Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Oct;37(5):717-720. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.5.717.
Anterior Cervical Osteophytes Causing Dysphagia and Paradoxical Vocal Cord Motion Leading to Dyspnea and Dysphonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. spotdoc88@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2266591
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.5.717
Abstract
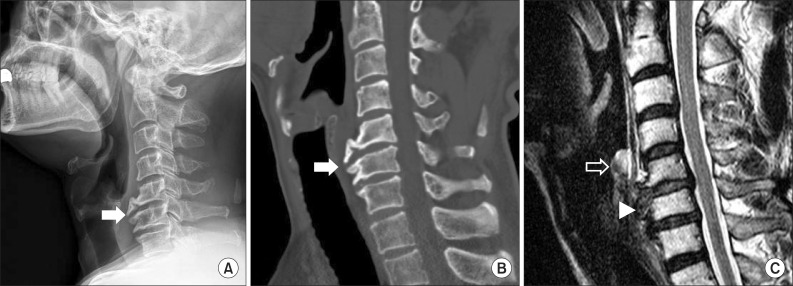
- Anterior cervical osteophytes are common and usually asymptomatic in elderly people. Due to mechanical compressions, inflammations, and tissues swelling of osteophytes, patients may be presented with multiple complications, such as dysphagia, dysphonia, dyspnea, and pulmonary aspiration. Paradoxical vocal cord motion is an uncommon disease characterized by vocal cord adductions during inspiration and/or expiration. This condition can create shortness of breath, wheezing, respiratory stridor or breathy dysphonia. We report a rare case demonstrating combined symptoms of dyspnea, dysphonia as well as dysphagia at the same time in a patient with asymptomatic anterior cervical osteophytes. Moreover, this is the first report demonstrating that anterior osteophytes can be a possible etiological factor for paradoxical vocal cord motion that induces serious respiratory symptoms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Postoperative respiratory difficulty due to asymptomatic anterior cervical osteophyte after brain tumor surgery: a case report
Hye Won Shin, Joon Chul Jang, Hyong Hwan Lim, Min Kyung Park, Go Eun Bae, Seung Uk Choi, Ji Yong Park
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2016;69(6):640-643. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2016.69.6.640.
Reference
-
1. Granville LJ, Musson N, Altman R, Silverman M. Anterior cervical osteophytes as a cause of pharyngeal stage dysphagia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998; 46:1003–1007. PMID: 9706891.
Article2. Ahn YJ, Hahn SH, Yang BK, Yi SR, Yoo JH, Yoon DJ, et al. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis associated with dysphonia and dysphagia: a case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2006; 13:327–331.
Article3. Forrest LA, Husein T, Husein O. Paradoxical vocal cord motion: classification and treatment. Laryngoscope. 2012; 122:844–853. PMID: 22434681.
Article4. Karaman E, Duman C, Alimoglu Y, Isildak H, Oz F. Paradoxical vocal cord motion: haloperidol usage in acute attack treatment. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20:1602–1604. PMID: 19816305.5. Kim SK, Choi BR, Kim CG, Chung SH, Choe JY, Joo KB, et al. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Korea. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:2032–2035. PMID: 15468371.6. Gamache FW Jr, Voorhies RM. Hypertrophic cervical osteophytes causing dysphagia: a review. J Neurosurg. 1980; 53:338–344. PMID: 7420148.7. Demuynck K, Van Calenbergh F, Goffin J, Verschakelen J, Demedts M, Van de Woestijne K. Upper airway obstruction caused by a cervical osteophyte. Chest. 1995; 108:283–284. PMID: 7606974.
Article8. Kapetanakis S, Vasileiadis I, Papanas N, Goulimari R, Maltezos E. Can a giant cervical osteophyte cause dysphagia and airway obstruction? A case report. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2011; 123:291–293. PMID: 21484285.
Article9. Faruqi S, Thirumaran M, Blaxill P. An osseous cause of dysphagia. Med J Aust. 2008; 188:671. PMID: 18513179.
Article10. Marra A, Dario A, Scamoni C, Pozzi M, Soldati M, Dorizzi A. Dysphagia due to anterior cervical osteophyte: case report. J Neurosurg Sci. 1991; 35:229–231. PMID: 1812251.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Giant Anterior Cervical Osteophyte Leading to Dysphagia
- Unilateral Vocal Cord Palsy Caused by Cervical Osteophyte
- A Case of Spontaneous Massive Pharyngeal Bleeding Caused by Anterior Cervical Osteophytes
- A Case of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Dysphagia
- Early Detection of Anterior Cervical Osteophytes Causing Dysphagia by Esophagogastroduodenoscopy