Ann Dermatol.
2014 Dec;26(6):769-771. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.6.769.
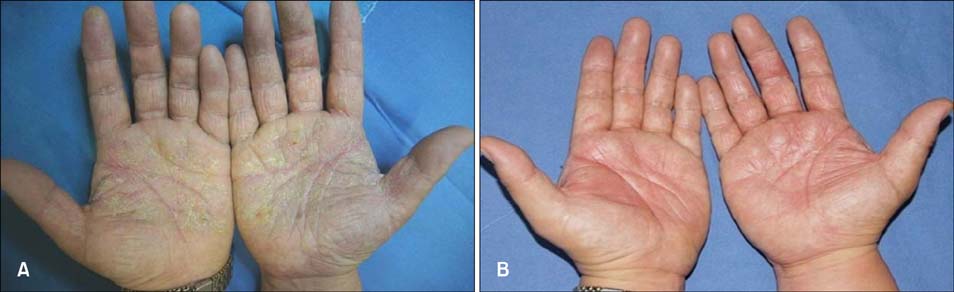
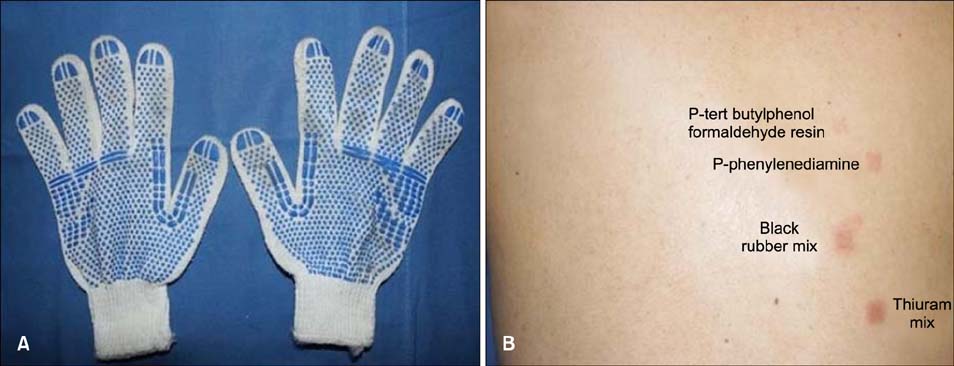
Hyperkeratotic Hand Eczema due to Use of Rubber Gloves While Driving
- Affiliations
-
- 1Deparment of Dermatology, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hyeonekim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2264881
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.6.769
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Diepgen TL, Andersen KE, Brandao FM, Bruze M, Bruynzeel DP, Frosch P, et al. Hand eczema classification: a cross-sectional, multicentre study of the aetiology and morphology of hand eczema. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 160:353–358.
Article2. Warshaw EM. Therapeutic options for chronic hand dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004; 17:240–250.
Article3. Li L, Wang J. Contact hypersensitivity in hand dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2002; 47:206–209.
Article4. Shah D, Chowdhury MM. Rubber allergy. Clin Dermatol. 2011; 29:278–286.
Article5. Ozkaya E, Elinç-Aslan MS. Black rubber sensitization by bicycle handgrips in a child with palmar hyperhidrosis. Dermatitis. 2011; 22:E10–E12.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Contact Urticaria from a Latex Glove Occurred to an Operationg Room Nurse
- A Case of Allergic Contact Dermatitis Due to Rubber Glove and Cement
- Simple Molding Method for Post-distant Flap Stated Finger by Using Surgical Rubber Gloves
- A Study of the Latex Allergy in Operating Room Nurses
- Review on Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Research Advancements on the Use of Medical Gloves Concerning Hand Dermatitis Among Health Care Workers