J Breast Cancer.
2012 Jun;15(2):252-254. 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.2.252.
An Incidentally Detected Breast Cancer on Tc-99m MIBI Cardiac Scintigraphy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Diskapi Yildirim Beyazit Teaching and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey. duray@superonline.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Diskapi Yildirim Beyazit Teaching and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey.
- KMID: 2242201
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2012.15.2.252
Abstract
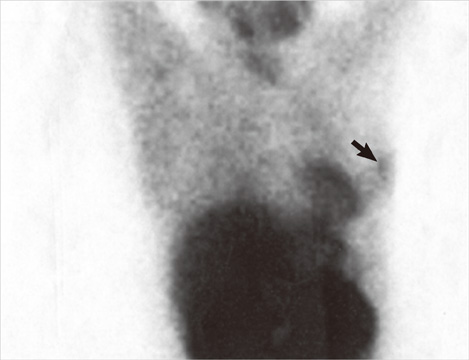
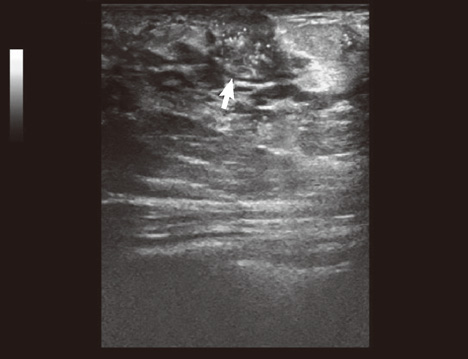
- Tc-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) scintigraphy is generally used as a second-line diagnostic tool for obscured breast lesions. When the entire field of view is examined carefully, it is often possible to detect additional lesions unrelated to the initial intent and purpose of the examination. Herein we present a case of breast cancer incidentally detected by cardiac Tc-99m MIBI scintigraphy. An area of uptake was detected in the breast during a cardiac imaging test. Further evaluation of this lesion revealed a histopathological diagnosis of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Sensitivity of this scintigraphic technique is not enough sufficient to use this test as a screening test for breast cancer, but it may provide supplemental information. Since it is not uncommon to find incidental lesions during imaging studies, examination of the image field may help clinicians find otherwise unrecognized or undiagnosed pathologies.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Colletti PM. Incidental findings on cardiac imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 191:882–884.
Article2. Haller S, Kaiser C, Buser P, Bongartz G, Bremerich J. Coronary artery imaging with contrast-enhanced MDCT: extracardiac findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 187:105–110.
Article3. Northam M, Koonce J, Ravenel JG. Pulmonary nodules detected at cardiac CT: comparison of images in limited and full fields of view. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 191:878–881.
Article4. Mathieu I, Mazy S, Willemart B, Destine M, Mazy G, Lonneux M. Inconclusive triple diagnosis in breast cancer imaging: is there a place for scintimammography? J Nucl Med. 2005. 46:1574–1581.5. Sadeghi R, Zakavi SR, Forghani MN, Aryana K, Kakhki VR, Ayati NK, et al. The efficacy of Tc-99m sestamibi for sentinel node mapping in breast carcinomas: comparison with Tc-99m antimony sulphide colloid. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2010. 13:1–4.6. Hod N, Mindlin L, Horne T. Detection of occult breast carcinoma during evaluation of a skeletal tumor by Tc-99m MIBI scintigraphy. Isr Med Assoc J. 2003. 5:296–297.7. Conrad GR, Sloan DA, Sinha P. Detection of late chest wall recurrence of breast carcinoma during Tc-99m sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 2003. 28:408–409.
Article8. Arbab AS, Koizumi K, Arai T, Mera K, Miyazaki A, Otaka M. Incidental detection of breast cancer during T1-201 myocardial SPECT study. Ann Nucl Med. 1995. 9:143–144.
Article9. Sickles EA. Mammographic features of "early" breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984. 143:461–464.
Article10. Moskowitz M. The predictive value of certain mammographic signs in screening for breast cancer. Cancer. 1983. 51:1007–1011.
Article11. Campeau RJ, Kronemer KA, Sutherland CM. Concordant uptake of Tc-99m sestamibi and Tl-201 in unsuspected breast tumor. Clin Nucl Med. 1992. 17:936–937.
Article12. Waxman AD. The role of (99m)Tc methoxyisobutylisonitrile in imaging breast cancer. Semin Nucl Med. 1997. 27:40–54.
Article13. Khalkhali I, Villanueva-Meyer J, Edell SL, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, Baum JK, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-sestamibi breast imaging: multicenter trial results. J Nucl Med. 2000. 41:1973–1979.14. Taillefer R, Robidoux A, Lambert R, Turpin S, Laperrière J. Technetium-99m-sestamibi prone scintimammography to detect primary breast cancer and axillary lymph node involvement. J Nucl Med. 1995. 36:1758–1765.15. Ramakrishna G, Miller TD. Significant breast uptake of Tc-99m sestamibi in an actively lactating woman during SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2004. 11:222–223.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study for Biological Characteristics of Breast Cancer with Tc-99m MIBI Scintigraphy
- A Study of the Biological Characteristics of Breast Cancer by Using Tc-99m MIBI Scintigraphy
- Tc-99m MIBI and Tl-201 Uptake in a Thymic Carcinoma
- Usefulness of Tc-99m MIBI Scan in the Postoperative Follow Up Of Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
- Diagnostic Role of Tc-99m MIBI Scintimammography in Suspected Breast Cancer Patients: Results of Unicenter Trial