Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2016 Feb;20(1):17-22. 10.14701/kjhbps.2016.20.1.17.
Mirizzi's syndrome: lessons learnt from 169 patients at a single center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgical Gastroenterology, Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India. doc.ashokgupta@gmail.com
- KMID: 2243027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/kjhbps.2016.20.1.17
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
Mirizzi's syndrome (MS) poses great diagnostic and management challenge to the treating physician. We presented our experience of MS cases with respect to clinical presentation, diagnostic difficulties, surgical procedures and outcome.
METHODS
Prospectively maintained data of all surgically treated MS patients were analyzed.
RESULTS
A total of 169 MS patients were surgically managed between 1989 and 2011. Presenting symptoms were jaundice (84%), pain (75%) and cholangitis (56%). Median symptom duration s was 8 months (range, <1 to 240 months). Preoperative diagnosis was possible only in 32% (54/169) of patients based on imaging study. Csendes Type II was the most common diagnosis (57%). Fistulization to the surrounding organs (bilio-enteric fistulization) were found in 14% of patients (24/169) during surgery. Gall bladder histopathology revealed xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis in 33% of patients (55/169). No significant difference in perioperative morbidity was found between choledochoplasty (use of gallbladder patch) (15/89, 17%) and bilio-enteric anastomosis (4/28, 14%) (p=0.748). Bile leak was more common with choledochoplasty (5/89, 5.6%) than bilio-enteric anastomosis (1/28, 3.5%), without statistical significance (p=0.669).
CONCLUSIONS
Preoperative diagnosis of MS was possible in only one-third of patients in our series. Significant number of patients had associated fistulae to the surrounding organs, making the surgical procedure more complicated. Awareness of this entity is important for intraoperative diagnosis and consequently, for optimal surgical strategy and good outcome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
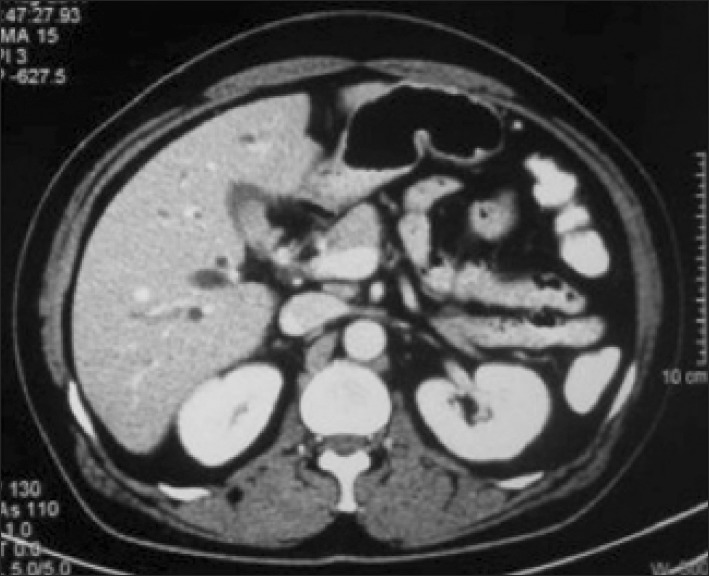
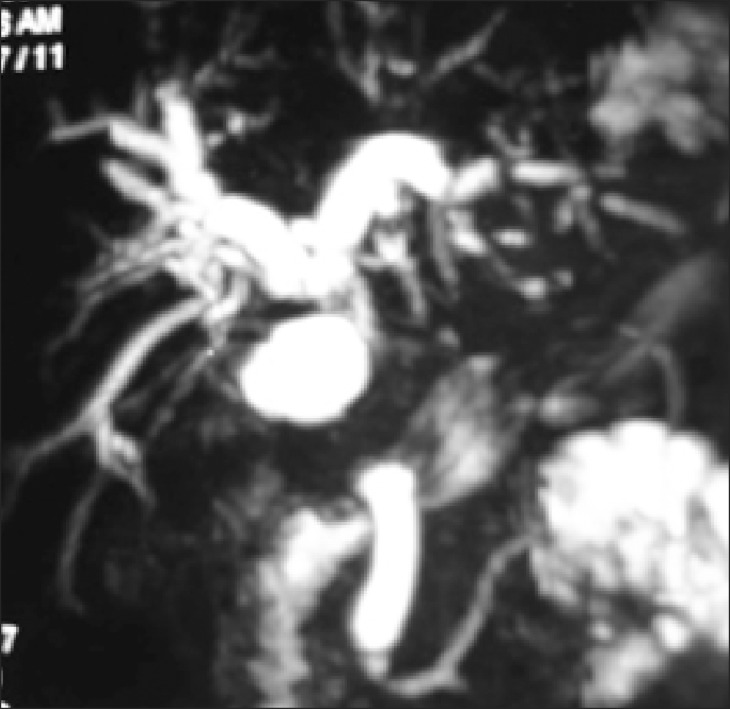
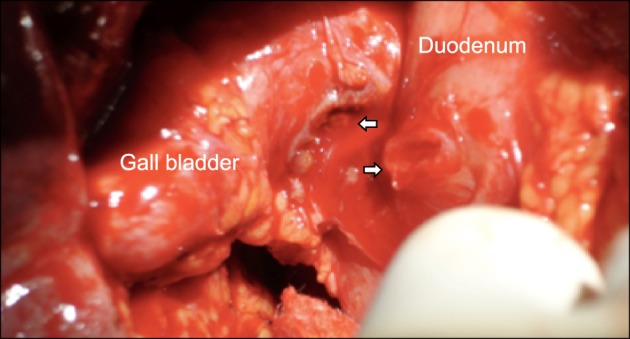
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pemberton M, Wells AD. The Mirizzi syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 1997; 73:487–490. PMID: 9307740.
Article2. Csendes A, Díaz JC, Burdiles P, Maluenda F, Nava O. Mirizzi syndrome and cholecystobiliary fistula: a unifying classification. Br J Surg. 1989; 76:1139–1143. PMID: 2597969.
Article3. Redaelli CA, Büchler MW, Schilling MK, Krähenbühl L, Ruchti C, Blumgart LH, et al. High coincidence of Mirizzi syndrome and gallbladder carcinoma. Surgery. 1997; 121:58–63. PMID: 9001552.
Article4. Prasad TL, Kumar A, Sikora SS, Saxena R, Kapoor VK. Mirizzi syndrome and gallbladder cancer. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006; 13:323–326. PMID: 16858544.
Article5. Beltran MA, Csendes A, Cruces KS. The relationship of Mirizzi syndrome and cholecystoenteric fistula: validation of a modified classification. World J Surg. 2008; 32:2237–2243. PMID: 18587614.
Article6. Tan KY, Chng HC, Chen CY, Tan SM, Poh BK, Hoe MN. Mirizzi syndrome: noteworthy aspects of a retrospective study in one centre. ANZ J Surg. 2004; 74:833–837. PMID: 15456425.
Article7. Milone M, Musella M, Maietta P, Guadioso D, Pisapia A, Coretti G, et al. Acute acalculous cholecystitis determining Mirizzi syndrome: case report and literature review. BMC Surg. 2014; 14:90. PMID: 25399060.
Article8. Ibrarullah M, Saxena R, Sikora SS, Kapoor VK, Saraswat VA, Kaushik SP. Mirizzi's syndrome: identification and management strategy. Aust N Z J Surg. 1993; 63:802–806. PMID: 8274124.
Article9. Johnson LW, Sehon JK, Lee WC, Zibari GB, McDonald JC. Mirizzi's syndrome: experience from a multi-institutional review. Am Surg. 2001; 67:11–14. PMID: 11206888.10. Abou-Saif A, Al-Kawas FH. Complications of gallstone disease: Mirizzi syndrome, cholecystocholedochal fistula, and gallstone ileus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:249–254. PMID: 11866258.
Article11. Greiasov VI, Perfil'ev VV, Shchepkin SP, Petrichenko AV, Sivokon NI, Chuguevskiĭ VM. Diagnostics and surgical tactics for Mirizzi syndrome. Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2008; (11):31–34. PMID: 19301493.12. Moon JH, Cho YD, Cheon YK, Ryu CB, Kim YS, Kim JO, et al. Wire-guided intraductal US in the assessment of bile duct strictures with Mirizzi syndrome-like features at ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:873–879. PMID: 12447301.
Article13. Al-Akeely MH, Alam MK, Bismar HA, Khalid K, Al-Teimi I, Al-Dossary NF. Mirizzi syndrome: ten years experience from a teaching hospital in Riyadh. World J Surg. 2005; 29:1687–1692. PMID: 16311870.
Article14. Safioleas M, Stamatakos M, Safioleas P, Smyrnis A, Revenas C, Safioleas C. Mirizzi syndrome: an unexpected problem of cholelithiasis. Our experience with 27 cases. Int Semin Surg Oncol. 2008; 5:12. PMID: 18495037.
Article15. Shah OJ, Dar MA, Wani MA, Wani NA. Management of Mirizzi syndrome: a new surgical approach. ANZ J Surg. 2001; 71:423–427. PMID: 11450919.
Article16. Chowbey PK, Sharma A, Mann V, Khullar R, Baijal M, Vashistha A. The management of Mirizzi syndrome in the laparoscopic era. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2000; 10:11–14. PMID: 10872519.
Article17. Yeh CN, Jan YY, Chen MF. Laparoscopic treatment for Mirizzi syndrome. Surg Endosc. 2003; 17:1573–1578. PMID: 12964062.
Article18. Antoniou SA, Antoniou GA, Makridis C. Laparoscopic treatment of Mirizzi syndrome: a systematic review. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:33–39. PMID: 19466486.
Article19. Schäfer M, Schneiter R, Krähenbühl L. Incidence and management of Mirizzi syndrome during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc. 2003; 17:1186–1190. PMID: 12739118.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mirizzi syndrome: one case report
- Laparoscopic management of Mirizzi syndrome with liver cirrhosis using indocyanine green mapping: A case report and review of the literature
- Mirizzi Syndrome-Diagnostic Dilemma for Surgeons
- Mirizzi Syndrome: A Single Center Experience
- Minimally Invasive Approach Using Digital Single-Operator Peroral Cholangioscopy-Guided Electrohydraulic Lithotripsy and Endoscopic Nasogallbladder Drainage for the Management of High-Grade Mirizzi Syndrome