Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Feb;38(1):29-37. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.29.
Ultrasonographic Diaphragmatic Motion Analysis and Its Correlation With Pulmonary Function in Hemiplegic Stroke Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Eulji University Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. danielpjy@naver.com
- KMID: 2266537
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.29
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate diaphragmatic motion via M-mode ultrasonography and to correlate it with pulmonary function in stroke patients.
METHODS
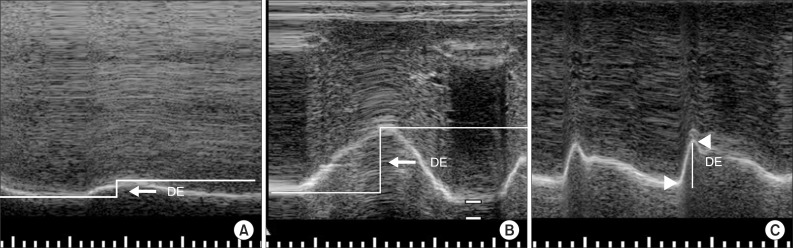
This was a preliminary study comprised of ten stroke patients and sixteen healthy volunteers. The M-mode ultrasonographic probe was positioned in the subcostal anterior region of the abdomen for transverse scanning of the diaphragm during quiet breathing, voluntary sniffing, and deep breathing. We analyzed diaphragmatic motion and the relationship between diaphragmatic motion and pulmonary function.
RESULTS
All stroke patients had restrictive pulmonary dysfunction. Compared to that exhibited by control subjects, stroke patients exhibited a significant unilateral reduction in motion on the hemiplegic side, primarily during volitional breathing. Diaphragmatic excursion in right-hemiplegic patients was reduced on both sides compared to that in control subjects. However, diaphragmatic excursion was reduced only on the left side and increased on the right side in left-hemiplegic patients compared to that in control subjects. Left diaphragmatic motion during deep breathing correlated positively with forced vital capacity (rho=0.86, p=0.007) and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (rho=0.79, p=0.021).
CONCLUSION
Reductions in diaphragmatic motion and pulmonary function can occur in stroke patients. Thus, this should be assessed prior to the initiation of rehabilitation therapy, and M-mode ultrasonography can be used for this purpose. It is a non-invasive method providing quantitative information that is correlated with pulmonary function.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aminoff MJ, Sears TA. Spinal integration of segmental, cortical and breathing inputs to thoracic respiratory motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971; 215:557–575. PMID: 4336048.
Article2. Manning HL, Leiter JC. Respiratory control and respiratory sensation in a patient with a ganglioglioma within the dorsocaudal brain stem. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:2100–2106. PMID: 10852794.
Article3. Guz A. Brain, breathing and breathlessness. Respir Physiol. 1997; 109:197–204. PMID: 9342797.
Article4. Houston JG, Morris AD, Grosset DG, Lees KR, McMillan N, Bone I. Ultrasonic evaluation of movement of the diaphragm after acute cerebral infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995; 58:738–741. PMID: 7608679.
Article5. Cohen E, Mier A, Heywood P, Murphy K, Boultbee J, Guz A. Diaphragmatic movement in hemiplegic patients measured by ultrasonography. Thorax. 1994; 49:890–895. PMID: 7940429.
Article6. Houston JG, Fleet M, Cowan MD, McMillan NC. Comparison of ultrasound with fluoroscopy in the assessment of suspected hemidiaphragmatic movement abnormality. Clin Radiol. 1995; 50:95–98. PMID: 7867276.
Article7. Ayoub J, Metge L, Dauzat M, Lemerre C, Pourcelot L, Prefaut C, et al. Diaphragm kinetics coupled with spirometry: M-mode ultrasonographic and fluoroscopic study: preliminary results. J Radiol. 1997; 78:563–568. PMID: 9537172.8. Boussuges A, Gole Y, Blanc P. Diaphragmatic motion studied by M-mode ultrasonography: methods, reproducibility, and normal values. Chest. 2009; 135:391–400. PMID: 19017880.9. Testa A, Soldati G, Giannuzzi R, Berardi S, Portale G, Gentiloni Silveri N. Ultrasound M-mode assessment of diaphragmatic kinetics by anterior transverse scanning in healthy subjects. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2011; 37:44–52. PMID: 21144957.10. Cocchiarella L, Andersson G. Guides to the evaluation of permanent impairment. 5th ed. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association;2001.11. Roffe C, Sills S, Wilde K, Crome P. Effect of hemiparetic stroke on pulse oximetry readings on the affected side. Stroke. 2001; 32:1808–1810. PMID: 11486109.
Article12. Young DA, Simon G. Certain movements measured on inspiration-expiration chest radiographs correlated with pulmonary function studies. Clin Radiol. 1972; 23:37–41. PMID: 5032861.
Article13. Houston JG, Morris AD, Howie CA, Reid JL, McMillan N. Technical report: quantitative assessment of diaphragmatic movement: a reproducible method using ultrasound. Clin Radiol. 1992; 46:405–407. PMID: 1493655.14. Harris RS, Giovannetti M, Kim BK. Normal ventilatory movement of the right hemidiaphragm studied by ultrasonography and pneumotachography. Radiology. 1983; 146:141–144. PMID: 6849035.
Article15. Gierada DS, Curtin JJ, Erickson SJ, Prost RW, Strandt JA, Goodman LR. Diaphragmatic motion: fast gradient-recalled-echo MR imaging in healthy subjects. Radiology. 1995; 194:879–884. PMID: 7862995.
Article16. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS statement on respiratory muscle testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:518–624. PMID: 12186831.17. Nachtmann A, Siebler M, Rose G, Sitzer M, Steinmetz H. Cheyne-Stokes respiration in ischemic stroke. Neurology. 1995; 45:820–821. PMID: 7723977.
Article18. Bassetti C, Aldrich MS. Sleep apnea in acute cerebrovascular diseases: final report on 128 patients. Sleep. 1999; 22:217–223. PMID: 10201066.
Article19. Khedr EM, El Shinawy O, Khedr T, Aziz Ali YA, Awad EM. Assessment of corticodiaphragmatic pathway and pulmonary function in acute ischemic stroke patients. Eur J Neurol. 2000; 7:323–330. PMID: 10886317.
Article20. Roffe C, Sills S, Halim M, Wilde K, Allen MB, Jones PW, et al. Unexpected nocturnal hypoxia in patients with acute stroke. Stroke. 2003; 34:2641–2645. PMID: 14576377.
Article21. Ali K, Cheek E, Sills S, Crome P, Roffe C. Day-night differences in oxygen saturation and the frequency of desaturations in the first 24 hours in patients with acute stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007; 16:239–244. PMID: 18035240.
Article22. Fugl-Meyer AR, Linderholm H, Wilson AF. Restrictive ventilatory dysfunction in stroke: its relation to locomotor function. Scand J Rehabil Med Suppl. 1983; 9:118–124. PMID: 6585933.23. Takazakura R, Takahashi M, Nitta N, Murata K. Diaphragmatic motion in the sitting and supine positions: healthy subject study using a vertically open magnetic resonance system. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004; 19:605–609. PMID: 15112310.
Article24. Similowski T, Catala M, Rancurel G, Derenne JP. Impairment of central motor conduction to the diaphragm in stroke. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 154(2 Pt 1):436–441. PMID: 8756819.
Article25. Maskill D, Murphy K, Mier A, Owen M, Guz A. Motor cortical representation of the diaphragm in man. J Physiol. 1991; 443:105–121. PMID: 1822523.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of Respiratory Function following Rehabilitation in Acute Hemiplegic Stroke Patients
- Comparison of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical Findings in Hemiplegic Shoulder
- Ultrasonographic and Physical Examination to Investigate the Cause of Painful Hemiplegic Shoulder
- Correlation of Swallowing Function With Bilateral Diaphragmatic Movement in Hemiplegic Stroke Patients
- Unilateral Congenital Diaphragmatic Eventration Mimicking Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia