J Rheum Dis.
2014 Oct;21(5):241-247. 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.5.241.
Sleep Disturbances in Korean Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis are Associated with Increased Disease Activity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea. mdkim9111@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Neurology, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2222947
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2014.21.5.241
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the prevalence of sleep disturbance in Korean patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and its association with disease activity and depression.
METHODS
Forty patients with AS and eighty healthy controls were included in this study. Sleep quality was assessed using the Korean version of Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI). Depression was assessed by the Korean version of Beck depression inventory second edition (BDI-2). Ankylosing spondylitis disease activity score-C-reactive protein (ASDAS-CRP) was used to evaluate disease activity. Patients were dichotomized into a good sleeper group (PSQI< or =5) and a poor sleeper group (PSQI>5).
RESULTS
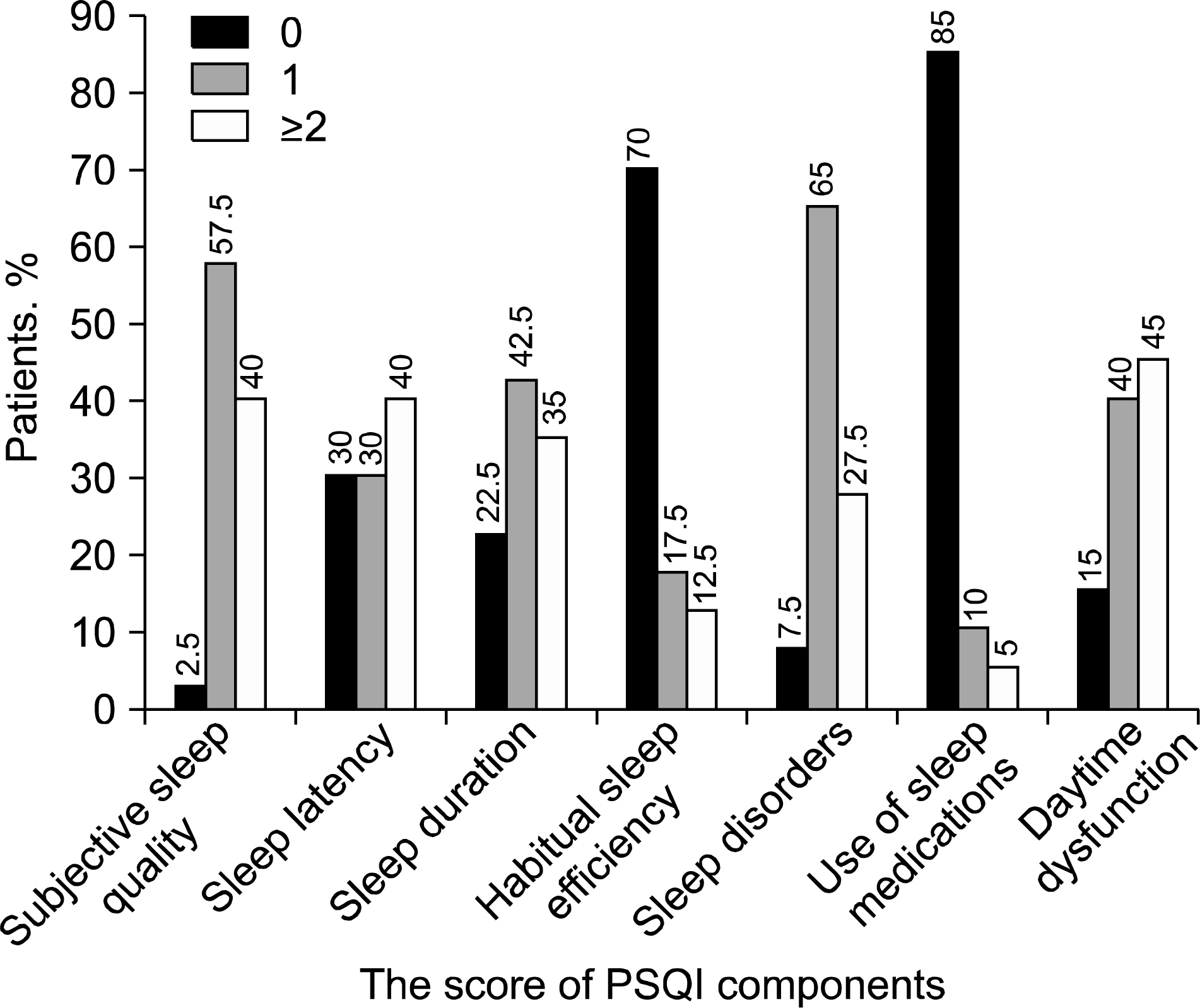
The mean total PSQI score of patients with AS was 7.23+/-3.84. It was higher than that of the control subjects. AS patients had higher scores in all of the PSQI components, except for the use of sleep medication. Sixty percent of the AS patients were classified as poor sleepers. The mean BASDAI, ASDAS-CRP, and BDI-2 scores of the poor sleeper group were higher than that of the good sleeper group. Significantly, higher disease activity according to ASDAS-CRP was associated with poor sleep quality and depression. Multiple regression analysis revealed that the duration of morning stiffness and depression were independent risk factors that influenced poor sleep quality.
CONCLUSION
Sleep disturbances are prevalent amongst Korean patients with AS. Lower quality of sleep is significantly associated with higher disease activity and depression. Therefore, optimal management to improve sleep quality in patients with AS is important.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index is Associated With the Quality of Sleep in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
Byung Wook Song, Hye-Jin Jeong, Bo Young Kim, Yong Won Cho, Chang-Nam Son, Sung-Soo Kim, Sang-Hyon Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2021;28(3):143-149. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.3.143.Sleep Disturbance in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Han Joo Baek
J Rheum Dis. 2014;21(6):279-281. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.6.279.
Reference
-
1. Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Khan MA, Braun J. Concepts and epidemiology of spondyloarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:401–17.
Article2. Dougados M, van der Linden S, Juhlin R, Huitfeldt B, Amor B, Calin A, et al. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991; 34:1218–27.
Article3. Heiberg T, Lie E, van der Heijde D, Kvien TK. Sleep problems are of higher priority for improvement for patients with ankylosing spondylitis than for patients with other inflammatory arthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:872–3.
Article4. Hultgren S, Broman JE, Gudbjörnsson B, Hetta J, Lindqvist U. Sleep disturbances in outpatients with ankylosing spondylitisa questionnaire study with gender implications. Scand J Rheumatol. 2000; 29:365–9.5. Hakkou J, Rostom S, Mengat M, Aissaoui N, Bahiri R, Hajjaj-Hassouni N. Sleep disturbance in Moroccan patients with ankylosing spondylitis: prevalence and relationships with disease-specific variables, psychological status and quality of life. Rheumatol Int. 2013; 33:285–90.
Article6. Kim TJ, Oh KT, Ju EK, Lee HS, Kim TH, Jun JB, et al. Health-related quality of life in Korean patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2002; 9(Suppl):S106–16.7. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:361–8.8. Sohn SI, Kim do H, Lee MY, Cho YW. The reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Sleep Breath. 2012; 16:803–12.
Article9. Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994; 21:2286–91.10. Lukas C, Landewé R, Sieper J, Dougados M, Davis J, Braun J, et al. Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society. Development of an ASAS-endorsed disease activity score (ASDAS) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:18–24.
Article11. Machado P, Landewé R, Lie E, Kvien TK, Braun J, Baker D, et al. Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society. Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS): defining cutoff values for disease activity states and improvement scores. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:47–53.
Article12. Lim SY, Lee EJ, Jeong SW, Kim HC, Jeong CH, Jeon TY, et al. The validation study of Beck Depression Scale 2 in Korean version. Anxiety Mood. 2011; 7:48–53.13. Ohayon MM, Hong SC. Prevalence of insomnia and associated factors in South Korea. J Psychosom Res. 2002; 53:593–600.
Article14. Li Y, Zhang S, Zhu J, Du X, Huang F. Sleep disturbances are associated with increased pain, disease activity, depression, and anxiety in ankylosing spondylitis: a case-control study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012; 14:R215.
Article15. Batmaz İ, Sarı yı ldız MA, Dilek B, Bez Y, Karakoç M, Çevik R. Sleep quality and associated factors in ankylosing spondylitis: relationship with disease parameters, psychological status and quality of life. Rheumatol Int. 2013; 33:1039–45.
Article16. Da Costa D, Zummer M, Fitzcharles MA. Determinants of sleep problems in patients with spondyloarthropathy. Musculoskeletal Care. 2009; 7:143–61.
Article17. Braun J, Bollow M, Neure L, Seipelt E, Seyrekbasan F, Herbst H, et al. Use of immunohistologic and in situ hy-bridization techniques in the examination of sacroiliac joint biopsy specimens from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:499–505.
Article18. Lange U, Teichmann J, Stracke H. Correlation between plasma TNF-alpha, IGF-1, biochemical markers of bone metabolism, markers of inflammation/disease activity, and clinical manifestations in ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Med Res. 2000; 5:507–11.19. François RJ, Neure L, Sieper J, Braun J. Immunohistological examination of open sacroiliac biopsies of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: detection of tumour necrosis factor alpha in two patients with early disease and transforming growth factor beta in three more advanced cases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:713–20.20. Krueger JM. The role of cytokines in sleep regulation. Curr Pharm Des. 2008; 14:3408–16.
Article21. Chennaoui M, Sauvet F, Drogou C, Van Beers P, Langrume C, Guillard M, et al. Effect of one night of sleep loss on changes in tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) levels in healthy men. Cytokine. 2011; 56:318–24.
Article22. Rudwaleit M, Gooch K, Michel B, Herold M, Thörner A, Wong R, et al. Adalimumab improves sleep and sleep quality in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2011; 38:79–86.
Article23. Dew MA, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Buysse DJ, Hoch CC, Jennings R, et al. Psychosocial correlates and sequelae of electroencephalographic sleep in healthy elders. J Gerontol. 1994; 49:8–18.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index is Associated With the Quality of Sleep in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
- Clinieal Values of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ( SPECT ) in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Sleep Disturbance in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Prevention And Surgical Correction Of Deformity
- Synovial Fluid Adenosine Deaminse Activity in the Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Gouty Arthritis