Korean Circ J.
2011 Nov;41(11):689-691. 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.11.689.
Delayed Perforation of the Right Ventricular Wall by a Single Standard-Caliber Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Detected by Multidetector Computed Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, Kobe, Japan. yan527@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Kobe City Medical Center General Hospital, Kobe, Japan.
- KMID: 2225081
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2011.41.11.689
Abstract
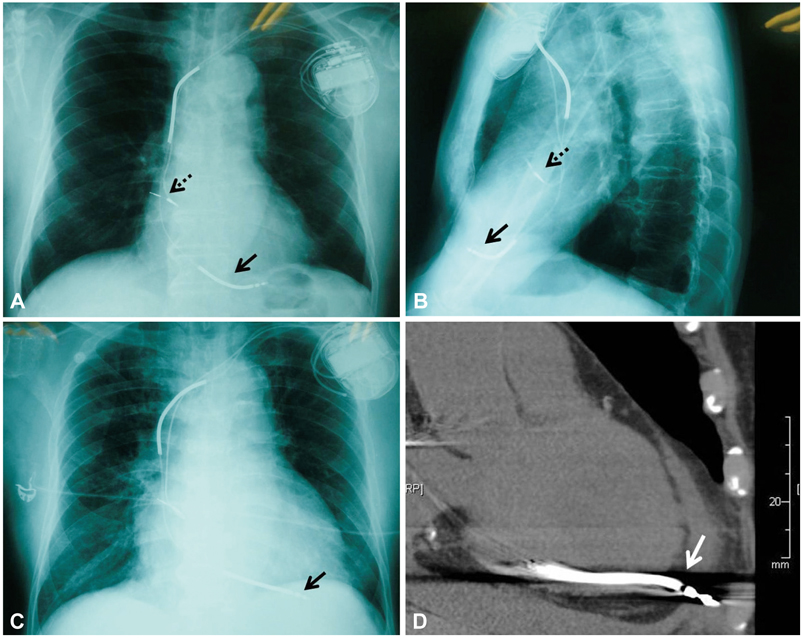
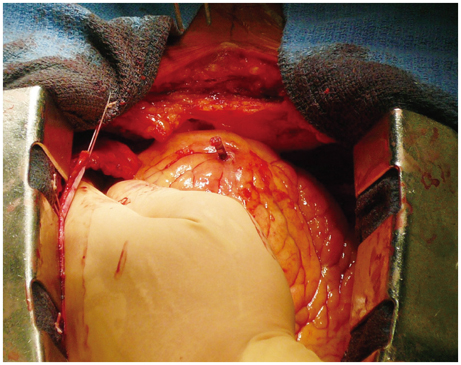
- We present an unusual case of a delayed right ventricular perforation by a single standard-caliber implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead, which manifested 14 days after implantation. Multidetector computed tomography could clearly display the lead perforation, and allow for identification of the associated sequelae such as pericardial effusion and planning the lead extraction strategy.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Polin GM, Zado E, Nayak H, et al. Proper management of pericardial tamponade as a late complication of implantable cardiac device placement. Am J Cardiol. 2006. 98:223–225.2. Takahashi T, Bhandari AK, Watanuki M, Cannom DS, Sakurada H, Hiraoka M. High incidence of device-related and lead-related complications in the dual-chamber implantable cardioverter defibrillator compared with the single-chamber version. Circ J. 2002. 66:746–750.3. Schwartzman D, Nallamothu N, Callans DJ, Preminger MW, Gottlieb CD, Marchlinski FE. Postoperative lead-related complications in patients with nonthoracotomy defibrillation lead systems. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995. 26:776–786.4. Henrikson CA, Leng CT, Yuh DD, Brinker JA. Computed tomography to assess possible cardiac lead perforation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2006. 29:509–511.5. Hirschl DA, Jain VR, Spindola-Franco H, Gross JN, Haramati LB. Prevalence and characterization of asymptomatic pacemaker and ICD lead perforation on CT. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2007. 30:28–32.6. Danik SB, Mansour M, Singh J, et al. Increased incidence of subacute lead perforation noted with one implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2007. 4:439–442.7. Ellis CR, Rottman JN. Increased rate of subacute lead complications with small-caliber implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads. Heart Rhythm. 2009. 6:619–624.8. Turakhia M, Prasad M, Olgin J, et al. Rates and severity of perforation from implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads: a 4-year study. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2009. 24:47–52.9. Lee DS, Krahn AD, Healey JS, et al. Evaluation of early complications related to De Novo cardioverter defibrillator implantation insights from the Ontario ICD database. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010. 55:774–782.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Extraction by Conventional Traction and Counter-Traction Technique
- Transvenous Implantation of an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator in a Patient Who Had Undergone Tricuspid Valve Replacement
- Where is the Lead? Inappropriate Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Shock Caused by Extreme Twiddling
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator as a treatment for massive left ventricular fibroma-induced ventricular arrhythmia in a child
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator Lead Extraction by Conventional Traction and Counter-Traction Technique