Korean J Leg Med.
2012 May;36(1):74-84. 10.7580/KoreanJLegMed.2012.36.1.74.
DNA-Based Identification of Necrophagous Fly Species Using Abdominal-B (Abd-B) Homeobox Sequence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Forensic Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jjhwang411@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2250322
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/KoreanJLegMed.2012.36.1.74
Abstract
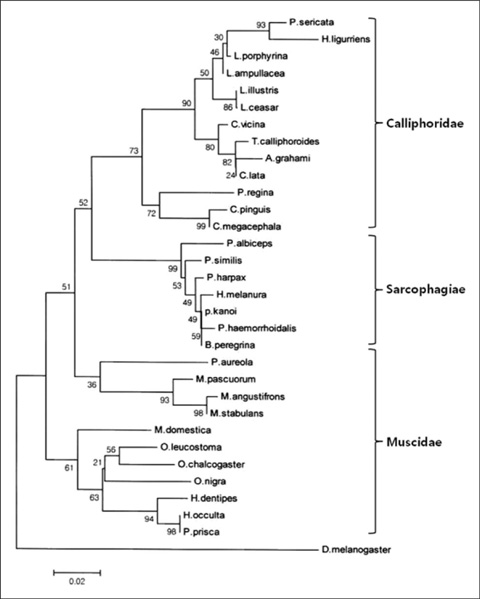
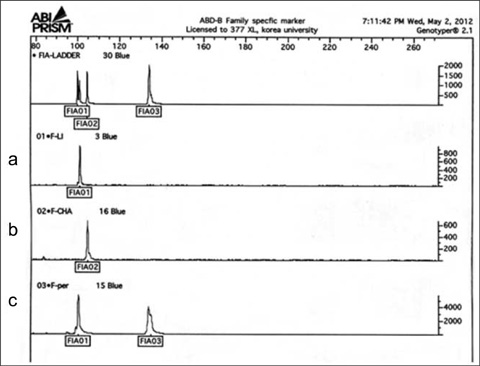
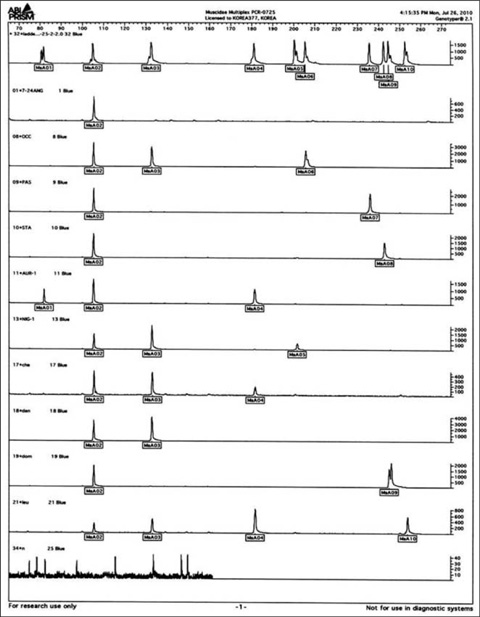
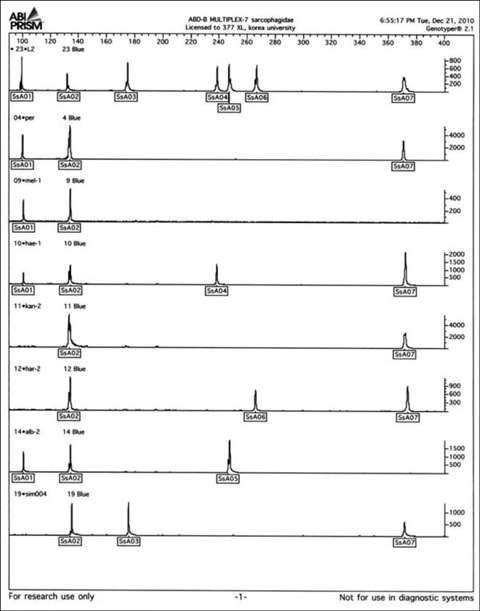
- In medicolegal investigations, correct identification of the necrophagous fly species collected around and on the corpse is an essential step for estimating the postmortem interval (PMI). Therefore, forensic pathologists and entomologists investigating deaths due to violent crimes need a rapid, easy-to-use protocol to identify fly species found on corpses. A rapid and robust DNA-based tool that can distinguish between various immature and mature species from the Calliphoridae, Muscidae, and Sarcophagidae families would be ideal for such investigations. To date, the DNA barcode initiative is the best approach for identifying species-specific nucleotide sequences. We have developed 3 sequence-characterized amplified region (SCAR)-based identification systems derived from the Abdominal-B homeobox sequences of 17 fly species belonging to the Muscidae and Sarcophagidae. The flies used in this study were collected in Korea. These assay systems can classify 17 forensically important fly species into the dipteran family group and reliably distinguish them from inter- and intraspecific fly species through a 2-step multiplex PCR. This novel approach may also be used as an alternative to conventional DNA-based identification methods.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Benecke M. Six forensic entomology cases: description and commentary. J Forensic Sci. 1998. 43:797–805.2. Sukontason KL, Ngern-Klun R, Sripakdee D, Sukontason K. Identifying fly puparia by clearing technique: application to forensic entomology. Parasitol Res. 2007. 101:1407–1416.3. Mendonca PM, dos Santos-Mallet JR, de Mello RP, Gomes L, de Carvalho Queiroz MM. Identification of fly eggs using scanning electron microscopy for forensic investigations. Micron. 2008. 39:802–807.4. Sperling FA, Anderson GS, Hickey DA. DNA-based approach to the identification of insect species used for postmortem interval estimation. J Forensic Sci. 1994. 39:418–427.5. Wells JD, Sperling FA. A DNA-based approach to the identification of insect species used for postmortem interval estimation and partial sequencing of the cytochrome oxydase b subunit gene I: a tool for the identification of European species of blow flies for postmortem interval estimation. J Forensic Sci. 2000. 45:1358–1359.6. Harvey ML, Dadour IR, Gaudieri S. Mitochondrial DNA cytochrome oxidase I gene: potential for distinction between immature stages of some forensically important fly species (Diptera) in western Australia. Forensic Sci Int. 2003. 131:134–139.7. Chen WY, Hung TH, Shiao SF. Molecular identification of forensically important blow fly species (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Taiwan. J Med Entomol. 2004. 41:47–57.8. Park SH, Zhang Y, Piao H, et al. Sequences of the cytochrome C oxidase subunit I (COI) gene are suitable for species identification of Korean Calliphorinae flies of forensic importance (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J Forensic Sci. 2009. 54:1131–1134.9. Harvey ML, Gaudieri S, Villet MH, Dadour IR. A global study of forensically significant calliphorids: implications for identification. Forensic Sci Int. 2008. 177:66–76.10. Maddison WP, Knowles LL. Inferring phylogeny despite incomplete lineage sorting. Syst Biol. 2006. 55:21–30.11. Song Z, Wang X, Liang G. Species identification of some common necrophagous flies in Guangdong province, southern China based on the rDNA internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2). Forensic Sci Int. 2008. 175:17–22.12. Nelson LA, Wallman JF, Dowton M. Identification of forensically important Chrysomya (Diptera: Calliphoridae) species using the second ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS2). Forensic Sci Int. 2008. 177:238–247.13. Akam M. Hox and HOM: homologous gene clusters in insects and vertebrates. Cell. 1989. 57:347–349.14. Dhawan S, Gopinathan KP. Phylogeny of the insect homeobox gene (hox) cluster. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2005. 3:42–46.15. Lamka ML, Boulet AM, Sakonju S. Ectopic expression of UBX and ABD-B proteins during Drosophila embryogenesis: competition, not a functional hierarchy, explains phenotypic suppression. Development. 1992. 116:841–854.16. Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007. 24:1596–1599.17. Kalendar R, Lee D, Schulman AH. FastPCR Software for PCR Primer and Probe Design and Repeat Search. Genes, Genomes and Genomics. 2009. 3:1–14.18. Guarnera EA, Mariluis JC. Human case of disseminated cutaneous myiasis due to Phaenicia sericata. Bol Chil Parasitol. 1986. 41:79–82.19. Debry RW, Timm AE, Dahlem GA, Stamper T. mtDNA-based identification of Lucilia cuprina (Wiedemann) and Lucilia sericata (Meigen) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in the continental United States. Forensic Sci Int. 2010. 202:102–109.20. Vanin S, Tasinato P, Ducolin G, et al. Use of Lucilia species for forensic investigations in Southern Europe. Forensic Sci Int. 2008. 177:37–41.21. Wells JD, Wall R, Stevens JR. Phylogenetic analysis of forensically important Lucilia flies based on cytochrome oxidase I sequence: a cautionary tale for forensic species determination. Int J Legal Med. 2007. 121:229–233.22. Stevens J, Wall R. Species, sub-species and hybrid populations of the blowflies Lucilia cuprina and Lucilia sericata (Diptera:Calliphoridae). Proc Biol Sci. 1996. 263:1335–1341.23. Kethidi DR, Roden DB, Ladd TR, Krell PJ, Retnakaran A, Feng Q. Development of SCAR markers for the DNAbased detection of the Asian long-horned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2003. 52:193–204.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- DNA-based Identification of Forensically Important Blow Fly Species in Korea; Aldrichina grahami, Calliphora lata, Calliphora vicina and Phormia regina
- Comparison of Mitochondrial Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit I (CO I) Sequences of Five Blow Fly Species in Korea
- Molecular Identification of Six Necrophagous Fly Species (Family: Muscidae) by Mitochondrial Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit I
- Identification Blow Fly Species in Korea by Mitochondrial DNA 'Barcodes'
- A Literature Review on the Growth Rate Experiment for Necrophagous Fly Species Commonly Observed in Korea and Consideration for Minimum Postmortem Interval Estimation