Korean J Hematol.
2005 Mar;40(1):54-57. 10.5045/kjh.2005.40.1.54.
A Case of Serum Amino Acid Disturbance with Hyperammonemia in Patient with Primary Amyloidosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hemakim@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, National Health Insurance Cooperation, Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2252368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2005.40.1.54
Abstract
- There have been reports that hyperammonemia and amino acid disturbance can cause loss of consciousness in patients with multiple myelomas and normal liver function. We experienced a case of a 71-years-old female patient with amyloidosis, who had shown disturbance of consciousness. At that time, the serum ammonia level was elevated; serum amino acids disturbance was also noted. In particular, the decrease in branched-chain amino acids and increase in aromatic amino acids results in a low Fisher ratio. The Fisher ratio, the ratio of branched-chain to aromatic amino acids, has been suggested as an important indicator of consciousness disturbance. We report, for the first time in Korea, a case of amyloidosis, with mental disturbance due to serum amino acid disturbance.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
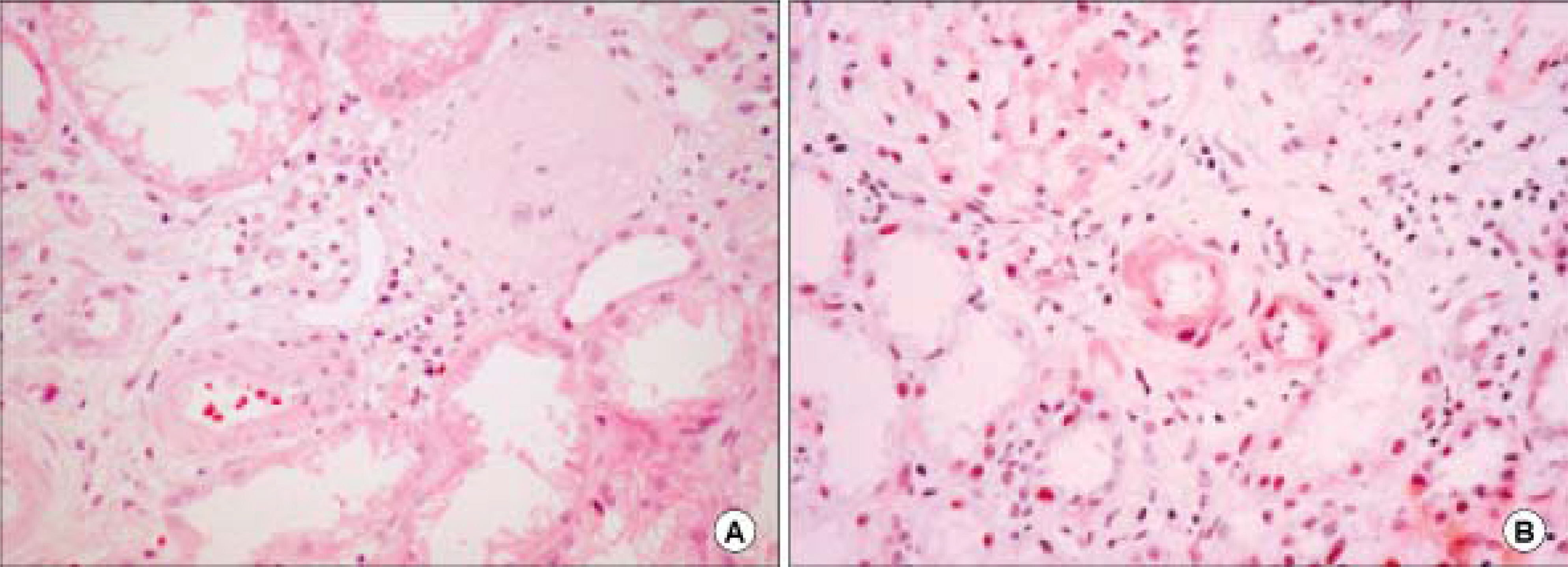
Figure
Reference
-
1). Falk RH, Comenzo RL, Skinner M. The systemic amyloidoses. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:898–909.
Article2). Lee JH, Ko YW, Maeng HY, et al. A case of serum amino acid disturbance with hyperammonemia in a patient with multiple myeloma. Korean J Hematol. 2002; 37:84–7.3). Seo YM, Eom HS, Kim JK, et al. A case of hyperammonemic encephalopathy with serum amino acid alteration in multiple myeloma. Korean J Hematol. 2003; 38:64–7.4). Matsuzaki H, Hata H, Sonoki T, et al. Serum amino acid disturbance in multiple myeloma with hyperammonemia. Int J Hematol. 2006. 131–7.5). Matsuzaki H, Uchiba M, Yoshimura K, et al. Hyperammonemia in multiple myeloma. Acta Haematol. 1990; 84:130–4.
Article6). Fujii S, Fukuda S, Sezaki T, Murakami M. Clinicopathological study of multiple myeloma associated with hyperammonemia. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1998; 39:27–33.7). Watson AJ, Chambers T, Karp JE, Risch VR, Walker WG, Brusilow SW. Transient idiopathic hyperammo-naemia in adults. Lancet. 1985; 2:1271–4.
Article8). Takimoto Y, Imanaka F, Hayashi Y, Morioka S. A patient with ammonia-producing multiple myeloma showing hyperammonemic encephalopathy. Leukemia. 1996; 10:918–9.9). Kwan L, Wang C, Levitt L. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:1674–5.
Article10). Holahan JR. Hyperammonemia: elevated ammonia levels in multiple myeloma. Am J Med. 2004; 116:210–1.
Article11). Weng TI, Shih FF, Chen WJ. Unusual causes of hyperammonemia in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. 2004; 22:105–7.
Article12). Tsunoda S, Sasaki R, Miwa A, Sakurabayashi I, Miura Y. Coma, hyperviscosity syndrome, hyperammonemia and myelofibrosis in a patient with IgG, lambda type multiple myeloma. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1989; 30:361–5.13). Caminal L, Castellanos E, Mateos V, Astudillo A, Moreno C, Dieguez MA. Hyperammonaemic encephalopathy as the presenting feature of IgD multiple myeloma. J Intern Med. 1993; 233:277–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Serum Amino Acid Disturbance with Hyperammonemia in a Patient with Multiple Myeloma
- Hyperammonemia in a Patient with Late-Onset Ornithine Carbamoyltransferase Deficiency
- A Case of Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy with Serum Amino Acid Alteration in Multiple Myeloma
- CT and MR Imaging in 3 Patients with Hyperammonemia Due to Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency
- Primary localized amyloidosis of the bladder: a case report