Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Sep;7(3):282-290. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.282.
Shaft Fractures of Both Forearm Bones: The Outcomes of Surgical Treatment with Plating Only and Combined Plating and Intramedullary Nailing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. hurym197@3hanmail.net
- KMID: 2234080
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.282
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Plate fixation is the most commonly used technique for the treatment of shaft fractures of both forearm bones (SFBFBs). However, all fractures are difficult to treat with plate fixation because of soft tissue injuries, fracture patterns, or the patient's condition. The purpose of this study is to compare the functional results of plate fixation only and combined plate and intramedullary (IM) nail fixation in SFBFBs.
METHODS
Fifty-nine cases of SFBFBs that were surgically treated from June 2007 to July 2012 were retrospectively reviewed. In this study, 47 cases that were followed up for more than 12 months were included. All SFBFBs were divided into two groups according to the methods used for internal fixation: plate fixation only (group A) and combined plate and IM nail fixation (group B). The fixation methods were determined intraoperatively. Plate fixation was considered as the first option in all cases, but combined plate and IM nail fixation was selected as the second option if it was difficult to be fixed with plate only. Groups A and B comprised of 31 and 16 cases, respectively. The functional results were evaluated by the Grace and Eversmann rating system and the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) questionnaire.
RESULTS
In groups A and B, a radiologic union was achieved in 30/31 and 14/16 cases and average union time was 11.1 and 17.8 weeks, respectively. According to the Grace and Eversmann rating system, group A had excellent results in 15 cases, good in 14, acceptable in one, and unacceptable in one. Group B had excellent results in three cases, good in nine, acceptable in two, and unacceptable in two. The average DASH score was 7.1 points (range, 0 to 19.2 points) in group A and 15.1 points (range, 0 to 29.6 points) in group B. Three cases of nonunion with unacceptable results achieved a bony union by additional procedures and the functional results of these cases improved to good or excellent.
CONCLUSIONS
The functional results and the average union time were superior in group A than in group B. However, we think that combined fixation is a useful method for SFBFBs that cannot be treated with plate fixation only.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Bone Nails/*statistics & numerical data
Bone Plates/*statistics & numerical data
Female
Forearm/surgery
Fracture Fixation, Intramedullary/adverse effects/*methods/*statistics & numerical data
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Radius Fractures/epidemiology/*surgery
Range of Motion, Articular/*physiology
Retrospective Studies
Treatment Outcome
Ulna Fractures/epidemiology/*surgery
Young Adult
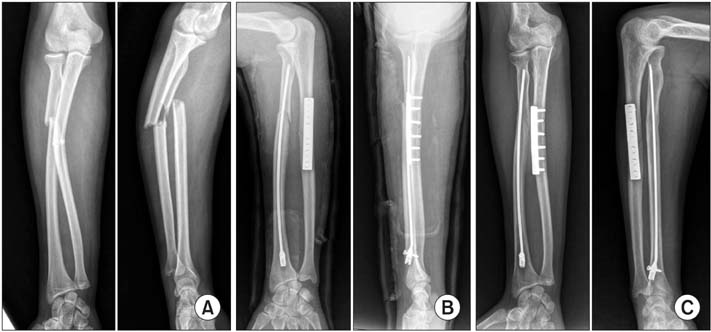
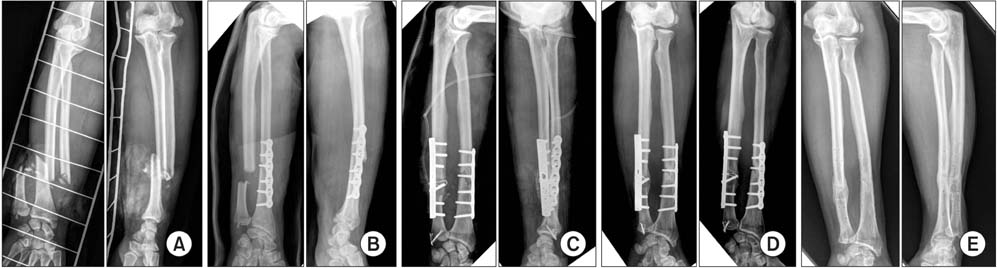
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of Bending Strength among Plate, Steinmann Pin, and Headless Compression Screw Fixations for Proximal Ulnar Shaft Fracture in Sawbones
Jinyoung Han, Jin Rok Oh, Jaewoong Um
Arch Hand Microsurg. 2020;25(4):267-273. doi: 10.12790/ahm.20.0065.Clinical Outcome of Forearm Segmental Fracture after Open Reduction and Plate Fixation
In Tae Hong, Dong Won Kim, Gyu Chol Jang, Soo Hong Han
Arch Hand Microsurg. 2018;23(1):46-53. doi: 10.12790/ahm.2018.23.1.46.
Reference
-
1. Dumont CE, Thalmann R, Macy JC. The effect of rotational malunion of the radius and the ulna on supination and pronation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(7):1070–1074.2. Matthews LS, Kaufer H, Garver DF, Sonstegard DA. The effect on supination-pronation of angular malalignment of fractures of both bones of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982; 64(1):14–17.3. Moss JP, Bynum DK. Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna in adults. Hand Clin. 2007; 23(2):143–151.4. Lee SK, Kim KJ, Lee JW, Choy WS. Plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nailing for both forearm bones fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(5):769–776.5. Jones DB Jr, Kakar S. Adult diaphyseal forearm fractures: intramedullary nail versus plate fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2011; 36(7):1216–1219.6. Ozkaya U, Kilic A, Ozdogan U, Beng K, Kabukcuoglu Y. Comparison between locked intramedullary nailing and plate osteosynthesis in the management of adult forearm fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2009; 43(1):14–20.7. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R, Willenegger H. Manual of internal fixation: techniques recommended by the AO-ASIF group. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer;1991.8. Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58(4):453–458.9. Grace TG, Eversmann WW Jr. Forearm fractures: treatment by rigid fixation with early motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980; 62(3):433–438.10. Hudak PL, Amadio PC, Bombardier C. Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand): the Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG). Am J Ind Med. 1996; 29(6):602–608.11. Rehman S, Sokunbi G. Intramedullary fixation of forearm fractures. Hand Clin. 2010; 26(3):391–401.12. Droll KP, Perna P, Potter J, Harniman E, Schemitsch EH, McKee MD. Outcomes following plate fixation of fractures of both bones of the forearm in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(12):2619–2624.13. Sage FP, Smith H. Medullary fixation of forearm fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957; 39(1):91–98.14. Lee YH, Lee SK, Chung MS, Baek GH, Gong HS, Kim KH. Interlocking contoured intramedullary nail fixation for selected diaphyseal fractures of the forearm in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(9):1891–1898.15. Jones DJ, Henley MB, Schemitsch EH, Tencer AF. A biomechanical comparison of two methods of fixation of fractures of the forearm. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9(3):198–206.16. Saka G, Saglam N, Kurtulmus T, et al. New interlocking intramedullary radius and ulna nails for treating forearm diaphyseal fractures in adults: a retrospective study. Injury. 2014; 45:Suppl 1. S16–S23.17. Kang CN, Kim JH, Kim DW, et al. The operative treatment of the shaft fractures of the forearm bone: operative comparison in intramedullary fixation to plate fixation on treatment of the both forearm bone fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1998; 11(1):63–69.18. Kim MH, Yoo MJ, Jung HG, et al. Treatment of diaphyseal fractures of forearm both bones: comparison between plate fixation and Rush pin intramedullary nailing. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19(2):215–220.19. Wei SY, Born CT, Abene A, Ong A, Hayda R, DeLong WG Jr. Diaphyseal forearm fractures treated with and without bone graft. J Trauma. 1999; 46(6):1045–1048.20. Wright RR, Schmeling GJ, Schwab JP. The necessity of acute bone grafting in diaphyseal forearm fractures: a retrospective review. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11(4):288–294.21. Goldfarb CA, Ricci WM, Tull F, Ray D, Borrelli J Jr. Functional outcome after fracture of both bones of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(3):374–379.22. Bot AG, Doornberg JN, Lindenhovius AL, Ring D, Goslings JC, van Dijk CN. Long-term outcomes of fractures of both bones of the forearm. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93(6):527–532.23. Duncan R, Geissler W, Freeland AE, Savoie FH. Immediate internal fixation of open fractures of the diaphysis of the forearm. J Orthop Trauma. 1992; 6(1):25–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Evaluation on Diaphyseal Fractures of the Both Forearm Bones in Adults
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing Versus conventional Kuntscher Intramedullary Nailing for Fracture of the Femoral Shaft
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Tibial Shaft Fractures: Comparative Study between Reamed and Unreamed Nailing
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing of Forearm Shaft Fractures in Adults
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for the Femoral Shaft Fractures