Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Oct;38(5):658-664. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.5.658.
Reduction of Continuous Theta Burst Stimulation-Induced Motor Plasticity in Healthy Elderly With COMT Val158Met Polymorphism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chooncheon, Korea. wooky@hallym.or.kr
- 2Hallym Institute of Translational Genomics & Bioinformatics, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea.
- 3ILSONG Institute of Life Science, Hallym University, Anyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2266500
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.5.658
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To delineate whether cortical plasticity induced by continuous theta burst stimulation (cTBS) differed according to catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene polymorphism in healthy older adults.
METHODS
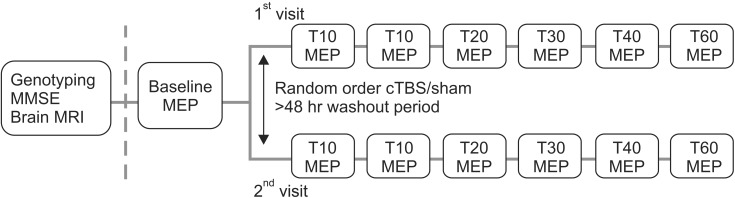
Eighteen healthy older volunteers (mean age 73.78+/-5.04; 12 females and 6 males) were recruited. Volunteers randomly assigned in either a sham-first or real cTBS first group participated in two separate TMS visits with at least a 2-day wash-out period. Genotyping was carried out at baseline by a separate researcher who was blinded. cTBS was delivered in a hot spot over M1 at an active motor threshold of 80%. Motor evoked potentials (MEPs) were obtained at 120% of the resting motor threshold before and after sham/cTBS.
RESULTS
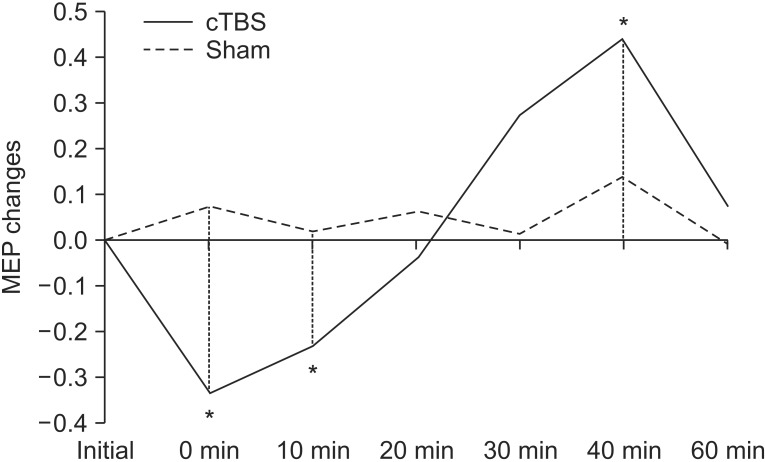
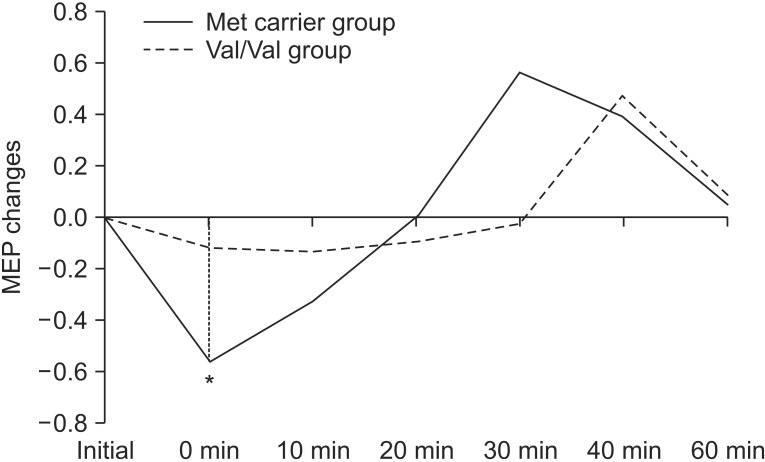
The relative MEP to baseline was significantly decreased 0 and 10 minutes post-stimulation and increased 40 minutes post-stimulation, as compared with the sham condition. Immediately after cTBS, the Val/Val group had a significantly reduced relative MEP value, as compared with the MET carrier group.
CONCLUSION
In healthy older persons, cTBS-induced motor plasticity was reduced in the COMT Val/Val group as compared with the 158Met carrier group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stefan K, Kunesch E, Benecke R, Cohen LG, Classen J. Mechanisms of enhancement of human motor cortex excitability induced by interventional paired associative stimulation. J Physiol. 2002; 543(Pt 2):699–708. PMID: 12205201.
Article2. Pascual-Leone A. Disrupting the brain to guide plasticity and improve behavior. Prog Brain Res. 2006; 157:315–329. PMID: 17167918.
Article3. Lee L, Siebner H, Bestmann S. Rapid modulation of distributed brain activity by Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of human motor cortex. Behav Neurol. 2006; 17:135–148. PMID: 17148833.
Article4. Huang YZ, Edwards MJ, Rounis E, Bhatia KP, Rothwell JC. Theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex. Neuron. 2005; 45:201–206. PMID: 15664172.
Article5. Doeltgen SH, Ridding MC. Low-intensity, short-interval theta burst stimulation modulates excitatory but not inhibitory motor networks. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011; 122:1411–1416. PMID: 21195662.
Article6. Freitas C, Perez J, Knobel M, Tormos JM, Oberman L, Eldaief M, et al. Changes in cortical plasticity across the lifespan. Front Aging Neurosci. 2011; 3:5. PMID: 21519394.
Article7. Oberman L, Ifert-Miller F, Najib U, Bashir S, Woollacott I, Gonzalez-Heydrich J, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation provides means to assess cortical plasticity and excitability in humans with fragile x syndrome and autism spectrum disorder. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2010; 2:26. PMID: 21423512.
Article8. Muller-Dahlhaus JF, Orekhov Y, Liu Y, Ziemann U. Interindividual variability and age-dependency of motor cortical plasticity induced by paired associative stimulation. Exp Brain Res. 2008; 187:467–475. PMID: 18320180.
Article9. Inghilleri M, Conte A, Curra A, Frasca V, Lorenzano C, Berardelli A. Ovarian hormones and cortical excitability: an rTMS study in humans. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004; 115:1063–1068. PMID: 15066531.
Article10. Lee M, Kim SE, Kim WS, Lee J, Yoo HK, Park KD, et al. Interaction of motor training and intermittent theta burst stimulation in modulating motor cortical plasticity: influence of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e57690. PMID: 23451258.
Article11. Antal A, Chaieb L, Moliadze V, Monte-Silva K, Poreisz C, Thirugnanasambandam N, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene polymorphisms shape cortical plasticity in humans. Brain Stimul. 2010; 3:230–237. PMID: 20965453.
Article12. Li Voti P, Conte A, Suppa A, Iezzi E, Bologna M, Aniello MS, et al. Correlation between cortical plasticity, motor learning and BDNF genotype in healthy subjects. Exp Brain Res. 2011; 212:91–99. PMID: 21537966.
Article13. Goldberg TE, Weinberger DR. Genes and the parsing of cognitive processes. Trends Cogn Sci. 2004; 8:325–335. PMID: 15242692.
Article14. Bertolino A, Rubino V, Sambataro F, Blasi G, Latorre V, Fazio L, et al. Prefrontal-hippocampal coupling during memory processing is modulated by COMT val-158met genotype. Biol Psychiatry. 2006; 60:1250–1258. PMID: 16950222.
Article15. de Frias CM, Annerbrink K, Westberg L, Eriksson E, Adolfsson R, Nilsson LG. COMT gene polymorphism is associated with declarative memory in adulthood and old age. Behav Genet. 2004; 34:533–539. PMID: 15319576.
Article16. Raz N, Rodrigue KM, Kennedy KM, Land S. Genetic and vascular modifiers of age-sensitive cognitive skills: effects of COMT, BDNF, ApoE, and hypertension. Neuropsychology. 2009; 23:105–116. PMID: 19210038.
Article17. Molina-Luna K, Pekanovic A, Rohrich S, Hertler B, Schubring-Giese M, Rioult-Pedotti MS, et al. Dopamine in motor cortex is necessary for skill learning and synaptic plasticity. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e7082. PMID: 19759902.
Article18. Witte AV, Kurten J, Jansen S, Schirmacher A, Brand E, Sommer J, et al. Interaction of BDNF and COMT polymorphisms on paired-associative stimulation-induced cortical plasticity. J Neurosci. 2012; 32:4553–4561. PMID: 22457502.
Article19. Rossi S, Hallett M, Rossini PM, Pascual-Leone A. Safety of TMS Consensus Group. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009; 120:2008–2039. PMID: 19833552.
Article20. Rossini PM, Barker AT, Berardelli A, Caramia MD, Caruso G, Cracco RQ, et al. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord and roots: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical application. Report of an IFCN committee. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1994; 91:79–92. PMID: 7519144.
Article21. Noohi F, Boyden NB, Kwak Y, Humfleet J, Burke DT, Muller ML, et al. Association of COMT val158met and DRD2 G>T genetic polymorphisms with individual differences in motor learning and performance in female young adults. J Neurophysiol. 2014; 111:628–640. PMID: 24225542.22. Wolf ME, Mangiavacchi S, Sun X. Mechanisms by which dopamine receptors may influence synaptic plasticity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003; 1003:241–249. PMID: 14684450.
Article23. Li XH, Wang JY, Gao G, Chang JY, Woodward DJ, Luo F. High-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus restores neural and behavioral functions during reaction time task in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Res. 2010; 88:1510–1521. PMID: 20025062.
Article24. Lindenberger U, Nagel IE, Chicherio C, Li SC, Heekeren HR, Backman L. Age-related decline in brain resources modulates genetic effects on cognitive functioning. Front Neurosci. 2008; 2:234–244. PMID: 19225597.25. Li SC, Sikstrom S. Integrative neurocomputational perspectives on cognitive aging, neuromodulation, and representation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2002; 26:795–808. PMID: 12470691.
Article26. Lang N, Speck S, Harms J, Rothkegel H, Paulus W, Sommer M. Dopaminergic potentiation of rTMS-induced motor cortex inhibition. Biol Psychiatry. 2008; 63:231–233. PMID: 17604004.
Article27. Cheeran BJ, Ritter C, Rothwell JC, Siebner HR. Mapping genetic influences on the corticospinal motor system in humans. Neuroscience. 2009; 164:156–163. PMID: 19409217.
Article28. Leenders KL, Antonini A, Thomann R, Locher JT, Maitre L, Gerebtzoff A, et al. Savoxepine: striatal dopamine-D2 receptor occupancy in human volunteers measured using positron emission tomography (PET). Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1993; 44:135–140. PMID: 8095895.
Article29. Erixon-Lindroth N, Farde L, Wahlin TB, Sovago J, Halldin C, Backman L. The role of the striatal dopamine transporter in cognitive aging. Psychiatry Res. 2005; 138:1–12. PMID: 15708296.
Article30. Kaasinen V, Vilkman H, Hietala J, Nagren K, Helenius H, Olsson H, et al. Age-related dopamine D2/D3 receptor loss in extrastriatal regions of the human brain. Neurobiol Aging. 2000; 21:683–688. PMID: 11016537.
Article31. Suhara T, Fukuda H, Inoue O, Itoh T, Suzuki K, Yamasaki T, et al. Age-related changes in human D1 dopamine receptors measured by positron emission tomography. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1991; 103:41–45. PMID: 1826059.
Article32. Backman L, Ginovart N, Dixon RA, Wahlin TB, Wahlin A, Halldin C, et al. Age-related cognitive deficits mediated by changes in the striatal dopamine system. Am J Psychiatry. 2000; 157:635–637. PMID: 10739428.33. Volkow ND, Gur RC, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Moberg PJ, Ding YS, et al. Association between decline in brain dopamine activity with age and cognitive and motor impairment in healthy individuals. Am J Psychiatry. 1998; 155:344–349. PMID: 9501743.34. Enoch MA, Waheed JF, Harris CR, Albaugh B, Goldman D. COMT Val158Met and cognition: main effects and interaction with educational attainment. Genes Brain Behav. 2009; 8:36–42. PMID: 19076243.
Article35. Hamada M, Murase N, Hasan A, Balaratnam M, Rothwell JC. The role of interneuron networks in driving human motor cortical plasticity. Cereb Cortex. 2013; 23:1593–1605. PMID: 22661405.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Impaired Set-Shifting Ability in Patients with Eating Disorders, Which Is Not Moderated by Their Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Val158Met Genotype
- The Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Val158Met Polymorphism Contributes to the Risk of Breast Cancer in the Chinese Population: An Updated Meta-Analysis
- Association Study of Val158Met Polymorphism of Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Gene and Cognitive Markers in Schizophrenia
- An Association Study of the 5-HTTLPR and COMT Genes Polymorphisms and Personality Traits
- An Association Study of COMT Gene Polymorphism with Korean Alcoholism