Korean Circ J.
2012 Aug;42(8):562-564. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.8.562.
A Case of Severe Pulmonary Thromboembolism in a Young Male With Klinefelter Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Cardiovascular Center, Myongji Hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. chodk123@paran.com
- KMID: 2225007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.8.562
Abstract
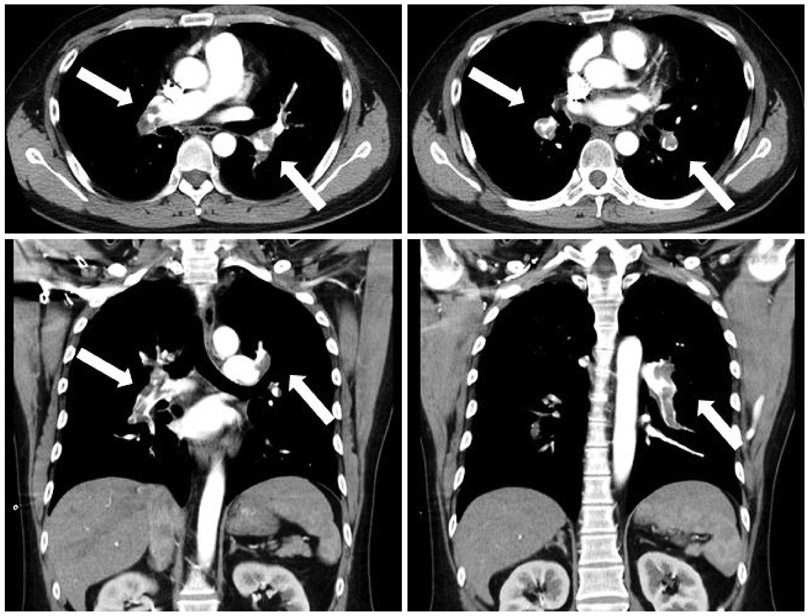
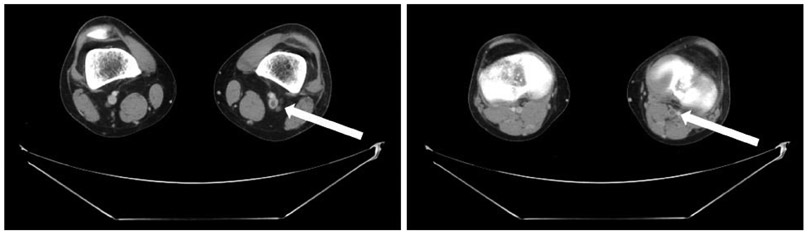
- A young male patient diagnosed with Klinefelter syndrome was admitted to our hospital via the emergency room with chief complaints of acute chest pain and dyspnea. Pulmonary thromboembolism was diagnosed from his chest CT images. His symptoms improved after he underwent thrombolysis and anticoagulation treatment. Klinefelter syndrome has a tendency towards hypercoagulability due to hormonal imbalance and one or more inherited thromophilic factors. Thus, Klinefelter syndrome patients with a past medical history of venous thromboembolism require continuous oral anticoagulation therapy for a period of at least six months.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schwartz ID, Root AW. The Klinefelter syndrome of testicular dysgenesis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1991. 20:153–163.2. Bojesen A, Juul S, Gravholt CH. Prenatal and postnatal prevalence of Klinefelter syndrome: a national registry study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:622–626.3. Ratcliffe S. Long-term outcome in children of sex chromosome abnormalities. Arch Dis Child. 1999. 80:192–195.4. Moon HJ, Rhim CY, Kim GW, et al. Risk factors of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in Korean. Korean Circ J. 2005. 35:474–479.5. Campbell WA, Price WH. Venous thromboembolic disease in Klinefelter's syndrome. Clin Genet. 1981. 19:275–280.6. Bennet A, Sie P, Caron P, et al. Plasma fibrinolytic activity in a group of hypogonadic men. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1987. 47:23–27.7. Caron P, Bennet A, Camare R, Louvet JP, Boneu B, Sié P. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma is related to testosterone in men. Metabolism. 1989. 38:1010–1015.8. Winkler UH. Effects of androgens on haemostasis. Maturitas. 1996. 24:147–155.9. Lane DA, Philippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood. 2005. 106:2605–2612.10. Sprengers ED, Kluft C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987. 69:381–387.11. Lapecorella M, Marino R, De Pergola G, Scaraggi FA, Speciale V, De Mitrio V. Severe venous thromboembolism in a young man with Klinefelter's syndrome and heterozygosis for both G20210A prothrombin and factor V Leiden mutations. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2003. 14:95–98.