Korean Circ J.
2007 Mar;37(3):130-133. 10.4070/kcj.2007.37.3.130.
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in the 8th Week of Pregnancy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Sejong General Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. yoorimbin@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2227085
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2007.37.3.130
Abstract
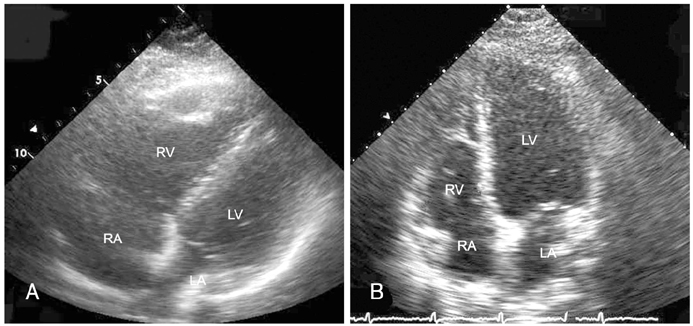
- A 29-year-old woman in her 8th week of pregnancy was referred to our hospital for swelling in the lower extremities, rapid onset of dyspnea (1 hr) and pre-syncope. Severe right ventricular dysfunction and moderate pulmonary hypertension were detected using 2-dimentional Doppler echocardiography. In addition, left calf vein and proximal thromboses were detected by venous compression ultrasound imaging. After successful thrombolytic treatment, the patient quickly recovered and was discharged from hospital on subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin. She delivered a normal, healthy infant at full-term (40 weeks).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cogo A, Lensing AW, Prandoni P, Hirsh J. Distribution of thrombosis in patients with symptomatic deep vein thrombosis: implications for simplifying the diagnostic process with compression ultrasound. Arch Intern Med. 1993. 153:2777–2780.2. Moser KM, LeMoine JR. Is embolic risk conditioned by location of deep venous thrombosis? Ann Intern Med. 1981. 94:439–444.3. Aaro LA, Juergens JL. Thrombophlebitis associated with pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971. 109:1128–1136.4. Heit JA, Kobbervig CE, James AH, Petterson TM, Bailey KR, Melton LJ 3rd. Trends in the incidence of venous thromboembolism during pregnancy or postpartum: a 30-year population-based study. Ann Intern Med. 2005. 143:697–706.5. Remy-Jardin M, Remy J. Spiral CT angiography of the pulmonary circulation. Radiology. 1999. 212:615–636.6. Richard HW. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003. 107:23 Suppl 1. I4–I8.7. Clark P, Brennand J, Conkie JA, McCall F, Greer IA, Walker ID. Activated protein C sensitivity, protein C, protein S and coagulation in normal pregnancy. Thromb Haemost. 1998. 79:1166–1170.8. Greer IA. Bloom AL, Forbes CD, Thomas DP, Tuddenham EG, editors. Haemostasis and thrombosis in pregnancy. Haemostasis and Thrombosis. 1994. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone;987–1015.9. Dahlback B, Hillarp A, Rosen S, Zoller B. Resistance to activated protein C, the FV: Q506 allele, and venous thrombosis. Ann Hematol. 1996. 72:166–176.10. Macklon NS, Greer IA, Bowman AW. An ultrasound study of gestational and postural changes in the deep venous system of the leg in pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997. 104:191–197.11. Macklon NS, Greer IA. The deep venous system in the puerperium: an ultrasound study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997. 104:198–200.12. Rodger MA, Walker M, Wells PS. Diagnosis and treatment of venous thromboembolism in pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2003. 16:279–296.13. Ginsberg JS, Hirsh J, Rainbow AJ, Coates G. Risks to the fetus of radiologic procedures used in the diagnosis of maternal venous thromboembolic disease. Thromb Haemost. 1989. 61:189–196.14. Nazeyrollas P, Metz D, Jolly D, et al. Use of transthoracic Doppler echocardiography combined with clinical and electrocardiographic data to predict acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 1996. 17:779–786.15. McConnell MV, Solomon SD, Rayan ME, Come PC, Goldhaber SZ, Lee RT. Regional right ventricular dysfunction detected by echocardiography in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol. 1996. 78:469–473.16. Torbicki A, Kurzyna M, Ciurzynski M, et al. Proximal pulmonary emboli modify right ventricular ejection pattern. Eur Respir J. 1999. 13:616–621.17. Tengborn L, Bergqvist D, Matzsch T, Bergqvist A, Hedner U. Recurrent thromboembolism in pregnancy and puerperium: is there a need for thromboprophylaxis? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989. 160:90–94.18. Badaracco MA, Vessey MP. Recurrence of venous thromboembolic disease and use of oral contraceptives. Br Med J. 1974. 1:215–217.19. Murin S, Romano PS, White RH. Comparison of outcomes after hospitalization for deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Thromb Haemost. 2002. 88:407–414.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Thromboembolism in a Severely Obese Man
- Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosed by Ultrasonography During Puerperium Following Cesarean Section
- Two Cases of Pulmonary Thromboembolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis Developed After Cesarean Section
- An Acute Pulmonary Embolism Accompanying Greater Saphenous Vein Thrombosis
- A Case of Antiphospholipid Syndrome Refractory to Secondary Anticoagulating Prophylaxis after Deep Vein Thrombosis-Pulmonary Embolism