Predictors of the Severity and Serious Outcomes of Anaphylaxis in Korean Adults: A Multicenter Retrospective Case Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 6Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 7Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 8Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 9Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 10Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 11Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 13Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 15Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Dong-A University, College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2260148
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.1.22
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Differences in definitions of the condition, relevant triggers, and the geographical locations of study centers, cause estimates of the prevalence of anaphylaxis to vary. Recent epidemiological data indicate that the incidence of anaphylaxis is rising.
METHODS
To investigate the causes and clinical features of anaphylaxis in Korean adults, factors associated with the severity of the condition, and serious outcomes, a retrospective medical record review was performed on adult patients diagnosed with anaphylaxis between 2007 and 2011 in 15 University Hospitals of South Korea.
RESULTS
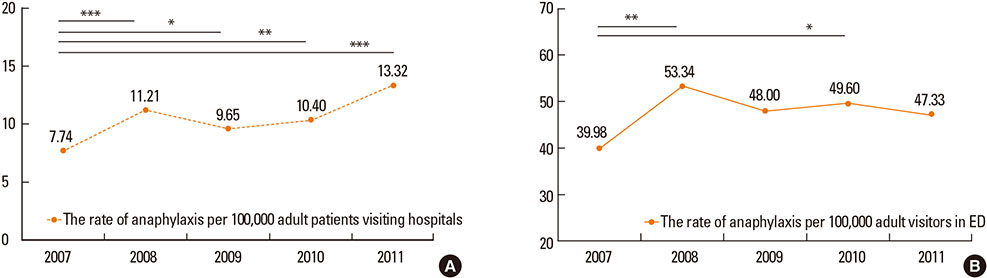
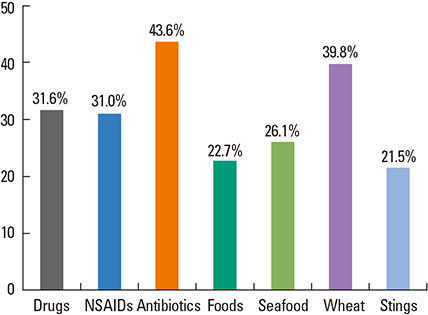
A total of 1,806 cases (52% male, age 16-86 years) were reported. Cutaneous symptoms (84.0%), combined with respiratory (53.9%) and/or cardiovascular (55.4%) symptoms, were the most frequent presentations. Using a recognized grading system, 1,776 cases could be classified as either mild, 340; moderate, 690; or severe, 746. Although eliciting factors varied significantly by age, gender, and regional and seasonal factors, drugs (46.5%; including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and radiocontrast media) were the most common cause of anaphylaxis, followed by foods (24.2%), insect stings (16.4%), exercise (5.9%), and unknown etiology (7.0%). All of age, multi-organ involvement, a history of allergic disease, and drug-induced anaphylaxis, were significant predictors of serious outcomes requiring hospital admission or prolongation of hospital stay. Epinephrine auto-injectors were prescribed for 7.4% of reported cases.
CONCLUSIONS
The principal causes of anaphylaxis in Korean adults were drugs, food, and insect stings. Drug-associated anaphylaxis, a history of allergic disease, multi-organ involvement, and older age, were identified as predictors of serious outcomes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 13 articles
-
Seasonal and regional variations in the causes of anaphylaxis in Korean adults
Yeon-Kyung Lee, Mi Kyeong Kim, Hye-Ryun Kang, Tae-Bum Kim, Seong-Wook Sohn, Hye-Kyung Park, Young-Il Koh, Gwang Cheon Jang, Cheol-Woo Kim, Young-Koo Jee, Gyu-Young Hur, Joo-Hee Kim, Sang-Heon Kim, Gil-Soon Choi, Soo-Keol Lee, Hae-Sim Park, Young-Min Ye,
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(3):187-193. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.3.187.Favorable outcome of omalizumab treatment in a patient with idiopathic anaphylaxis
Ga-Young Ban, Eun-Mi Yang, Ji-Hye Kim, Yoo-Seob Shin, Young-Min Ye, Dong-Ho Nahm, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(5):380-383. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.5.380.Anaphylaxis following mushrooms ingestion
Dae-Hong Seo, Young-Soo Lee, Ga-Young Ban, Moon-Gyung Yoon, Ji-Hye Kim, Yoo-Seob Shin, Hae-Sim Park, Young-Min Ye
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(1):82-85. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.1.82.A single hospital survey of anaphylaxis awareness among health care providers and medical students
Dae-Hong Seo, Young-Min Ye, Su-Chin Kim, Ga-Young Ban, Ji-Hye Kim, Yoo-Seob Shin, Hae-Sim Park, Soo-Young Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(2):133-139. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.133.Acute urticaria with angioedema following sea hare ingestion
Jin-Soo Park, Ji-Hye Kim, Moon-Gyung Yoon, Jung-Eun Kim, Yoo Seob Shin
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(1):61-64. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.1.61.Anaphylaxis: diagnosis, management, and current barriers
Hyun Jung Jin
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(2):79-81. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.2.79.The past, present, and future of the research on food allergy in Korean children
Kangmo Ahn
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S44-S51. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S44.Drug-induced anaphylaxis: Analysis of the Pharmacovigilance Database
Sujeong Kim, Han-Ki Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2020;8(1):1-2. doi: 10.4168/aard.2020.8.1.1.Analysis of individual case safety reports of drug-induced anaphylaxis to the Korea Adverse Event Reporting System
Min Kyoung Cho, Mira Moon, Hyun Hwa Kim, Dong Yoon Kang, Ju-Yeun Lee, Sang-Heon Cho, Hye-Ryun Kang
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2020;8(1):30-35. doi: 10.4168/aard.2020.8.1.30.Are Registration of Disease Codes for Adult Anaphylaxis Accurate in the Emergency Department?
Byungho Choi, Sun Hyu Kim, Hyeji Lee
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(2):137-143. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.2.137.Electronic Consultation Support System for Radiocontrast Media Hypersensitivity Changes Clinicians' Behavior
Min-Suk Yang, Sang-Il Choi, Woo-Jung Song, Sae-Hoon Kim, Sang-Heon Cho, Kyung-Up Min, Jae-Hyoung Kim, Yoon-Seok Chang
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(2):165-171. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.2.165.Accuracy for registration of disease codes in pediatric anaphylaxis
Yeon Joo Cho, Sun Hyu Kim, Hyeji Lee, Byungho Choi, Mi Jin Kim, Jung Seok Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(3):159-164. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.3.159.Epidemiology of food allergy in Korean children
Taek Ki Min, Bok Yang Pyun, Hyun Hee Kim, Yong-Mean Park, Gwang Cheon Jang, Hye-Young Kim, Hye Yung Yum, Jihyun Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Sooyoung Lee, Kyung Won Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Jeong-Min Lee, Woo Kyung Kim, Tae Won Song, Jeong Hee Kim, Yong Ju Lee, You Hoon Jeon, So-Yeon Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(1):4-13. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.1.4.
Reference
-
1. Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, Motala C, Ortega Martell JA, Platts-Mills TA, Ring J, Thien F, Van Cauwenberge P, Williams HC. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:832–836.2. Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilò MB, El-Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, Sanchez-Borges M, Senna GE, Sheikh A, Thong BY. World Allergy Organization. World allergy organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011; 4:13–37.3. Ben-Shoshan M, Clarke AE. Anaphylaxis: past, present and future. Allergy. 2011; 66:1–14.4. Jung JW, Jeon EJ, Kim JW, Choi JC, Shin JW, Kim JY, Park IW, Choi BW. A fatal case of intravascular coagulation after bee sting acupuncture. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:107–109.5. Kim S, Yoon SY, Park SY, Kwon HS, Cho YS, Moon HB, Kim TB. A case of idiopathic anaphylaxis followed by acute liver injury. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:245–247.6. Wood RA, Camargo CA Jr, Lieberman P, Sampson HA, Schwartz LB, Zitt M, Collins C, Tringale M, Wilkinson M, Boyle J, Simons FE. Anaphylaxis in America: The prevalence and characteristics of anaphylaxis in the United States. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:461–467.7. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim TW, Kwon JW, Lee SM, Kim SH, Kwon HS, Park CH, Park HW, Kim SS, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY, Chang YS. Epidemiologic and clinical features of anaphylaxis in Korea. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:31–36.8. Techapornroong M, Akrawinthawong K, Cheungpasitporn W, Ruxrungtham K. Anaphylaxis: a ten years inpatient retrospective study. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2010; 28:262–269.9. Kim MJ, Choi GS, Um SJ, Sung JM, Shin YS, Park HJ, Ye YM, Nahm DH, Lee SY, Park HS. Anaphylaxis; 10 years' experience at a university hospital in Suwon. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 28:298–304.10. Park HJ, Kim SH. Factors associated with shock in anaphylaxis. Am J Emerg Med. 2012; 30:1674–1678.11. Brown SG. Clinical features and severity grading of anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:371–376.12. Son CK, Do SR, Jang YS, Kim EJ, Shin ES, Jin JH. 2011 patient survey in Korea. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2012.13. Cetinkaya F, Incioglu A, Birinci S, Karaman BE, Dokucu AI, Sheikh A. Hospital admissions for anaphylaxis in Istanbul, Turkey. Allergy. 2013; 68:128–130.14. Hsin YC, Hsin YC, Huang JL, Yeh KW. Clinical features of adult and pediatric anaphylaxis in Taiwan. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2011; 29:307–312.15. Park M, Kim D, Ahn K, Kim J, Han Y. Prevalence of immediate-type food allergy in early childhood in seoul. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:131–136.16. Wong GW, Leung TF, Ko FW. Changing prevalence of allergic diseases in the Asia-pacific region. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:251–257.17. Lertnawapan R, Maek-a-nantawat W. Anaphylaxis and biphasic phase in Thailand: 4-year observation. Allergol Int. 2011; 60:283–289.18. Decker WW, Campbell RL, Manivannan V, Luke A, St Sauver JL, Weaver A, Bellolio MF, Bergstralh EJ, Stead LG, Li JT. The etiology and incidence of anaphylaxis in Rochester, Minnesota: a report from the Rochester Epidemiology Project. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:1161–1165.19. Koplin JJ, Martin PE, Allen KJ. An update on epidemiology of anaphylaxis in children and adults. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 11:492–496.20. Worm M, Edenharter G, Ruëff F, Scherer K, Pföhler C, Mahler V, Treudler R, Lang R, Nemat K, Koehli A, Niggemann B, Hompes S. Symptom profile and risk factors of anaphylaxis in Central Europe. Allergy. 2012; 67:691–698.21. Gelincik A, Demirtürk M, Yılmaz E, Ertek B, Erdogdu D, Çolakoğlu B, Büyüköztürk S. Anaphylaxis in a tertiary adult allergy clinic: a retrospective review of 516 patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 110:96–100.22. Tang ML, Osborne N, Allen K. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:351–356.23. Lim DH. Epidemiology of anaphylaxis in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:351–354.24. Steele R, Camacho-Halili M, Rosenthal B, Davis-Lorton M, Aquino M, Fonacier L. Anaphylaxis in the community setting: determining risk factors for admission. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012; 109:133–136.25. Sheikh A, Alves B. Age, sex, geographical and socio-economic variations in admissions for anaphylaxis: analysis of four years of English hospital data. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:1571–1576.26. Mulla ZD, Simon MR. Hospitalizations for anaphylaxis in Florida: epidemiologic analysis of a population-based dataset. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007; 144:128–136.27. Liew WK, Williamson E, Tang ML. Anaphylaxis fatalities and admissions in Australia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:434–442.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The past, present, and future of research on anaphylaxis in Korean children
- Predictors of Anaphylaxis in Korean Adults
- Clinical Features of Patients with Anaphylaxis at a Single Hospital
- Clinical Features of Adult Patients with Anaphylaxis Associated with Food in Gwangju and Chonnam Area
- A Case of Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis