effect of shock wave stimulation on hypertonic plantar flexor muscles in patients with cerebral palsy: a placebo-controlled study. J Rehabil Med. 2010; 42:339–343. PMID: 20358168.
Article23. Vidal X, Morral A, Costa L, Tur M. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy (rESWT) in the treatment of spasticity in cerebral palsy: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. NeuroRehabilitation. 2011; 29:413–419. PMID: 22207070.
Article24. Kim DY, Park CI, Na SI, Park YS. Quantitative assessment of the effect of tizanidine on spasticity in stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2003; 27:471–479.25. Blackburn M, van Vliet P, Mockett SP. Reliability of measurements obtained with the Modified Ashworth Scale in the lower extremities of people with stroke. Phys Ther. 2002; 82:25–34. PMID: 11784275.
Article26. Odeen I, Knutsson E. Evaluation of the effects of muscle stretch and weight load in patients with spastic paraplegia. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1981; 13:117–121. PMID: 7347432.27. Lee SJ, Kwon BS, Park CH. The effect of passive stretching on the spasticity of ankle plantar flexor muscles. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2001; 25:987–992.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and Quantitative Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Rheologic Effect in the Patients with Post-stroke Upper Limb Spasticity: A Case Report
- The Effect of Shock Wave Therapy on Upper Limb Spasticityin the Patients with Stroke
- Spasticity and Electrophysiologic Changes after Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Gastrocnemius
- Effect of Shock Wave Therapy on Upper Limb Spasticity in Chronic Stroke
- Effective Site for the Application of Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Therapy on Spasticity in Chronic Stroke: Muscle Belly or Myotendinous Junction