Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Sep;7(3):410-413. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.410.
Multilevel Thoracolumbar Spondylolysis with Spondylolisthesis at L4 on L5
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. osdryd@gmail.com
- KMID: 2234100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.410
Abstract
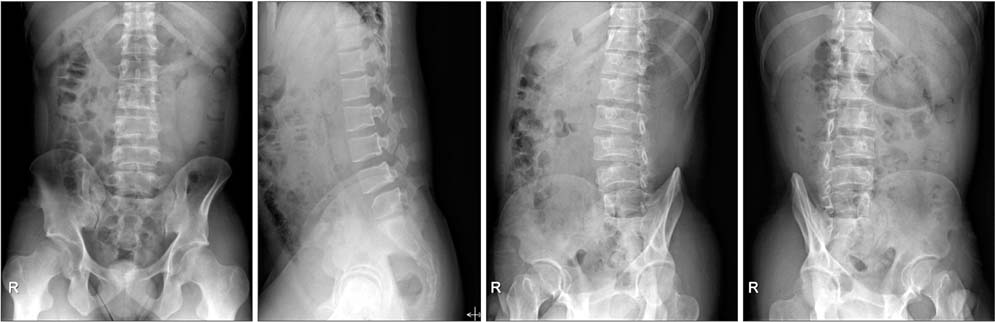
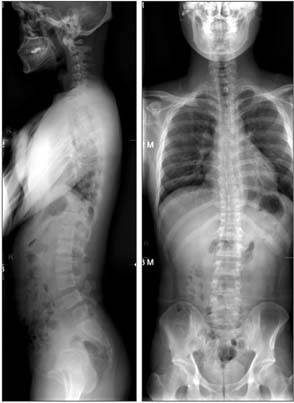
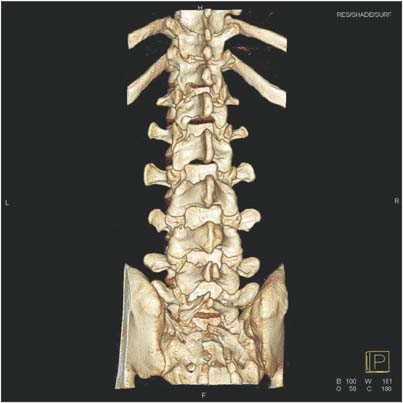
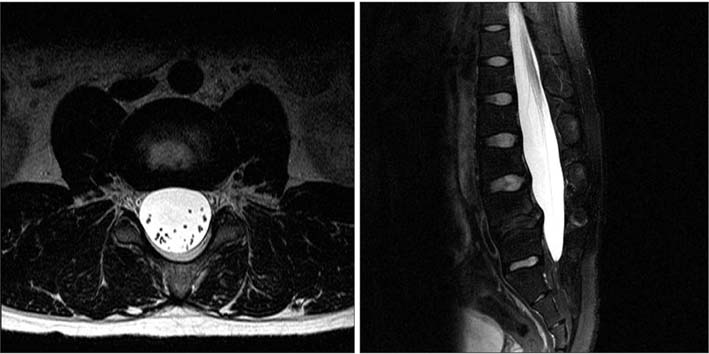
- A 24-year-old male patient was initially evaluated for persistent back pain. The visual analogue scale (VAS) score was 7 points. Physical examination revealed a decreased range of lumbar spinal motion, which caused pain. Simple X-ray revealed Meyerding grade 1 spondylolisthesis at L4 on L5, with mild dome-shaped superior endplate and consecutive multilevel spondylolysis at T12-L5. Standing anteroposterior and lateral views of the entire spine revealed normal balance of sagittal and coronal alignment. A computed tomography scan revealed bilateral spondylolysis at T12-L4, left unilateral spondylolysis at L5, and spina bifida at L5 to sacral region. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed mild dural ectasia at the lumbar region. Due to the absence of any neurological symptoms, the patient was managed conservatively. He was rested a few weeks with corset brace and physiotherapy. After treatment, his back pain improved, VAS score changed from 7 to 2, and he was able to return to normal activity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park KH, Ha JW, Kim HS, et al. Multiple levels of lumbar spondylolysis: a case report. Asian Spine J. 2009; 3(1):35–38.
Article2. Ravichandran G. Multiple lumbar spondylolyses. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1980; 5(6):552–557.
Article3. Stewart TD. The age incidence of neural-arch defects in Alaskan natives, considered from the standpoint of etiology. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953; 35(4):937–950.
Article4. Blackburne JS, Velikas EP. Spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1977; 59(4):490–494.
Article5. Sairyo K, Sakai T, Yasui N, et al. Newly occurred L4 spondylolysis in the lumbar spine with pre-existence L5 spondylolysis among sports players: case reports and biomechanical analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129(10):1433–1439.
Article6. Sevrain A, Aubin CE, Gharbi H, Wang X, Labelle H. Biomechanical evaluation of predictive parameters of progression in adolescent isthmic spondylolisthesis: a computer modeling and simulation study. Scoliosis. 2012; 7(1):2.
Article7. Sakai T, Sairyo K, Takao S, Nishitani H, Yasui N. Incidence of lumbar spondylolysis in the general population in Japan based on multidetector computed tomography scans from two thousand subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(21):2346–2350.
Article8. Mesfin A, Ahn NU, Carrino JA, Sponseller PD. Ten-year clinical and imaging follow-up of dural ectasia in adults with Marfan syndrome. Spine J. 2013; 13(1):62–67.
Article9. Pizzutillo PD, Hummer CD 3rd. Nonoperative treatment for painful adolescent spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1989; 9(5):538–540.
Article10. Park HJ, Shim YJ, Kim WK, Yang JH. Cervical spondylolysis with dysplasia: a case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2009; 16(3):210–214.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Transitional Vertebra in Spondylolysis and Spondyloytic Spondylolisthesis
- Multiple Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
- The Clinical Evaluation of Spondylolisthesis
- Segmental Lordosis of the Spondylolytic Vertebrae in Adolescent Lumbar Spondylolysis: Differences between Bilateral L5 and L4 Spondylolysis
- Sacralization of L5 in Radiological Studies of Degenerative Spondylolisthesis at L4-L5