Ann Dermatol.
2013 Feb;25(1):126-128. 10.5021/ad.2013.25.1.126.
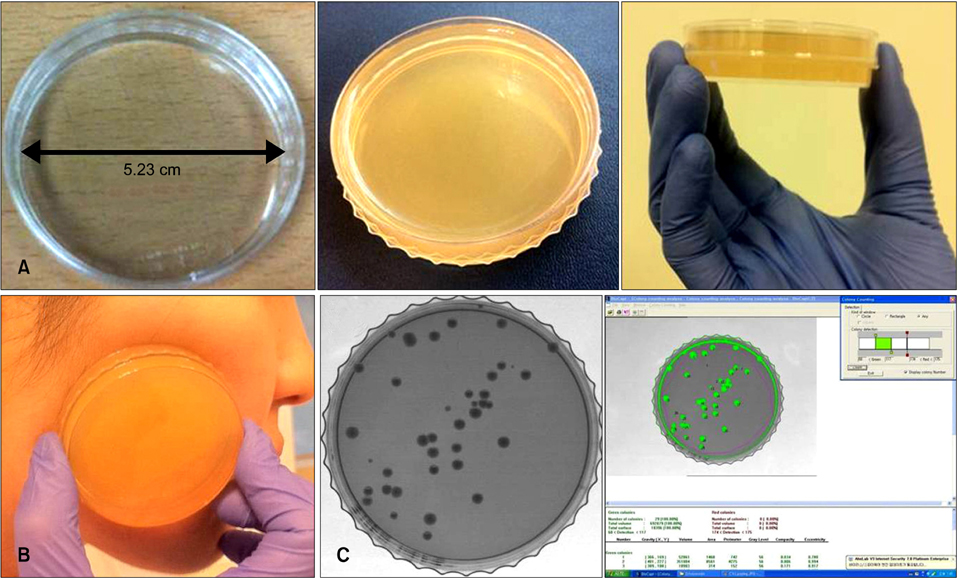
Stamp-Form Contact Plate: A Simple and Useful Culture Method for Microorganisms of the Skin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. gcpark@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2265992
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.1.126
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bunikowski R, Mielke ME, Skarabis H, Worm M, Anagnostopoulos I, Kolde G, et al. Evidence for a disease-promoting effect of Staphylococcus aureus-derived exotoxins in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 105:814–819.
Article2. Keyworth N, Millar MR, Holland KT. Swab-wash method for quantitation of cutaneous microflora. J Clin Microbiol. 1990. 28:941–943.
Article3. Evans CA, Stevens RJ. Differential quantitation of surface and subsurface bacteria of normal skin by the combined use of the cotton swab and the scrub methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1976. 3:576–581.
Article4. Lee DK, Cho MK, Son SJ, Jeong BK, Kim DJ. Bacterial culture using tape method in atopic dermatitis and non-atopic dermatitis. Korean J Dermatol. 2001. 39:292–299.5. Sung HC, Jung HD, Park KD, Lee WJ, Lee SJ, Kim DW. A quantitative culture study of staphylococcus aureus in adolescent and adult patients with atopic dermatitis using the contact-plate sampling technique. Korean J Dermatol. 2007. 45:673–679.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Quantitative Culture Study of Staphylococcus aureus in Adolescent and Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis using the Contact-plate Sampling Technique
- Clinical Significance of Nocturnal Penile Tumescence Monitoring with Stamps
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis Associated with Orthopedic Implants
- A Study on the Contamination of Saline Used in the Operation
- Microbial Contamination of Contact Lens Storage Cases in Contact Lens-induced Keratitis Patients