J Rheum Dis.
2011 Dec;18(4):288-291. 10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.288.
A Case of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor-Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Wallace Memorial Baptist Hospital, Busan, Korea. choong@wmbh.co.kr
- KMID: 2223132
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2011.18.4.288
Abstract
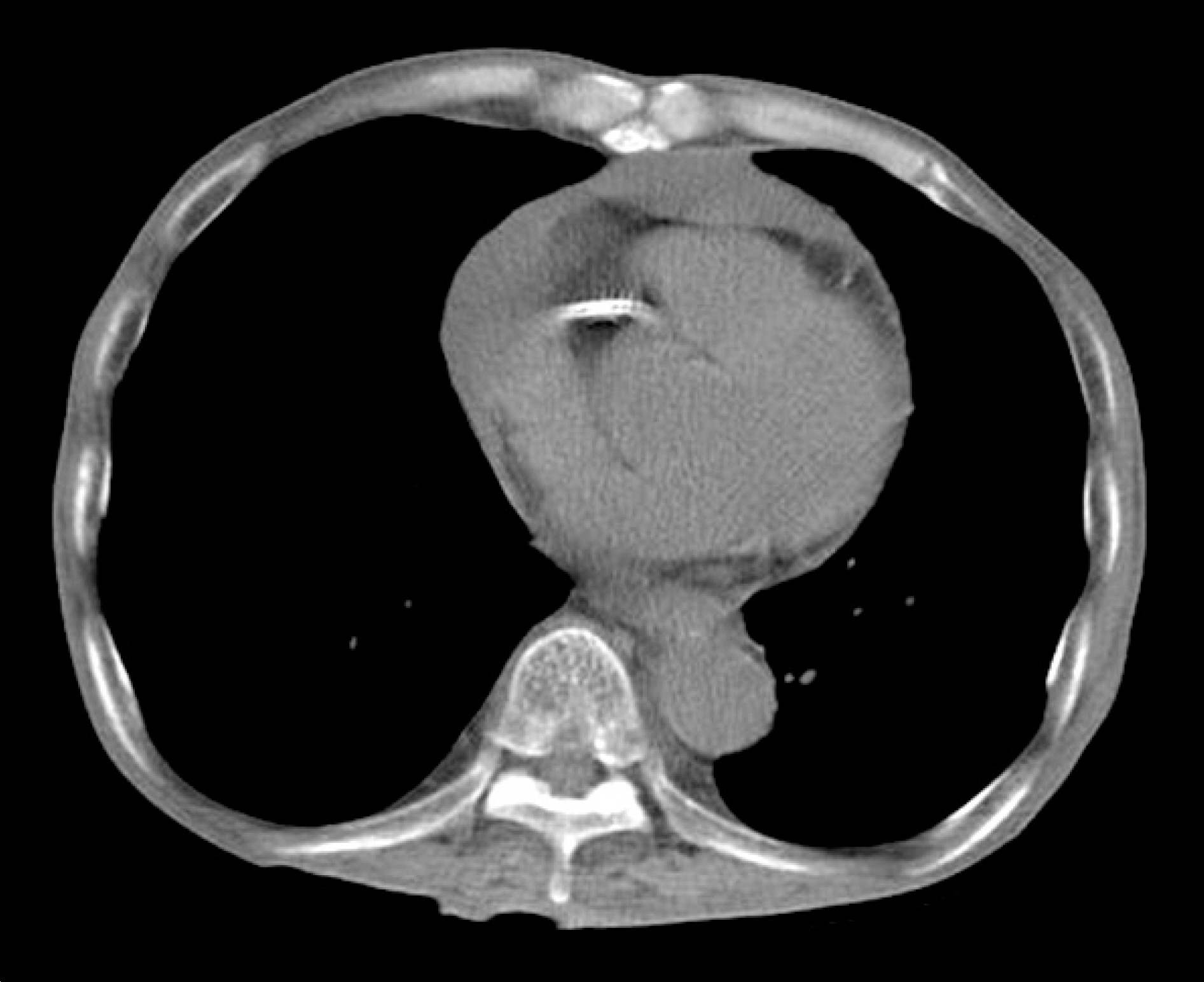
- Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is defined as a lupus-like syndrome related to continuous drug exposure which resolves after discontinuation of the offending drug. Here we report a case of a 70-year-old man who developed drug-induced lupus erythematosus after receiving angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor medication for unstable angina pectoris, for 5 years. He was hospitalized with arthralgia, edema, and newly developed pleural effusion. The serum analysis revealed an elevated level of antinuclear antibody and antihistone antibody. After discontinuation of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor and receiving a course of prednisolone treatment, his symptoms and pleural effusion improved. To the best of our knowledge, this is, the first case report of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor-induced systemic lupus erythematosus in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Pramatarov KD. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Clin Dermatol. 1998; 16:367–77.
Article2. Chen M, Crowson AN, Woofter M, Luca MB, Magro CM. Docetaxel (taxotere) induced subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 4 cases. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:818–20.3. Hess E. Drug-related lupus. N Engl J Med. 1988; 318:1460–2.
Article4. Hoffman BJ. Sensitivity to sulfadiazine resembling acute disseminated lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1945; 51:190–2.
Article5. Antonov D, Kazandjieva J, Etugov D, Gospodinov D, Tsankov N. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Clin Dermatol. 2004; 22:157–66.
Article6. Oh SR, Cho M, Ryu HS, Lee JH, Cho HJ, Choi MK, et al. A Case of Isoniazid Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007; 14:431–5.
Article7. Park CO, Goo J, Ahn SK. A case of propylthiouracil-induced lupus erythematosus. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:467–9.8. Yung RL, Richardson BC. Drug-induced lupus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1994; 20:61–86.
Article9. Lee SL, CHase PH. Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: a critical review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1975; 5:83–103.10. Vedove CD, Del Giglio M, Schena D, Girolomoni G. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009; 301:99–105.
Article11. Rubin RL, Waga S. Antihistone antibodies in SLE. J Rheumatol. 1987; 14:118.12. Park PW, Kim TY. Antinuclear antibodies in patients on medication with cardiovascular drugs and antihypergly-cemic agents. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2002; 24:215–20.13. Kallenberg CG, Hoorntje SJ, Smit AJ, Weening JJ, Donker AJ, Hoedemaeker PH, et al. Antinuclear and anti-native DNA antibodies during captopril treatment. Acta Med Scand. 1982; 211:297–300.
Article14. di Fazano CS, Bertin P. The pharmacological management of drug-induced rheumatic disorders. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2001; 2:1623–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors on Induced Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Activity in Rat Intestine
- Association of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphism with the Disease Activity of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Korean Children
- A Case of life-threatening Angioneurotic Edema Related to Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Adalimumab-induced Lupus Erythematosus Profundus in a Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus