J Rheum Dis.
2014 Oct;21(5):253-256. 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.5.253.
Localized Mesenteric Vasculitis in a Patient with Polymyalgia Rheumatica
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. cptmiller@cnuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2222949
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2014.21.5.253
Abstract
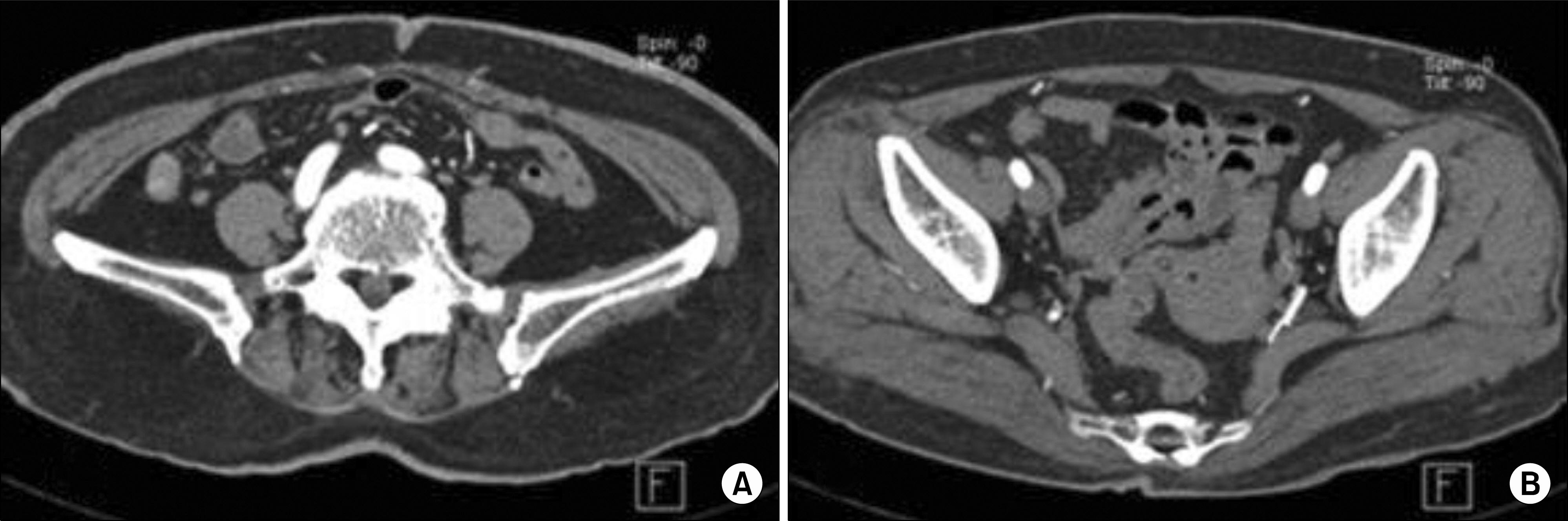
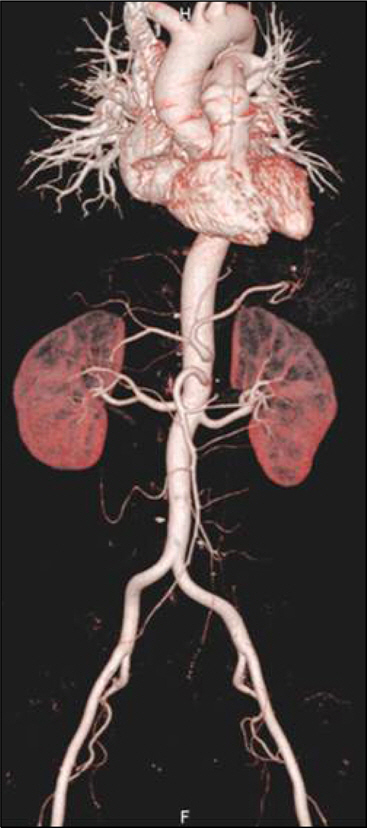
- Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is an uncommon disorder characterized by bilateral pain and stiffness in the shoulder and pelvic girdles. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis (GCA) occur in the same patient population and share a common pathogenesis. Giant cell arteritis predominantly affects the cranial arteries and rarely involves the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, giant cell arteritis has rarely been reported in Asians. Here, we present a case with 62-year-old Asian woman who developed polymyalgia rheumatica with localized vasculitis in the mesenteric arteries.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Salvarani C, Cantini F, Boiardi L, Hunder GG. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:261–71.
Article2. Weyand CM, Fulbright JW, Hunder GG, Evans JM, Goronzy JJ. Treatment of giant cell arteritis: interleukin-6 as a biologic marker of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:1041–8.
Article3. Pereira LS, Yoon MK, Hwang TN, Hong JE, Ray K, Porco T, et al. Giant cell arteritis in Asians: a comparative study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011; 95:214–6.
Article4. Annamalai A, Francis ML, Ranatunga SK, Resch DS. Giant cell arteritis presenting as small bowel infarction. J Gen Intern Med. 2007; 22:140–4.
Article5. Salvarani C, Calamia KT, Crowson CS, Miller DV, Broadwell AW, Hunder GG, et al. Localized vasculitis of the gastrointestinal tract: a case series. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:1326–35.
Article6. Herná ndez-Rodríguez J, Molloy ES, Hoffman GS. Singleorgan vasculitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2008; 20:40–6.7. Burke AP, Sobin LH, Virmani R. Localized vasculitis of the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995; 19:338–49.
Article8. Gonzalez-Gay MA, Vazquez-Rodriguez TR, Miranda-Filloy JA, Pazos-Ferro A, Garcia-Rodeja E. Localized vasculitis of the gastrointestinal tract: a case report and literature review. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008; 26(3 Suppl 49):S101–4.9. Garcia-Porrua C, Gutierrez-Duque O, Soto S, Garcia-Rodeja E, Gonzalez-Gay MA. Localized vasculitis of the gastrointestinal tract. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 35:403–6.
Article10. Will U, Gerlach R, Wanzar I, Urban H, Manger T, Meyer F. Isolated vasculitis of the stomach: a novel or rare disease with a difficult differential diagnosis. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:848–51.
Article11. Adajar MA, Painter T, Woloson S, Memark V. Isolated celiac artery aneurysm with splenic artery stenosis as a rare presentation of polyarteritis nodosum: a case report and review of the literature. J Vasc Surg. 2006; 44:647–50.
Article12. Vlahos K, Theodoropoulos GE, Lazaris ACh, Agapitos E, Christakopoulos A, Papatheodorou D, et al. Isolated colonic leukocytoclastic vasculitis causing segmental megacolon: report of a rare case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2005; 48:167–71.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of polymyalgia rheumatica
- Treatment Experience with Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A report of two cases
- Korean Epidemiologic Study of Polymyalgia Rheumatica
- Typical 18-FDG-PET/CT Findings of Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Case Report
- Successful Treatment of Polymyalgia Rheumatica with Prednisolone in Combination with Clarithromycin and Tacrolimus