Korean J Hematol.
2011 Mar;46(1):36-40. 10.5045/kjh.2011.46.1.36.
Characterization of antiphospholipid antibodies in chronic hepatitis B infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea. jiyoungh@cha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, CHA Kangnam Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2252017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2011.46.1.36
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Many infections are associated with antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs). The purpose of this study was to investigate the prevalence, persistence, clinical significance, and characteristics of aPLs in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected patients.
METHODS
This study included 143 patients with HBV infection and 32 healthy individuals as controls. The presence of anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL Ab), anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies (beta2GPI Ab), and lupus anticoagulant (LA) was assessed.
RESULTS
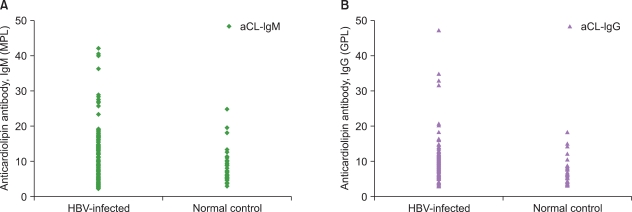
The total prevalence of aPLs in HBV-infected patients was 12.6% (18 of 143). Of these 18 patients, 15 had low to medium titers of aCL Ab (10 with IgM, 4 with IgG, and 1 with both isotypes). beta2GPI Ab and LA were detected in 3 (2.1%) and 2 (1.4%) patients with HBV infection, respectively. In follow-up specimens from 14 patients with elevated levels of aCL Ab or beta2GPI Ab, 10 (71.4%) showed the persistent presence of aPLs. No clinical manifestations related to aPLs were identified.
CONCLUSION
In HBV-infected patients, the most frequently detected antiphospholipid antibodies were IgM aCL Ab, which have a weak association with the clinical manifestations of APS. Unlike the transient presence reported for other infection-associated aPLs, most aPLs were persistently detected over a 12-week period in patients with HBV infection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antibodies
Antibodies, Anticardiolipin
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Follow-Up Studies
Hepatitis B virus
Hepatitis B, Chronic
Hepatitis, Chronic
Humans
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin M
Lupus Coagulation Inhibitor
Prevalence
Antibodies
Antibodies, Anticardiolipin
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulin M
Lupus Coagulation Inhibitor
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levine JS, Branch DW, Rauch J. The antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:752–763. PMID: 11882732.
Article2. Tarr T, Lakos G, Bhattoa HP, et al. Clinical thrombotic manifestations in SLE patients with and without antiphospholipid antibodies: a 5-year follow-up. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007; 32:131–137. PMID: 17916982.
Article3. Giannakopoulos B, Passam F, Rahgozar S, Krilis SA. Current concepts on the pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood. 2007; 109:422–430. PMID: 16985176.
Article4. Vega-Ostertag ME, Pierangeli SS. Mechanisms of aPL-mediated thrombosis: effects of aPL on endothelium and platelets. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2007; 9:190–197. PMID: 17531171.
Article5. Cervera R, Asherson RA. Antiphospholipid syndrome associated with infections: clinical and microbiological characteristics. Immunobiology. 2005; 210:735–741. PMID: 16325491.
Article6. Avcin T, Toplak N. Antiphospholipid antibodies in response to infection. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2007; 9:212–218. PMID: 17531174.
Article7. Sorice M, Pittoni V, Griggi T, et al. Specificity of anti-phospholipid antibodies in infectious mononucleosis: a role for anti-cofactor protein antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000; 120:301–306. PMID: 10792380.
Article8. Sène D, Piette JC, Cacoub P. Antiphospholipid antibodies, antiphospholipid syndrome and infections. Autoimmun Rev. 2008; 7:272–277. PMID: 18295729.
Article9. Bloom EJ, Abrams DI, Rodgers G. Lupus anticoagulant in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1986; 256:491–493. PMID: 3088292.
Article10. Blank M, Shoenfeld Y. Beta-2-glycoprotein-I, infections, antiphospholipid syndrome and therapeutic considerations. Clin Immunol. 2004; 112:190–199. PMID: 15240163.
Article11. Romero Gómez M, García ES, Lacomba DL, Marchante I, Grande L, Fernandez MC. Antiphospholipid antibodies are related to portal vein thrombosis in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000; 31:237–240. PMID: 11034005.12. Kida Y, Maeshima E, Yamada Y. Portal vein thrombosis in a patient with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis complicated with antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatol Int. 2009; 29:1495–1498. PMID: 19184031.
Article13. Ramos-Casals M, Cervera R, Lagrutta M, et al. Clinical features related to antiphospholipid syndrome in patients with chronic viral infections (hepatitis C virus/HIV infection): description of 82 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 38:1009–1016. PMID: 15034835.
Article14. Guglielmone H, Vitozzi S, Elbarcha O, Fernandez E. Cofactor dependence and isotype distribution of anticardiolipin antibodies in viral infections. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60:500–504. PMID: 11302873.
Article15. Ordi-Ros J, Villarreal J, Monegal F, Sauleda S, Esteban I, Vilardell M. Anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: characterization in relation to antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2000; 7:241–244. PMID: 10702499.
Article16. Harada M, Fujisawa Y, Sakisaka S, et al. High prevalence of anticardiolipin antibodies in hepatitis C virus infection: lack of effects on thrombocytopenia and thrombotic complications. J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:272–277. PMID: 10777156.
Article17. Zachou K, Liaskos C, Christodoulou DK, et al. Anti-cardiolipin antibodies in patients with chronic viral hepatitis are independent of beta2-glycoprotein I cofactor or features of antiphospholipid syndrome. Eur J Clin Invest. 2003; 33:161–168. PMID: 12588291.
Article18. Lee KS, Kim DJ. Management of Chronic Hepatitis B. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:447–488. PMID: 19054901.
Article19. Brandt JT, Triplett DA, Alving B, Scharrer I. Criteria for the diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants: an update. On behalf of the Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibody of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the ISTH. Thromb Haemost. 1995; 74:1185–1190. PMID: 8560433.20. Harel M, Aron-Maor A, Sherer Y, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y. The infectious etiology of the antiphospholipid syndrome: links between infection and autoimmunity. Immunobiology. 2005; 210:743–747. PMID: 16325492.
Article21. Amin NM. Antiphospholipid syndromes in infectious diseases. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2008; 22:131–143. PMID: 18207071.
Article22. Devreese K, Hoylaerts MF. Laboratory diagnosis of the antiphospholipid syndrome: a plethora of obstacles to overcome. Eur J Haematol. 2009; 83:1–16. PMID: 19226362.
Article23. Elefsiniotis IS, Diamantis ID, Dourakis SP, Kafiri G, Pantazis K, Mavrogiannis C. Anticardiolipin antibodies in chronic hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis D infection, and hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Relationship with portal vein thrombosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 15:721–726. PMID: 12811301.
Article24. Uthman IW, Gharavi AE. Viral infections and antiphospholipid antibodies. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 31:256–263. PMID: 11836658.
Article25. Dalekos GN, Zachou K, Liaskos C. The antiphospholipid syndrome and infection. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2001; 3:277–285. PMID: 11470045.
Article26. Alric L, Oskman F, Sanmarco M, et al. Association of antiphospholipid syndrome and chronic hepatitis C. Br J Rheumatol. 1998; 37:589–590. PMID: 9651099.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome associated with Chronic Hepatitis C
- Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome
- Brachial Artery Thrombosis in an 8-year-old Boy with Antiphospholipid Antibodies Induced by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection: a Case Report
- A Case of Mesenteric Thrombosis and Partal Hypertension Associated with Antiphospholipid in a Patient with Hepatitis C
- Successful Live Birth of Woman with Antiphospholipid Syndrome