Korean Circ J.
2013 Sep;43(9):607-614. 10.4070/kcj.2013.43.9.607.
Comparison of Coronary Plaque Components between Non-Culprit Lesions in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome and Target Lesions in Patients with Stable Angina: Virtual Histology-Intravascular Ultrasound Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Heart Center of Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. myungho@chollian.net
- 2Korea Cardiovascular Stent Institute of Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2224816
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2013.43.9.607
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
The differences in plaque characteristics between non-culprit lesions (NCL) in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients (ACS-NCL) and target lesions (TL) in stable angina (SA) patients (SA-TL) are not well understood. We used a virtual histology-intravascular ultrasound (VH-IVUS) to compare the plaque components between ACS-NCL and SA-TL.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
We compared VH-IVUS findings between 290 ACS-NCL and 276 SA-TL. VH-IVUS classified the color-coded tissue into four major components: green (fibrotic); yellow-green (fibro-fatty); white {dense calcium (DC)}; and red {necrotic core (NC)}. Thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA) was defined as a NC > or =10% of the plaque area in at least 3 consecutive frames without overlying fibrous tissue in the presence of > or =40% plaque burden.
RESULTS
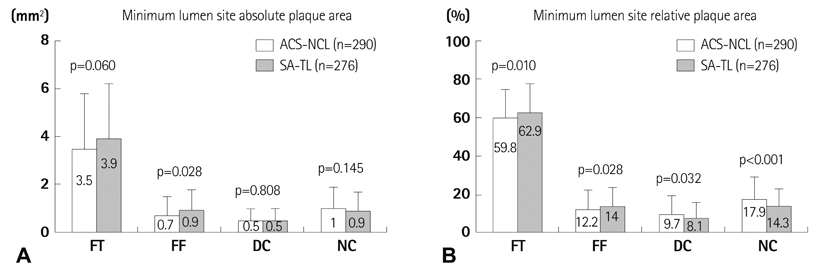
Although the plaque burden was significantly smaller (52+/-13% vs. 54+/-14%, p=0.044), ACS-NCL had a greater %NC area (17.9+/-11.6% vs. 14.3+/-8.7%, p<0.001) and %DC area (9.7+/-9.8% vs. 8.1+/-8.0%, p=0.032) compared with SA-TL at the minimum lumen site. By volumetric analysis, ACS-NCL had a greater %NC volume (15.8+/-9.2% vs. 13.9+/-7.4%, p=0.006) compared with SA-TL. TCFA was observed more frequently in ACS-NCL compared with SA-TL (27.6% vs. 18.1%, p=0.032). Independent predictors of TCFA by multivariate analysis were ACS {odds ratio (OR): 2.204, 95% CI: 1.321-3.434, p=0.021} and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (OR: 1.101; 95% CI 1.058-1.204, p=0.035).
CONCLUSION
Although the plaque burden was significantly smaller, ACL-NCL had more vulnerable plaque components compared with SA-TL, and ACS and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein were the independent predictors of TCFA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rodriguez-Granillo GA, García-García HM, Mc Fadden EP, et al. In vivo intravascular ultrasound-derived thin-cap fibroatheroma detection using ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 46:2038–2042.2. Hong MK, Mintz GS, Lee CW, et al. Comparison of virtual histology to intravascular ultrasound of culprit coronary lesions in acute coronary syndrome and target coronary lesions in stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 2007; 100:953–959.3. Missel E, Mintz GS, Carlier SG, et al. Necrotic core and its ratio to dense calcium are predictors of high-risk non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2008; 101:573–578.4. Hong YJ, Jeong MH, Choi YH, et al. Plaque characteristics in culprit lesions and inflammatory status in diabetic acute coronary syndrome patients. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009; 2:339–349.5. Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA Focused Update Incorporated Into the ACC/AHA 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2011; 123:e426–e579.6. O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2013; 127:e362–e425.7. Roberts WL, Moulton L, Law TC, et al. Evaluation of nine automated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein methods: implications for clinical and epidemiological applications. Part 2. Clin Chem. 2001; 47:418–425.8. Effects of tissue plasminogen activator and a comparison of early invasive and conservative strategies in unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction. Results of the TIMI IIIB Trial. Thrombolysis in Myocardial Ischemia. Circulation. 1994; 89:1545–1556.9. Mintz GS, Nissen SE, Anderson WD, et al. American College of Cardiology Clinical Expert Consensus Document on Standards for Acquisition, Measurement and Reporting of Intravascular Ultrasound Studies (IVUS). A report of the American College of Cardiology Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001; 37:1478–1492.10. Nair A, Kuban BD, Tuzcu EM, Schoenhagen P, Nissen SE, Vince DG. Coronary plaque classification with intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis. Circulation. 2002; 106:2200–2206.11. Okubo M, Kawasaki M, Ishihara Y, et al. Tissue characterization of coronary plaques: comparison of integrated backscatter intravascular ultrasound with virtual histology intravascular ultrasound. Circ J. 2008; 72:1631–1639.12. Yamamoto M, Takano M, Okamatsu K, et al. Relationship between thin cap fibroatheroma identified by virtual histology and angioscopic yellow plaque in quantitative analysis with colorimetry. Circ J. 2009; 73:497–502.13. Davies MJ, Thomas A. Thrombosis and acute coronary-artery lesions in sudden cardiac ischemic death. N Engl J Med. 1984; 310:1137–1140.14. Farb A, Burke AP, Tang AL, et al. Coronary plaque erosion without rupture into a lipid core. A frequent cause of coronary thrombosis in sudden coronary death. Circulation. 1996; 93:1354–1363.15. Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Farb A, Schwartz SM. Lessons from sudden coronary death: a comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000; 20:1262–1275.16. Falk E, Shah PK, Fuster V. Coronary plaque disruption. Circulation. 1995; 92:657–671.17. Kunimasa T, Sato Y, Sugi K, Moroi M. Evaluation by multislice computed tomography of atherosclerotic coronary artery plaques in non-culprit, remote coronary arteries of patients with acute coronary syndrome. Circ J. 2005; 69:1346–1351.18. Kato K, Yonetsu T, Kim SJ, et al. Nonculprit plaques in patients with acute coronary syndromes have more vulnerable features compared with those with non-acute coronary syndromes: a 3-vessel optical coherence tomography study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012; 5:433–440.19. Stone GW, Maehara A, Lansky AJ, et al. A prospective natural-history study of coronary atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:226–235.20. Kubo T, Imanishi T, Kashiwagi M, et al. Multiple coronary lesion instability in patients with acute myocardial infarction as determined by optical coherence tomography. Am J Cardiol. 2010; 105:318–322.21. Jang IK, Tearney GJ, MacNeill B, et al. In vivo characterization of coronary atherosclerotic plaque by use of optical coherence tomography. Circulation. 2005; 111:1551–1555.22. Burke AP, Tracy RP, Kolodgie F, et al. Elevated C-reactive protein values and atherosclerosis in sudden coronary death: association with different pathologies. Circulation. 2002; 105:2019–2023.23. Hong YJ, Jeong MH, Choi YH, et al. Relation between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and coronary plaque components in patients with acute coronary syndrome: virtual histology-intravascular ultrasound analysis. Korean Circ J. 2011; 41:440–446.24. Li QX, Fu QQ, Shi SW, et al. Relationship between plasma inflammatory markers and plaque fibrous cap thickness determined by intravascular optical coherence tomography. Heart. 2010; 96:196–201.25. Bouki KP, Katsafados MG, Chatzopoulos DN, et al. Inflammatory markers and plaque morphology: an optical coherence tomography study. Int J Cardiol. 2012; 154:287–292.26. Nakachi T, Kosuge M, Hibi K, et al. C-reactive protein elevation and rapid angiographic progression of nonculprit lesion in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Circ J. 2008; 72:1953–1959.27. Park JP, Lee BK, Shim JM, et al. Relationship between multiple plasma biomarkers and vulnerable plaque determined by virtual histology intravascular ultrasound. Circ J. 2010; 74:332–336.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lesion Characteristics in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Comparison with Lesion in Patients with Stable Angina by Intravascular Ultrasound
- Plaque Characteristics and Clinical Presentation Associated with Coronary Artery Remodeling: An Intravascular Ultrasound Study
- Acute coronary syndrome and vulnerable plaque
- Plaque Morphology in Acute Coronary Syndrome: An Intravascular Ultrasound Study
- Practical Application of Coronary Imaging Devices in Cardiovascular Intervention