Korean Circ J.
2013 Nov;43(11):739-743. 10.4070/kcj.2013.43.11.739.
Usefulness of Intracoronary Epinephrine in Severe Hypotension during Percutaneous Coronary Interventions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. ptca82@gmail.com
- 2Department of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2224805
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2013.43.11.739
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Life-threatening hypotension during percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) is devastating for the patient and is associated with fatal adverse outcomes. The aim of our study was to assess the usefulness of intracoronary epinephrine in severe hypotension unresponsive to other measures during PCI.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
We analyzed the Pusan National University Yangsan hospital cardiac catheterization laboratory database to identify patients who underwent PCI from December 2008 to July 2012. The outcomes were changes of blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR) before and after intracoronary epinephrine and in-hospital mortality.
RESULTS
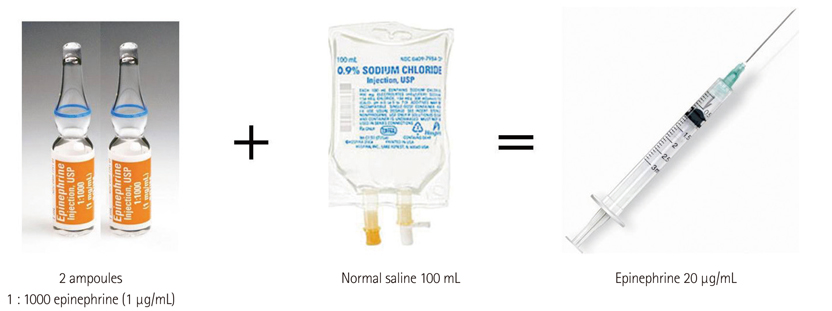
A total of 30 patients who were initially stable and received intracoronary epinephrine for severe hypotension during PCI were included. Following administration of intracoronary epinephrine (dose 181+/-24.8 microgram), systolic and diastolic BP (from 53.8+/-13.0 mm Hg up to 112.8+/-21.2 mm Hg, from 35+/-7.6 mm Hg up to 70.6+/-12.7 mm Hg, respectively) and HR (from 39.4+/-5.1 beats/min up to 96.8+/-29.3 beats/min) were increased. Additionally, 21 patients (70%) showed hemodynamically acceptable responses to intracoronary epinephrine without the intraaortic balloon pump and temporary pacemaker during the PCI. In-hospital mortality was 17% (n=5).
CONCLUSION
Although our study was small, intracoronary epinephrine was found to be well tolerated and resulted in prompt and successful recovery from severe hypotension in most patients when other measures were ineffective. Intracoronary epinephrine could be a safe and useful measure in patients developing severe hypotension during PCI.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Skelding KA, Goldstein JA, Mehta L, Pica MC, O'Neill WW. Resolution of refractory no-reflow with intracoronary epinephrine. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2002; 57:305–309.2. Kahn JK, Hartzler GO. Reversal of refractory hypotension with intracoronary epinephrine during coronary angioplasty. Am Heart J. 1993; 126:463–466.3. Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC. Adrenergic agonists and antagonists. In : Brunton LL, editor. Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 12th ed. McGraw-Hill;2010. p. 282–287.4. Otto CW, Yakaitis RW. The role of epinephrine in CPR: a reappraisal. Ann Emerg Med. 1984; 13(9 Pt 2):840–843.5. Zhong JQ, Dorian P. Epinephrine and vasopressin during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2005; 66:263–269.6. Kitsou V, Xanthos T, Stroumpoulis K, et al. Nitroglycerin and epinephrine improve coronary perfusion pressure in a porcine model of ventricular fibrillation arrest: a pilot study. J Emerg Med. 2009; 37:369–375.7. Grmec S, Mally S. Vasopressin improves outcome in out-of-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation of ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia: a observational cohort study. Crit Care. 2006; 10:R13.8. Robertson RM, Wood AJ, Vaughn WK, Robertson D. Exacerbation of vasotonic angina pectoris by propranolol. Circulation. 1982; 65:281–285.9. Kiss G, Corre O, Gueret G, et al. Management of cardiac arrest caused by coronary artery spasm: epinephrine/adrenaline versus nitrates. Heart Lung. 2009; 38:228–232.10. Baim DS. Epinephrine: a new pharmacologic treatment for no-reflow? Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2002; 57:310–311.11. Comroe JH. Nonrespiratory functions of the lungs and circulation. Physiology of respiration. 2nd ed. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers;1974. p. 285–282.12. Aral A, Oğuz M, Ozberrak H, et al. Hemodynamic advantages of left atrial epinephrine administration in open heart operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997; 64:1046–1049.13. Lucreziotti S, Sponzilli C, Castini D, Di Domenico E, Fiorentini C. Intracoronary epinephrine for contrast-medium-induced microvascular obstruction in a chronically hemodialyzed patient. Cardiology. 2005; 103:196–198.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- No-Reflow Phoenomenon by Intracoronary Thrombus in Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Intracoronary Radiation to Prevent Restenosis After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- A Case of a Successful Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Using Percusurge(r) System in a Massive Intracoronary Thrombi Patient
- A Case of Treatment of Acute Occlusion Complicating Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
- Intracoronary Thrombolysis and Delayed Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for the Treatment of Large Coronary Thrombi in a Patient with Polycythemia Vera