Korean J Androl.
2011 Dec;29(3):191-198. 10.5534/kja.2011.29.3.191.
Trauma and Reconstruction of the External Genitalia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. jaeyoungpark@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2226451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/kja.2011.29.3.191
Abstract
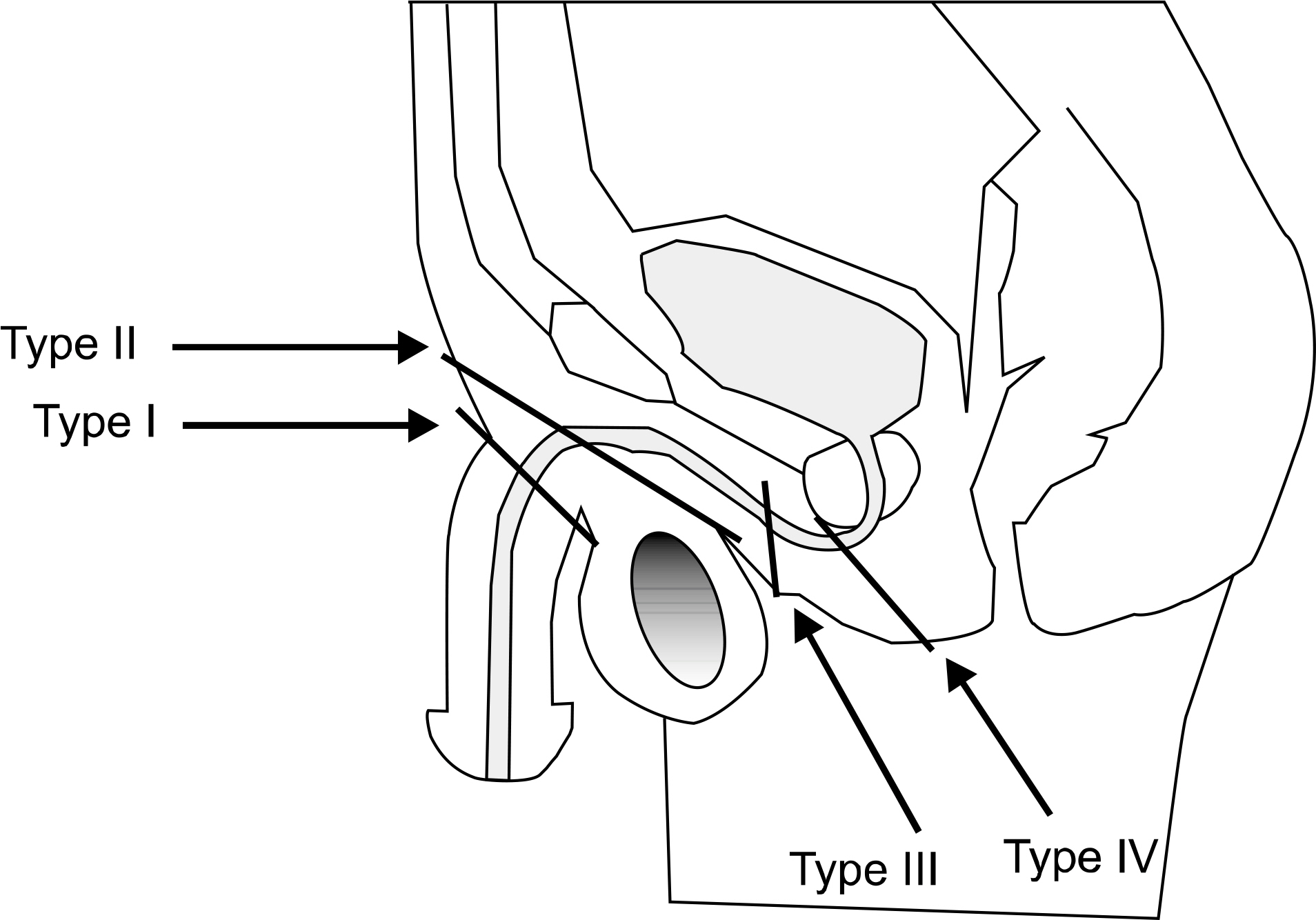
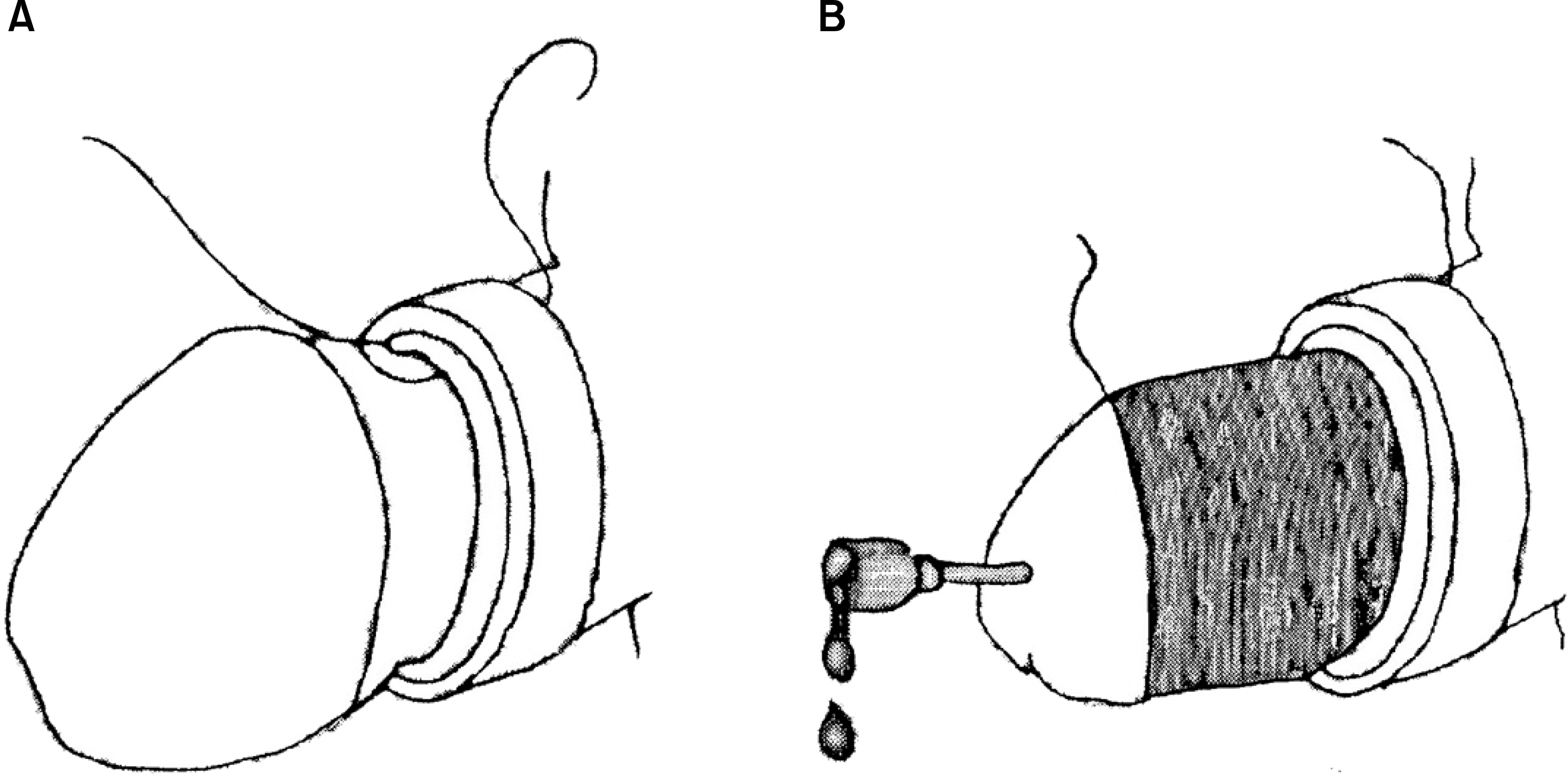
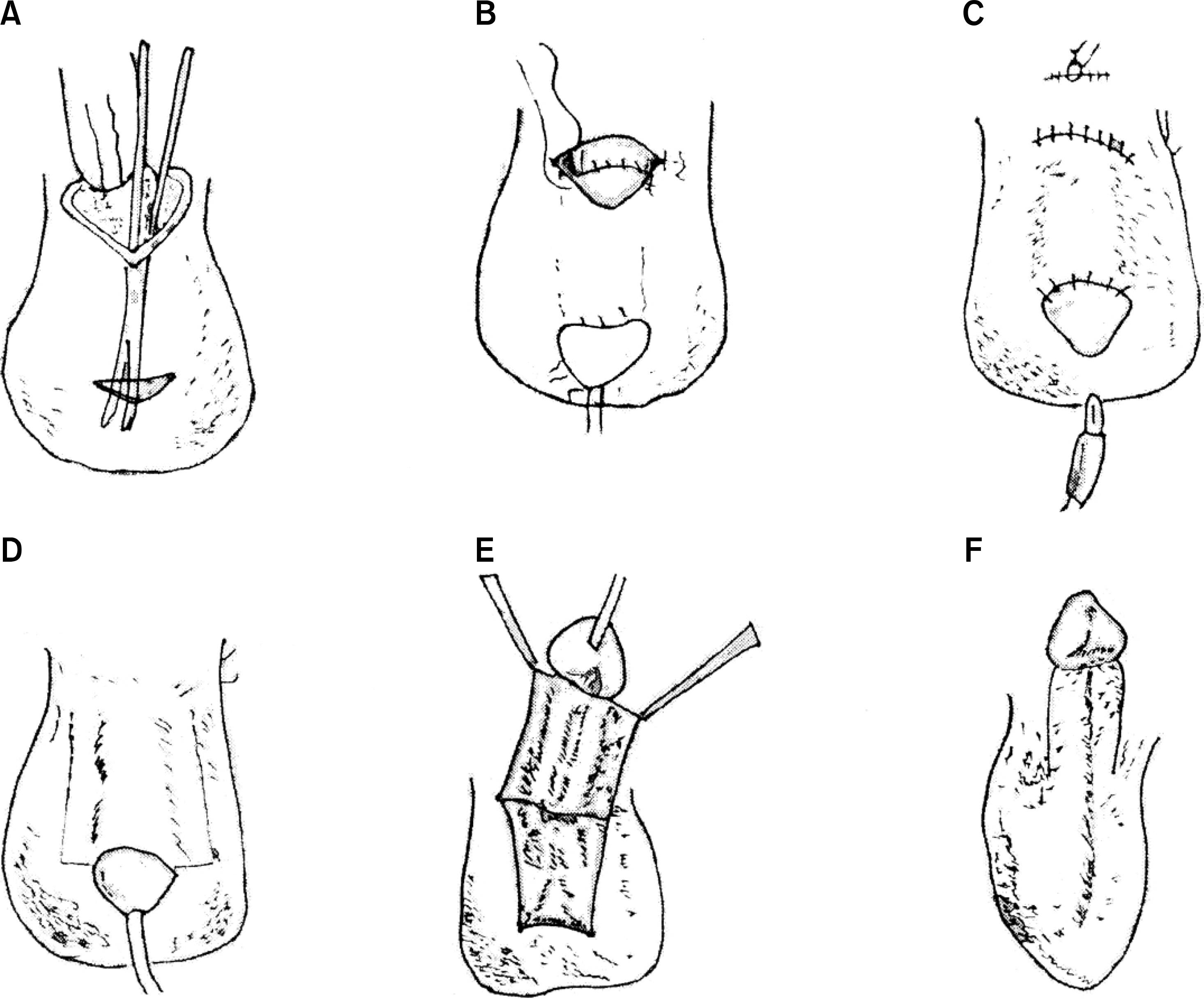
- External genitalia trauma including penis and scrotum often accompanies with genitourinary trauma or occurs independently, especially in male. External genitalia trauma is an emergent and serious condition like urinary system trauma but it has been unnoticed in urologic field. The treatment of external genitalia trauma is diverse according to the nature of trauma and injured anatomic site. The classification of trauma is important because it impacts the method of treatment however there has been no universe description about the classification of external genitalia trauma. The aim of this article is to summarize the methods of repairing defect in the penis and scrotum and the clinical application to the reparative treatment according to classification by its nature of injury.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1). Djakovic N, Plas E, Martinez-Pineiro L, Lynch T, Mor Y, Santucci R. Guidelines on urological trauma. EAU Guidelines. 2009. 1–84.2). Monga M, Hellstrom W. Testicular Trauma. Adolescent medicine (Philadelphia, Pa). 1996; 7:141.3). Rashid M, Sarwar SU. Avulsion injuries of the male external genitalia: classification and reconstruction with the customised radial forearm free flap. Br J Plast Surg. 2005; 58:585–92.
Article4). Allen FM, Thomas AR. Genital and Lower Urinary Tract Trauma. Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. Campbell's urology. 9th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2007. p. 2649–55.5). Gomes CM, Ribeiro-Filho L, Giron AM, Mitre AI, Figueira ER, Arap S. Genital trauma due to animal bites. J Urol. 2001; 165:80–3.
Article6). Cummings JM, Boullier JA. Scrotal dog bites. J Urol. 2000; 164:57–8.
Article7). Wolf JS Jr, Turzan C, Cattolica EV, McAninch JW. Dog bites to the male genitalia: characteristics, management and comparison with human bites. J Urol. 1993; 149:286–9.8). Mansson W. Bladder and Genital Trauma. 24th European Association of Urology Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 200917.9). Noh J, Kang TW, Heo T, Kwon DD, Park K, Ryu SB. Penile strangulation treated with the modified string method. Urology. 2004; 64:591.
Article10). El Atat R, Sfaxi M, Benslama MR, Amine D, Ayed M, Mouelli SB, et al. Fracture of the penis: management and longterm results of surgical treatment. Experience in 300 cases. J Trauma. 2008; 64:121–5.
Article11). Asgari MA, Hosseini SY, Safarinejad MR, Samadza-deh B, Bardideh AR. Penile fractures: evaluation, therapeutic approaches and longterm results. J Urol. 1996; 155:148–9.
Article12). Phonsombat S, Master VA, McAninch JW. Penetrating external genital trauma: a 30-year single institution experience. J Urol. 2008; 180:192–5.
Article13). McAninch JW, Kahn RI, Jeffrey RB, Laing FC, Krieger MJ. Major traumatic and septic genital injuries. J Trauma. 1984; 24:291–8.
Article14). Jezior JR, Brady JD, Schlossberg SM. Management of penile amputation injuries. World J Surg. 2001; 25:1602–9.
Article15). Gilbert DA, Winslow BH. Penis construction. Semin Urol. 1987; 5:262–9.16). Lowe MA, Chapman W, Berger RE. Repair of a traumatically amputated penis with return of erectile function. J Urol. 1991; 145:1267–70.
Article17). Bhanganada K, Chayavatana T, Pongnumkul C, Tonmukayakul A, Sakolsatayadorn P, Komaratat K, et al. Surgical management of an epidemic of penile amputations in Siam. Am J Surg. 1983; 146:376–82.
Article18). Shaw MB, Sadove AM, Rink RC. Reconstruction after total penile amputation and emasculation. Ann Plast Surg. 2003; 50:321–4.
Article19). Selvaggi G, Elander A. Penile reconstruction/formation. Curr Opin Urol. 2008; 18:589–97.
Article20). Kim SK, Lee KC, Kwon YS, Cha BH. Phalloplasty using radial forearm osteocutaneous free flaps in female-to-male transsexuals. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009; 62:309–17.
Article21). Felici N, Felici A. A new phalloplasty technique: the free anterolateral thigh flap phalloplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006; 59:153–7.
Article22). Vesely J, Hyza P, Ranno R, Cigna E, Monni N, Stupka I, et al. New technique of total phalloplasty with reinnervated latissimus dorsi myocutaneous free flap in female-to-male transsexuals. Ann Plast Surg. 2007; 58:544–50.
Article23). Altarac S. A case of testicle replantation. J Urol. 1993; 150:1507–8.
Article24). Morey A, McAninch JW. Genital skin loss and scrotal reconstruction. Ehrlich RM, Alter G, editors. Reconstructive and Plastic Surgery of the External Genitalia: Adult and Pediatric. Vol 1. Paris: Lavoisier;1999. p. 414–22.25). DeCastro BJ, Morey AF. Fibrin sealant for the reconstruction of fournier's gangrene sequelae. J Urol. 2002; 167:1774–6.
Article26). Horton CE, Dean JA. Reconstruction of traumatically acquired defects of the phallus. World J Surg. 1990; 14:757–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary (Congenital) Lymphedema of the External Genitalia
- First stage reconstruction of ambiguous external genitalia in children
- Cutaneous Diseases of the External Genitalia
- A Clinical Observation on Injuries of External Genitalia
- A Case of Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome with Bilateral Inguinal Gonads